New Initiatives
Home >> New InitiativesOutline of the 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025) for National Economic and Social Development and Vision 2035 of the People's Republic of China
Source: tppckte.org.cn | 2021-08-09 09:15 Click:
Contents
Part I A New Journey Towards a Modern Socialist Country
Chapter 1 Development Environment
Part II Innovation-Driven Development to Build New Strengths
Chapter 4 A Strategic Vision for Building Strength in Science and Technology
Chapter 5 Technological Innovation Capability of Enterprises
Chapter 6 Creativity and Talent Development
Chapter 7 Mechanisms for Scientific and Technological Innovation
Part III Industrial Modernization and the Foundation of Real Economy
Chapter 8 Strengthening Manufacturing
Chapter 9 Emerging Industries of Strategic Importance
Chapter 10 Development of the Service Sector
Chapter 11 Modern Infrastructure
Part IV A Robust Domestic Market and a New Development Paradigm
Chapter 12 Greater Domestic Circulation
Chapter 13 Domestic and International Circulation
Chapter 14 Strategies to Boost Domestic Demand
Part V An Initiative to Build a Digital China
Chapter 15 Pole Position in the Digital Economy
Chapter 18 A Healthy Digital Ecosystem
Part VI Comprehensive and In-depth Reform to Develop a Well-functioning Socialist Market Economy
Chapter 20 A Unified Market that Adheres to High Standards
Chapter 21 Fiscal Policy, Taxation, and the Financial System
Chapter 22 The Government's Economic Governance Capacity
Part VII Agricultural and Rural Development and Rural Revitalization
Chapter 23 Quality Issues and Competitiveness in the Agricultural Sector
Chapter 24 Rural Development Initiatives
Chapter 25 Integrated Urban-Rural Development
Chapter 26 Rural Revitalization to Be Pursued by Building on Success in Poverty Alleviation
Part VIII New Urbanization Strategy with a Focus on Quality Development
Chapter 27 Urban Residency Status for Rural Residents
Chapter 28 Spatial Distribution of Urban Centers
Chapter 29 Quality of Urban Living
Part IX Improving Regional Economic Structures and Promoting Coordinated Regional Development
Chapter 30 Land Use Planning and Environmental Protection
Chapter 31 Major Regional Development Strategies
Chapter 32 Coordinated Regional Development Strategies
Chapter 33 Development of the Marine Economy
Part X Socialist Cultural Development and China's Soft Power
Chapter 35 Public Cultural Services
Chapter 36 Cultural Industries
Part XI Green Development and Harmonious Co-existence between Humanity and Nature
Chapter 37 Improving the Ecosystem
Chapter 38 Continuous Environmental Improvement
Chapter 39 Faster Transformation for Green Development
Part XII Further Opening-up for Win-Win Cooperation
Chapter 40 A New Open Economy System
Chapter 41 Joint Pursuit of the Belt and Road Initiative
Chapter 42 Participating in the Reform and Development of the Global Governance System
Part XIII Promotion of Human Development
Chapter 43 Quality Education for All
Chapter 45 A National Strategy in Response to Population Aging
Part XIV A Focus on the People's Wellbeing: a Participatory Approach
Chapter 46 National Public Services
Chapter 47 An Employment-First Strategy
Chapter 48 Improving the Income Distribution Structure
Chapter 49 A Multi-Tiered Social Security System
Chapter 50 Basic Rights and Interests of Women, Children, and People with Disabilities
Chapter 51 Community-Level Participatory Governance
Part XV An Integrated Approach to Development and Security
Chapter 52 National Security and Capacity-building
Chapter 53 National Economic Security
Chapter 55 Social Stability and Security
Part XVI Modernization of National Defense and the Armed Forces as We Build National Prosperity
Chapter 56 Modernization of National Defense and the Military
Chapter 57 Strengthening National Defense in Tandem with Economic Growth
Part XVII Socialist Democracy, the Rule of Law, and Party and State Oversight Mechanisms
Chapter 58 Socialist Democracy
Chapter 59 Promotion of the Rule of Law
Chapter 60 Party and State Oversight Mechanisms
Part XVIII The Principle of "One Country, Two Systems" and National Reunification
Chapter 61 Lasting Prosperity and Stability in Hong Kong and Macao
Chapter 62 Peaceful Development of Cross-Straits Relations and National Reunification
Part XIX Implementation of This Plan
Chapter 63 The Overall Leadership Role of the CPC Central Committee
Chapter 65 Mechanisms for Implementing This Plan
Outline of the 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025) for National Economic and Social Development
and Vision 2035 of the People's Republic of China
March 13, 2021
The Outline of the 14th Five-Year Plan (2021-2025) for National Economic and Social Development and Vision 2035 of the People's Republic of China, compiled on the basis of the proposals of the CPC Central Committee for such a plan and vision, clarifies China's strategic intentions and the government's priorities, and guides market participants in their activities. It is a blueprint for China's new journey towards a socialist modern country and a joint action plan of the Chinese people.
Part I A New Journey Towards a Modern Socialist Country
The period covered by the 14th Five-Year Plan will be the first five years during which China begins its march towards the second Centenary Goal of building a modern socialist country by building on the success of achieving the first Centenary Goal of building a moderately well-off society.
Chapter 1 Development Environment
China has now entered a new stage of development on a stronger foundation, though profound changes have taken place in the conditions under which we pursue our development goals. We are facing new opportunities and challenges.
I. A decisive victory in building a moderately well-off society
The 13th Five-Year Plan period was the decisive stage in building a moderately well-off society. In the face of the complicated international situation and formidable domestic issues related to advancing reforms and development while maintaining stability, particularly under the grave impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China (CPC) with Comrade Xi Jinping at the core, has stayed true to the CPC’s original aspiration and kept the Party’s missions firmly in mind. It has united and led the entire Party and the Chinese people of all ethnic groups to pioneer and forge ahead, and worked hard to advance various undertakings of the Party and the country. China has made major breakthroughs in deepening reforms in all areas, made substantial progress in law-based governance in all respects, and has achieved remarkable results in ensuring full and strict governance over the Party. China’s system and capacity for governance have been modernized at an accelerated pace. These achievements comprehensively demonstrate the strong leadership of the CPC and the institutional strengths of socialism with Chinese characteristics.
Overall, China’s economy has performed stably and its structure has been consistently improved, with the country’s GDP now exceeding RMB 100 trillion. China has accomplished much towards becoming an innovative country and has made major advances in manned spaceflight, lunar exploration, deep-sea engineering, supercomputing, quantum information, “Fuxing” high-speed trains, large aircraft manufacture, and other fields. We have attained a decisive victory in the fight against poverty and the rural poor residents, 55.75 million in total, have been lifted out of poverty. The problem of absolute poverty, which had plagued the Chinese nation for thousands of years has been solved—a miracle in the history of mankind. Agricultural modernization has been steadily advanced, and the annual grain output has surpassed 650 million tons for several years. The goal of granting urban residency to 100 million people from rural areas and other permanent residents without local household registration has also been met. Solid steps have been taken to implement major regional development strategies. Pollution prevention and control efforts have been intensified, the target of reduction in the discharge of major pollutants has been exceeded, resources and energy have been used more efficiently, and there has been a notable improvement in the environment. Important progress has been made in addressing financial risks in this period. China has opened its door wider to the world, and the joint pursuit of the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) has yielded fruitful results. The living standards of the Chinese people have increased significantly. Considerable headway was made in ensuring the provision of equitable, quality education. Higher education is becoming universal. Over 60 million urban jobs were added, and the world’s largest social security system was established. China’s basic medical insurance covers 1.3 billion people and its basic old-age insurance covers nearly 1 billion people. More than 23 million housing units in urban shanty towns have now been renovated. The country has had major strategic success in the response to COVID-19, and the preparedness and capacity for coping with emergencies have been substantially improved. The country’s public cultural services have been consistently improved, and the cultural sector flourished. Notable advances have been made in the development of national defense and the armed forces, and the organizational structure of the military has undergone major changes. China’s national security has been comprehensively strengthened, and social harmony and stability have been maintained across the country.
The goals and tasks of the 13th Five-Year Plan have been successfully completed. China’s economic strength, scientific and technological strength, comprehensive national strength, and people’s living standards have now reached a new high. The country has made great and historic achievements in building a moderately well-off society and has taken a new and big stride towards the great rejuvenation of the Chinese nation. Today, socialist China stands taller and stronger in the East.
II. Profound changes in China’s development environment
China is now in an important period of strategic opportunity for development, and will remain so for some time to come, but the opportunities and challenges it faces are changing. The world today is undergoing major changes unprecedented in a century. The new round of technological revolution and industrial transformation is gaining momentum, and there is a profound shift in the balance of international power. Peace and development remain the themes of the times, and the concept of a community with a shared future for mankind is deeply rooted in people’s minds. At the same time, the international environment has become increasingly complex with obviously increased instability and uncertainty. The COVID-19 pandemic is exerting an extensive, far-reaching impact around the world—the global economy is in the doldrums, economic globalization is encountering headwinds, and dramatic changes are taking place in the global energy supply and demand landscape. The international economic and political landscapes are complex and changeable, and the world is entering a period of turbulent changes, with unilateralism, protectionism, and hegemonism posing a threat to world peace and development.
China has moved to a stage of development with a focus on quality improvement. It has significant institutional advantages, improved performance in governance, sound long-term economic fundamentals, a solid material foundation, rich human resources, vast market potential, strong economic resilience, and social stability, thus enjoying favorable conditions and strengths for further development. At the same time, unbalanced and inadequate development is still a prominent problem, and reform in key links and major fields remains a formidable task. China’s capacity for innovation cannot yet meet the need of pursuing development with a focus on quality improvement. The foundation of agriculture is not yet solid. There are still disparities in development between urban and rural areas and between regions and in income distribution. We have a long way to go in protecting the environment. In work on public wellbeing and social governance, there are still areas where we fall short.
We must keep in mind both the broad strategic goal of national rejuvenation and the profound changes unseen in a century in the world, and clearly understand the new features and requirements brought about by the changes in the principal contradictions in our society, as well as the new contradictions and challenges arising from the complicated international environment, while enhancing our awareness of opportunities and risks. We must keep in mind the basic fact that China is still in the primary stage of socialism, maintain a strategic resolve, and run our own affairs well. We should fully understand the laws governing development, be ready to fight, build our ability, evaluate worst-case scenarios, accurately perceive changes and scientifically respond to them, take the initiative to seek changes, be good at fostering opportunities amid crises and opening up new vistas in a shifting landscape, seize opportunities and deal with challenges while weighing up pros and cons, and forge ahead with confidence and courage.
During the period covered by the 14th Five-Year Plan, economic and social development will be guided by the following guidelines, principles, and strategic direction.
I. Guidelines
We must hold high the banner of socialism with Chinese characteristics; thoroughly implement the guiding principles of the 19th National Congress of the CPC and of the second, third, fourth, and fifth plenary sessions of the 19th CPC Central Committee; and follow the guidance of Marxism-Leninism, Mao Zedong Thought, Deng Xiaoping Theory, the Theory of Three Represents, the Scientific Outlook on Development, and Xi Jinping Thought on Socialism with Chinese Characteristics for a New Era. We must fully act on the Party’s basic theory, line, and policy, coordinate efforts to achieve economic, political, cultural, social, and ecological progress, and implement the strategy to make comprehensive efforts to build a great modern socialist country, deepen reform, advance law-based governance, and ensure full and strict governance over the Party. We must be committed to the new development philosophy of innovation, coordination, green development, opening-up, and sharing; uphold the underlying principle of pursuing progress while ensuring stability; pursue development with a focus on quality improvement; promote supply-side structural reforms as the main task; and make reforms and innovation the primary driving force in our endeavor to meet the fundamental goal of satisfying the people’s growing needs for a better life. We should ensure coordination in pursuing development and upholding security, accelerate the building of a modern economic system and expedite our efforts to create a new development paradigm with the domestic market as the mainstay and domestic and overseas markets reinforcing each other. We should also modernize China’s system and capacity for governance and realize long-term and stable economic development and social stability and harmony. By doing so, we will set the stage for building a modern socialist country in all respects.
II. Principles to follow
—Uphold the overall leadership of the CPC. We will adhere to and improve the Party’s institutions and mechanisms for leading economic and social development, adhere to and improve the socialist system with Chinese characteristics, continuously boost our capacity for implementing the new development philosophy and building a new development paradigm, and provide a fundamental guarantee for development with a focus on quality improvement.
—Commit to a people-centered approach. We must ensure the principal position of the people, and work towards common prosperity. We must insist that our development is for the people and depends on the people, and that its fruits are shared by the people. We must safeguard the fundamental interests of the people, stimulate their enthusiasm, initiative, and creativity, promote social equity, improve people’s wellbeing, and constantly help realize people’s aspiration for a better life.
—Stay true to the new development philosophy. We must ensure the new development philosophy is applied in full, in both letter and spirit and in every stage and aspect of development. We must build a new development paradigm, effectively change the development model, work hard for better quality, higher efficiency, and more robust drivers of economic growth through reform, and strive to achieve higher-quality development that is more efficient, equitable, sustainable and secured.
—Continue to deepen reform and opening-up. We must be fully committed to reform and opening-up and modernize China’s governance system and capacity. We must get rid of the institutional ailments that restrict development with a focus on quality improvement and high-quality life, strengthen major reform and opening-up measures that are conducive to improving the efficiency of resource allocation and mobilizing the enthusiasm of the whole society, and continuously enhance the driving force and vitality of development.
—Uphold system-based thinking. We must think ahead, plan the big picture, deploy strategically, and advance in a holistic manner. We must keep in mind both our internal and international imperatives, and balance development and security. By adhering to the national strategy, we need to give full play to the initiative of the central and local governments and people in various sectors, solidify our foundation, foster strengths, and tackle areas of weaknesses. We need to pay attention to preventing and resolving major risks and challenges, and ensure a balance between the quality, structure, scale, speed, efficiency, and security in terms of development.
III. Strategic direction
To promote development with a focus on quality improvement during the 14th Five-Year Plan period, we must ground our efforts in the new stage of development, apply the new development philosophy and create a new development paradigm. Understanding the new development stage is the realistic basis for implementing the new development philosophy and creating the new development paradigm. Implementing the new development philosophy provides a guide for understanding the new development stage and fostering the new development paradigm. Building the new development paradigm is a strategic choice in response to the opportunities and challenges in the new development stage and for implementing the new development philosophy. We must continue to deepening supply-side structural reforms, foster new demand through pursuing innovation-driven development and ensuring high-quality supply, and enhance the resilience of the supply system and its adaptability to domestic demand. We must build an effective system to boost domestic demand, expedite the establishment of a complete demand system, strengthen demand-side management, and build a robust domestic market. We must unswervingly push forward reform, get rid of institutional obstacles to economic circulation, and promote the flows of production factors and the integration at the stages of production, allocation, distribution, and consumption. We must be fully committed to greater opening-up, continue to deepen the opening-up based on the flow of production factors, stably expand the institution-based opening-up, and leverage the flows of the domestic economy to make China a major magnet for global production factors and resources. We must strengthen the leading role of domestic circulation, improve its efficiency and level via international circulation, and realize the mutual reinforcement of domestic and international circulation.
In accordance with the strategic arrangement for comprehensively building China into a modern socialist country, Vision 2035 and the main objectives for economic and social development during the 14th Five-Year Plan period are as follows.
I. Vision 2035
By 2035, China will basically achieve socialist modernization. Our economic and technological strength, and comprehensive national strength will increase significantly. We will make new strides in economic aggregate and the per capita income of urban and rural residents. Making major breakthroughs in core technologies in key areas, we will be a global leader in innovation, and will also achieve new industrialization, enhanced IT application, urbanization, and agricultural modernization, and complete building a modern economic system. We will have modernized the governance system and capacity, and the rights of the people to participate and to develop as equals will be adequately protected. The rule of law for the country, the government, and society will be comprehensively in place. China will become a powerful country in terms of culture, education, human capital, sports, and health. The well-rounded development of the people and social etiquette and civility will be significantly enhanced. China’s cultural soft power will grow much stronger. Eco-friendly work and lifestyle will be advanced to cover all areas of society. Carbon dioxide emissions will steadily decline after reaching a peak, and there will be a fundamental improvement in the environment after the goal of building a Beautiful China is met. The opening-up will reach a new stage with substantial growth in the country’s capabilities for participating in international economic cooperation and competition. The per capita GDP will reach the level of moderately developed countries and the size of the middle-income group will be significantly expanded. Equitable access to basic public services will be ensured. Disparities in development between urban and rural areas and between regions, and in living standards will be significantly reduced. The Peaceful China initiative will be pursued at a higher level. The modernization of national defense and the military will be achieved. People will lead a better life, and more notable and substantial progress will be achieved in well-rounded human development and in common prosperity for all.
II. Main objectives for economic and social development during the 14th Five-Year Plan period
—China will strive to make new strides in economic development during the period. Development is the foundation and the key for solving all of China’s problems. We must be fully committed to the new vision for development and realize sustained and healthy economic development based on a marked improvement in quality and efficiency. We will fully tap China’s growth potential, keep the average annual growth of GDP within an appropriate range, set annual targets for GDP growth on the basis of actual conditions, and ensure that overall labor productivity grows faster than GDP. The domestic market will be stronger, the economic structure will be further optimized, and the innovation capacity will be significantly improved. China’s R&D spending will increase by more than 7% annually, and is expected to account for a higher percentage of GDP than that during the 13th Five-Year Plan period. The upgrade of the industrial base and modernization of the industrial chains will be significantly improved, and the agricultural foundation will be strengthened. The balance of development between urban and rural areas and between regions will be significantly enhanced. The permanent urban residents will increase to 65% of the population, and significant progress will be made towards a modernized economy.
—New steps will be taken in reform and opening-up. China will further improve its socialist market economy with a high-standard market system in place. Market entities will be increasingly dynamic, and major progress will be achieved in the reform of the property rights system and the market-based allocation of factors of production. A more robust system of fair competition will prevail, and a new system of higher-standard open economy will take shape.
—China’s social etiquette and civility will be further enhanced. Core socialist values will be widely embraced, and significant improvement will be made in the intellectual, moral, scientific, cultural, and health standards of Chinese citizens. The systems for public cultural services and cultural industries will be further improved, the intellectual and cultural life of the Chinese people will become richer, the international influence of the Chinese culture will be further increased, and an even stronger bond will be forged among all the people of the Chinese nation.
—New progress will be made in building an ecological civilization. The territorial space will be better developed and protected. Remarkable results will be achieved in a shift towards eco-friendly work and lifestyle. Energy and resources will be more rationally allocated and much more efficiently used. Energy consumption per unit of GDP and carbon dioxide emissions per unit of GDP will be reduced by 13.5% and 18%, respectively. The total discharge of major pollutants will be consistently reduced. The forest coverage will reach 24.1%, and the environment will be consistently improved with a stronger defense for ecological security. The living environment in urban and rural areas will also be significantly improved.
—The well-being of people will be boosted. We will increase employment and create better quality jobs, while maintaining the surveyed urban unemployment rate within 5.5%. Per capita disposable income will grow in line with GDP growth, and the income distribution structure will be significantly improved. The access to basic public services will be much more equitable. All Chinese people will enjoy better education opportunities, with the average years of schooling among the working-age population rising to 11.3. The multi-tiered social security system will be improved, with basic old-age insurance covering 95% of the population. The health care system will be improved, and the average life expectancy will be increased by 1 year. What we have achieved in poverty alleviation will be consolidated and expanded, the rural revitalization strategy will be comprehensively carried forward, and solid strides will be made towards common prosperity for all.
—Further progress will be made in China’s governance capacity. Socialist democracy and the rule of law will be enhanced, so will be social fairness and justice. With improvements in the administration system, the government will better exercise its role, and its performance and credibility will be significantly enhanced. Social governance, especially primary-level governance, will be remarkably improved. Systems and mechanisms for forestalling and defusing major risks will be constantly improved, with the capacity to handle public emergencies significantly enhanced. Notable progress will be seen in preventing natural disasters, development security will be more effectively ensured, and major steps will be taken in the modernization of the national defense and armed forces.

Part II Innovation-Driven Development to Build New Strengths
Innovation remains at the heart of China’s modernization drive. The development of science and technology has increasingly assumed strategic importance for China’s national development. It is crucial to build cutting-edge technologies to spur economic growth, meet the country’s critical needs, and improve the people’s health. Indeed, success in building prosperity hinges on the development of science and education, talent building, and innovation, including institutional support for innovation.
Chapter 4 A Strategic Vision for Building Strength in Science and Technology
An action plan for building prosperity through science and technology will be developed, with a focus on strengthening institutional support on a national level and leveraging the advantages of our socialist market economy. It aims to encourage innovation and breakthroughs in core technologies in key areas and improve the overall efficiency of the innovation chain.
I. More rational allocation of scientific and technological resources
We will promote an optimal combination of innovation systems oriented towards the strategic needs of the country and work faster to enhance our strategic scientific and technological capability based on the development of national laboratories. Focusing on quantum information, photonics, micro and nanoelectronics, network communications, artificial intelligence, biomedicine, modern energy systems, and other major innovation areas, we will establish a group of national laboratories and reorganize national key laboratories, thus establishing a laboratory system with a rational structure and efficient operation. We will optimize and upgrade national engineering research centers and national technology innovation centers among other innovation bases, promote the optimal allocation of research resources and sharing of resources among research institutes, higher-education institutions, and enterprises, and support the development of new forms of innovators such as research universities and R&D institutions. We will promote the diversification of investors, the modernization of management systems, market-based operation mechanisms, and flexible employment mechanisms.
II. Encouraging ground-breaking scientific and technological innovation
We will formulate and implement strategic scientific programs and scientific projects in the basic and core areas concerning national security and development, and carry out pioneering and strategic national projects in artificial intelligence, quantum information, integrated circuits, life and health, brain science, biological breeding, aerospace science and technology, deep earth and deep sea, among other frontier fields. Based on the urgent and long-term needs of the country, we will concentrate our advantageous resources to make breakthroughs in core technologies in the key fields including new and sudden outbreak of infectious diseases, biosafety risk prevention and control, medicine and medical equipment, key components and parts and basic materials, and petroleum and natural gas exploration and development.
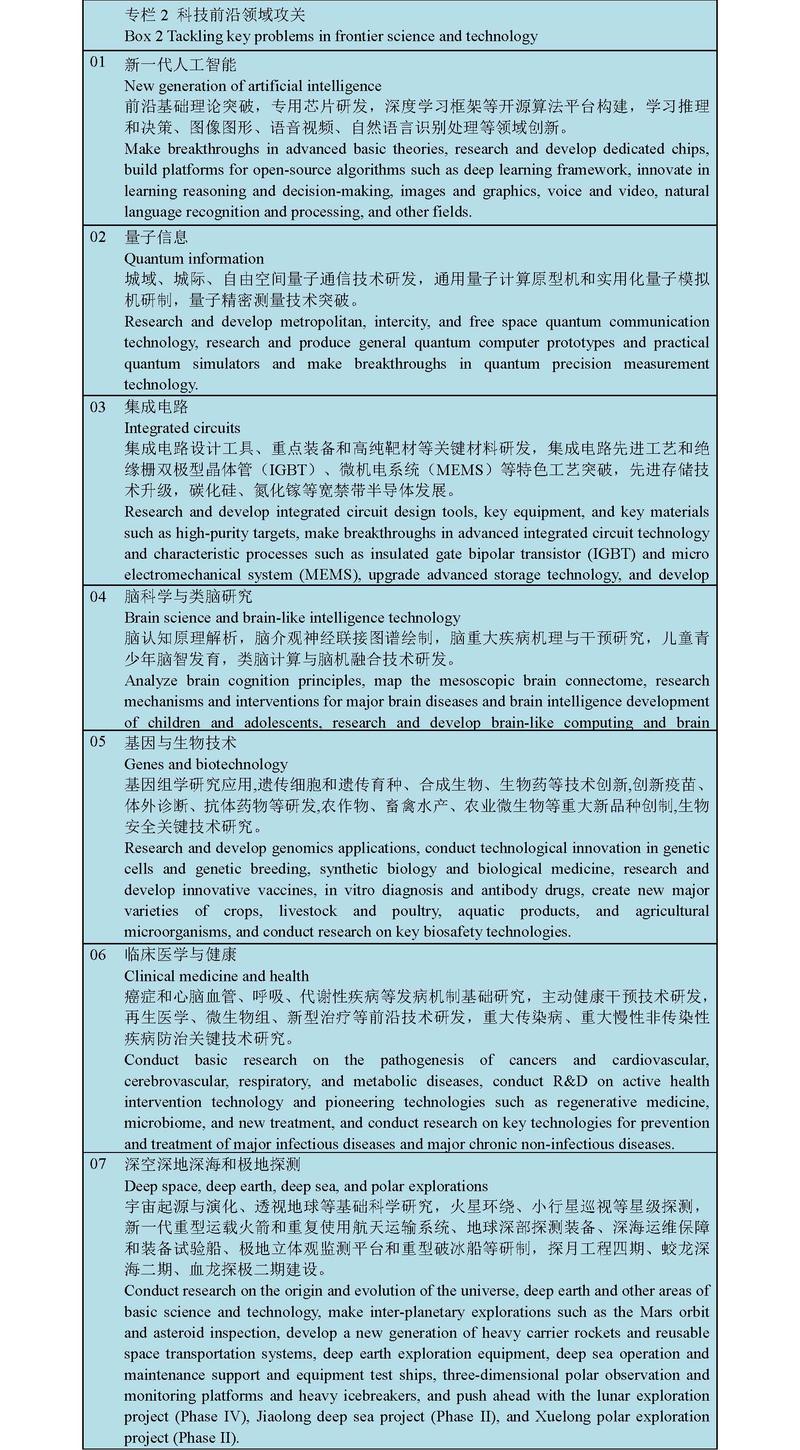
III. Strengthening basic research
We will strengthen the role of application-oriented research as a driving force, encourage free exploration, formulate and implement a 10-year action plan for basic research, and give priority to a group of research centers for fundamental disciplines. We will increase funding and improve the composition of spending for basic research, give preferential tax treatment to enterprises engaging in basic research, encourage the private sector to channel more resources to basic research through diverse means such as donations and investment, and form a mechanism for ensuring sustainable and stable funding. The spending on basic research will account for over 8% of total R&D spending. A sound evaluation system and incentive mechanism will be established and improved for long-term evaluation of basic research and for creating an environment conducive to basic research.
IV. Building major platforms for scientific and technological innovation
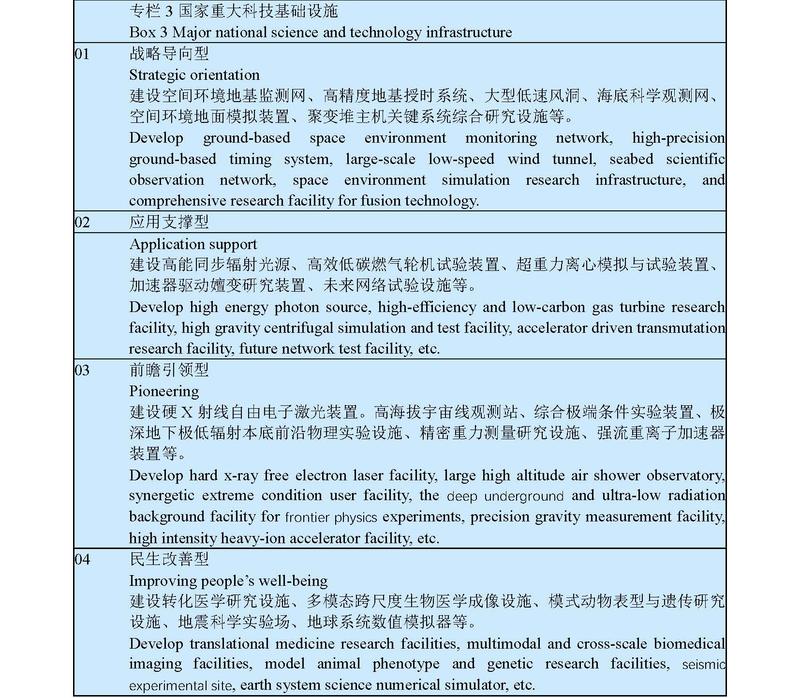
We will support the initiative of making Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area international centers for science and technology innovation, build comprehensive national science centers in Huairou in Beijing, Zhangjiang in Shanghai, Greater Bay Area, and Hefei in Anhui, and support the building of regional science and technology innovation centers in places where conditions permit. We will strengthen the innovation functions of national innovation demonstration zones, new and high-tech industry development zones, and economic and technological development zones. We will adopt an appropriate forward-thinking plan for major national science and technology infrastructure and ensure that it is better shared and more efficiently utilized. We will intensively build repositories of natural science and technology resources, national workstations (networks) for field observation and research and scientific big data centers; strengthen the R&D and manufacture of high-end research instruments and equipment; and build high-end national exchange platforms for research papers and scientific and technological information.
Chapter 5 Technological Innovation Capability of Enterprises
Market-oriented mechanisms for technological innovation will be in place to boost the role of enterprises in innovation, encourage the flow of resources to enterprises, and enable enterprises to play a major role in innovation with the support of universities, research institutes, and end-users.
I. Encouraging enterprises to increase R&D spending
More efforts will be made to implement inclusive policies such as granting an extra tax deduction on R&D costs and offering preferential tax treatment to high-tech enterprises. We will expand and improve the insurance compensation and incentive policies for the application of newly developed major technical equipment, give play to the leading and demonstrative roles of major projects, and support innovative products and services with government procurement policies. We will enhance the enterprises’ motivation for innovation by improving standards, quality, and competition regulations and other measures; build a robust assessment system for encouraging R&D efforts of state-owned enterprises, and establish an R&D reserve system featuring independent accounting, exemption from value increase assessment, and fault tolerance and error correction, to ensure that the annual growth rate of R&D expenditure of central state-owned industrial enterprises is significantly higher than the national average. At the same time, we will enhance preferential tax policies that encourage innovation in small and medium-sized scientific and technological enterprises.
II. Support for research and development of general-purpose technologies
China will focus on integrating and upgrading key general-purpose technology platforms, support leading enterprises in the industry to work with universities, research institutes, and upstream and downstream industrial enterprises in building national centers for industrial innovation and in undertaking major national science and technology projects. Qualified enterprises will be supported to cooperate with research institutes that have been transformed into enterprises, to establish industry research institutes and provide common technology services for public welfare. China will build new general-purpose technology platforms to tackle key problems encountered in multiple industries and fields. We will give play to the leading and supporting roles of large enterprises, support the growth of innovative micro, small, and medium enterprises into important sources of innovation, and promote collaborative innovation among large, medium, and small enterprises in the upstream, mid-stream, and downstream of the industrial chain. We will also encourage the establishment of mixed-ownership industrial technology research institutes on the basis of industrial clusters in places where conditions permit, to facilitate research and development in key generic technologies.
III. Innovation services for enterprises
China will give enterprises greater access to national research platforms, scientific and technological reports, and research data, innovate the mechanisms for applying scientific and technological achievements, and encourage the licensing of eligible government-financed scientific and technological achievements to small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). We will push forward the institutional reform for innovation and entrepreneurship and build specialized and market-oriented institutions for technology transfer and teams of technology managers. We will improve the financial support system for innovation, encourage financial institutions to develop fintech products such as intellectual property pledge financing and technology insurance, and carry out pilot projects of risk compensation for loans related to the application of scientific and technological achievements. We will also provide smooth financing channels for domestic listing of technology-based enterprises, enhance the “hard technology” characteristics of the Science and Technology Innovation Board as well as the function of the ChiNext stock market in serving growth-oriented innovative enterprises and startups, encourage the development of angel investment and venture capital, and give better play to the role of venture capital guide funds and private equity funds.
Chapter 6 Creativity and Talent Development
It is important to foster a culture that respects knowledge, encourages hard work and creativity, and is conducive to talent development. Reform is necessary to improve a full spectrum of talent management practices, including training, recruitment, and placement, thus giving full play to the role of talent, the most essential resource.
I. Building a contingent of high-calibre personnel
China will develop more world-class strategic talents and leading figures in science and technology and innovation teams in accordance with the laws of personnel development and research activities. The country will foster reserves of young scientists and engineers with international competitiveness, pay attention to developing and discovering talents through major scientific and technological tasks and major innovation bases, and support the establishment of post-doctoral innovation posts. The country will strengthen the training of innovative, skilled, and application-oriented personnel, implement knowledge renewal projects and skills upgrade initiatives, and build stronger teams of high-level engineers and highly skilled personnel. Efforts will be made to intensify the training of top students in basic disciplines, and build bases and frontier science centers for mathematics, physics, chemistry, biology, and other basic disciplines. We will implement a more open talent policy and build a research and innovation center that brings together excellent personnel at home and abroad. We will improve the policies for foreign high-calibre personnel and professionals who stay or reside in China for work, research, and exchange, improve the permanent residence system for foreigners in China, and explore the establishment of a skilled migration system. We will also improve the systems concerning salary and welfare, children’s education, social security, and tax incentives to provide an internationally competitive and attractive environment for overseas scientists to work in China.
II. Incentives for researchers
We will improve the evaluation and incentive mechanism, build a robust system to evaluate scientists and engineers based on the criteria of innovation ability, quality, effectiveness and contribution, and develop an income distribution mechanism that fully reflects the value of knowledge, technology, and other elements in innovation. We will carefully select leading and top-notch personnel, leverage their expertise and give them a greater say on technological routes and fund use. We will free up more space for researchers in an all-round manner and expand the “green channel” for research management. We will adopt a distribution policy oriented towards rewarding knowledge and improve the mechanism for researchers to share the benefits from their on-the-job inventions, vest in them the ownership or long-term right of use of their research results on a pilot basis, and increase their share of benefits. We will also deepen the reform of the academician system.
III. An ecosystem for innovation, entrepreneurship, and creativity
We will vigorously carry forward the spirit of scientists in the new era, strengthen research integrity, and improve the ethical system in science and technology. We will protect the property rights and innovation income of entrepreneurs according to law and give full play to the important role of entrepreneurs in steering innovation in the right direction, bringing together competent personnel and raising funds. We will promote the in-depth development of innovation, entrepreneurship, and creativity, and optimize the layout of the innovation and entrepreneurship demonstration bases. We will advocate an innovation and entrepreneurship culture of dedication, seeking better from best, concentration and tolerance of failure, and improve the trial-and-error mechanism that allows errors to be tolerated and corrected. To create a social climate that values science and innovation, and improve the scientific literacy of the people, we will uphold the spirit of scientists and craftsmanship, extensively carry out science popularization activities, and foster an interest in science among young people.
Chapter 7 Mechanisms for Scientific and Technological Innovation
Institutional reforms will proceed at a deeper level to improve the national science and technology governance system and national planning for the development of science and technology, and allow a holistic approach to deploying projects, facilities, personnel, and funds in key sectors.
I. Deeper reforms in the science and technology management system
We will accelerate the transformation of government functions in science and technology management, enhance the guiding role of planning and policies and the creation of an innovative environment, and reduce direct interventions in financial and physical resources and in projects. The government funding system for research will be consolidated, with an increased focus on strategic and key sectors, and the problems of compartmentalization and small and scattered funding will be effectively addressed. The approval, organization, and management of major scientific and technological projects will be reformed to grant more decision-making rights to research institutions and researchers. To this end we will implement a system of chief technology officers assuming responsibilities, implement a ranking system and a strong and open competition mechanism for selecting the best candidates to lead key research projects, and improve the funding mechanism to combine awards and subsidies. We will improve the evaluation mechanism of science and technology and the classified evaluation system for free exploration and task-oriented science and technology projects, establish an evaluation mechanism for science and technology projects on which a consensus is not yet achieved, and optimize science and technology award projects. We will establish and improve the modern research institution system and support the institutions to try out more flexible systems for human resources, post, and salary management. We will establish and improve the mechanism of free and orderly flow of innovation resources among institutions of higher learning, research institutions, and enterprises. In addition to these efforts, we will further promote pilot reforms for comprehensive innovation.
II. Protection of intellectual property rights
We will implement a strategy to make China strong on intellectual property rights, implement a strict intellectual property protection system, improve the related laws and regulations, and accelerate the legislation in emerging fields and new forms of business. We will strengthen judicial protection and administrative enforcement related to intellectual property rights, improve relevant systems of arbitration, mediation, notarization, and assistance in the protection of rights, build a better system of punitive damages for intellectual property infringements, and increase the compensation. We will optimize the patent subsidy and incentive policies and evaluation mechanisms to better protect and encourage high-value patents and develop patent-intensive industries. By reforming the ownership and distribution mechanism of state-owned intellectual property rights, we will give research institutions and institutions of higher learning a greater say in the disposition of intellectual properties. The intangible assets evaluation system will be improved, a management mechanism that combines incentives and supervision will be established, and public service platforms will be built for intellectual property protection and application.
III. Openness and cooperation in the field of science and technology
We will implement a more open, inclusive, mutually beneficial, and shared international strategy for cooperation in science and technology and more actively integrate ourselves into the global innovation network. We will pragmatically promote international cooperation in the fields of global epidemic prevention and control and public health, boost joint research and development with researchers from various countries focusing on climate change, human health, and other issues, take the lead in designing and initiating international big science programs and projects, and give play to the unique role of science funds. We will step up the opening-up of the national science and technology programs, launch a group of major science and technology cooperation projects, explore and establish a global research fund, and implement scientist exchange programs. We will also support the establishment of international scientific and technological organizations in China, and welcome foreign scientists to serve in scientific and technological academic organizations in China.
Part III Industrial Modernization and the Foundation of Real Economy
The focus of economic growth should be on the development of the real economy. Building national strength requires, in particular, strengthening manufacturing and improving product quality. Further integration of advanced manufacturing and modern services is called for. Improving infrastructure provides support and paves the way for new growth. It is important to strengthen institutional support for symbiotic interaction between the real economy, scientific and technological innovation, financial services, and talent development.
Chapter 8 Strengthening Manufacturing
It is crucial to build more secure, resilient, and efficient modern supply chains not subject to disruptions and outside interference. It is also crucial to ensure that the share of manufacturing in the economy remains stable, and to enhance the competitive advantages of the manufacturing sector with a focus on quality improvement.
I. Strengthening basic industrial capacities
We will carry out projects to rebuild industrial foundation and promptly resolve bottlenecks and weaknesses in basic spare parts and components, basic software, basic materials, basic processes, and fundamental industrial technology. Leveraging the leading enterprises in relevant sectors, we will step up efforts to make major breakthroughs in important products and core technologies in key fields and work quickly to make groundbreaking progress in engineering and industrialization. We will ensure the success of projects launched to achieve breakthroughs in key technical equipment, improve the incentive and risk compensation mechanisms, and promote the demonstration and application of newly developed equipment, materials, and software. We will improve the basic industrial infrastructure support system, establish a group of national centers for manufacturing innovation in key sectors, improve national quality infrastructure, build production application demonstration platforms and standard measurement, certification and accreditation, inspection and testing, test verification, and other industrial technology public service platforms, and improve the industrial database for technology and processes.
II. Modernization of industrial chains and supply chains
To establish more innovative, higher value-added, safer, and more reliable industrial chains and supply chains, we will pursue both economic efficiency and security, shore up our weaknesses, play to our strengths and do a good job in strategically designing supply chains and adopt targeted policies for different sectors. We will consolidate and improve the manufacturing chains, strengthen the support of resources, technology, and equipment, enhance international cooperation in industrial security, and drive the diversification of industrial and supply chains. Leveraging the industrial scale, supporting facilities, and first mover advantages in certain fields, we will consolidate and enhance the competitiveness of the whole industrial chain in sectors such as high-speed railway, electronic equipment, new energy, and shipbuilding, and create an industrial chain of overall strategic importance starting from complete machines that are in line with the direction of future industrial transformation. The plan for the regional industrial chains will be optimized to guide the key links in the chains to remain in China, and further enhance the capacity of the central and western regions and the northeast region as destinations of industrial relocation. We will implement production capacity reserve projects for emergency products and build regional bases for ensuring emergency material production. We will carry out programs to build leading enterprises that possess core competitiveness and can dominate in their respective ecosystems, support small and medium-sized enterprises to enhance their professional advantages, and foster “little giant” enterprises with high growth potential, advanced technology and strong market competitive edge as well as single-product specialists in the manufacturing industry. Technical and economic security assessment will be reinforced, and an industrial competitiveness investigation and evaluation program will be put into practice.
III. Upgrading the manufacturing industry
We will further implement intelligent manufacturing and green manufacturing projects, develop new service-oriented manufacturing models, and promote high-end, intelligent, and green manufacturing. We will foster advanced manufacturing clusters and promote the innovation and development of industries such as integrated circuits, aerospace equipment, high-tech ships and ocean engineering equipment, robots, advanced railway equipment, advanced power equipment, engineering machinery, high-end CNC machine tools, medicine and medical equipment. To transform and upgrade traditional industries, we will improve the layout and adjust the structure of petrochemical, iron and steel, nonferrous metals, building materials, and other raw material industries, expand the supply of high-quality products in light and textile industries, expedite the transformation and upgrade of enterprises in chemical, papermaking, and other key industries, and improve the green manufacturing system. We will continue to implement special projects to enhance the core competitiveness and technological transformation of the manufacturing industry, encourage enterprises to adopt advanced and readily applicable technologies, and strengthen equipment upgrading and large-scale application of new products. In terms of intelligent manufacturing, we will build demonstration factories and a better system of standards. Intensified efforts will be made to enhance quality, and to encourage manufacturers to increase the variety of products, raise their quality, and build the brands.
IV. Policy support for manufacturing cost reduction
We will intensify efforts to ensure the supply of factors of production, provide efficient services, consolidate and expand the results of tax and fee cuts, reduce the production and operating costs of enterprises, and enhance the embeddedness and competitiveness of the manufacturing industry. We will work to increase the plot ratio and use efficiency of industrial land and promote new industrial land use models. We will increase medium- and long-term loans and lines of credit for manufacturing, increase loans for technological transformation, and make sure equity investment and bond financing are more heavily weighted towards manufacturing. We will permit manufacturing enterprises to participate in market-oriented electricity transaction, regulate and reduce logistics charges in port shipping, road and railway transportation, and review and standardize charges related to enterprises. We will establish a mechanism to provide full cycle services for major manufacturing projects and build a system for entrepreneurs to participate in enterprise-related policy making. Support will be given to build comprehensive service platforms for information, technology, import and export, and digital transformation of SMEs.
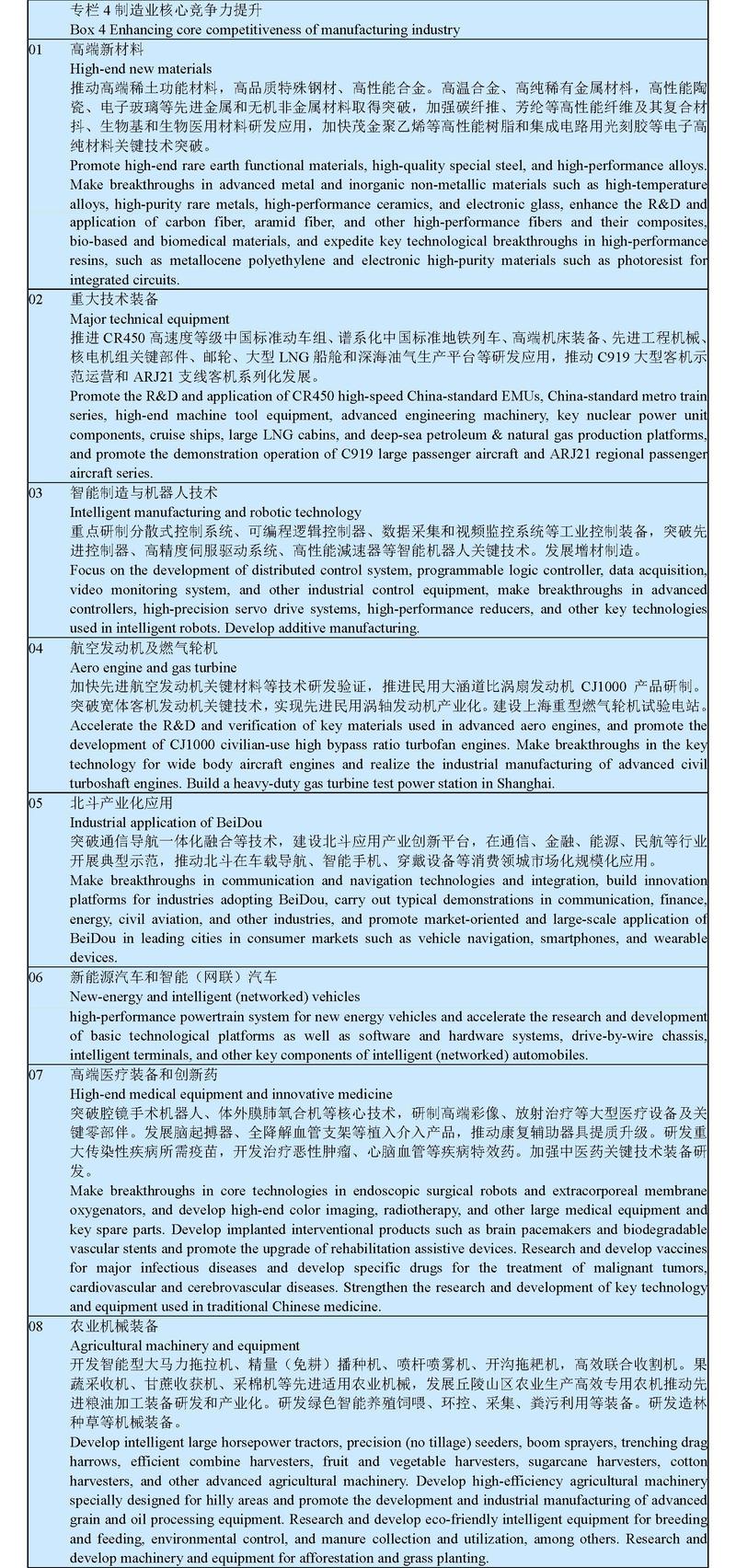
Chapter 9 Emerging Industries of Strategic Importance
In response to emerging technology trends, it is essential to foster pioneering and pillar industries, and promote the integrated development of emerging technology clusters of strategic importance, so that the contribution of such industries to GDP will exceed 17%.
I. New pillars of the industrial system
China will focus on the new generation of information technology, biotechnology, new energy, new materials, high-end equipment, new energy vehicles, environmental protection, aerospace, marine equipment, and other emerging industries of strategic importance, and accelerate the innovation and application of core technologies in key fields to enhance the country’s capacity of ensuring supply of productive factors and foster new drivers for industrial development. We will promote the integration and innovation of biotechnology and information technology, accelerate the development of biomedicine, biological breeding, biomaterials, bioenergy, and other industries, to enhance bioeconomy in size and strength. We will continue to promote and adopt the BeiDou Navigation Satellite System and facilitate its high-quality industrial development. We will further promote projects to develop China’s strategic emerging industry clusters, improve the mechanisms for organization, management, and professional promotion of industrial clusters, build public service complexes for innovation, and create growth drivers for emerging industries of strategic importance which have different characteristics, complementary advantages, and a reasonable structure. We will encourage technological innovation and the merger and restructuring of enterprises and avoid low-level replication. We will give full play to the guiding role of industrial investment funds and increase financing guarantee and risk compensation.
II. Forward-looking technology planning
In brain-like intelligence, quantum information, genetic technology, future network, deep-sea and aerospace exploration, hydrogen energy and energy storage, and other areas of cutting-edge technology and industrial transformation, we will organize and implement the plan for incubating and accelerating industries of the future, and plan and create a layout for such industries. In areas where we have prominent advantages in science and education resources and strong industrial foundation, we will establish a number of national research institutes on industrial technology of the future to strengthen multi-path exploration and multidisciplinary integration of cutting-edge technology and supply of disruptive technology, implement cross-sector industry integration demonstration projects, create future technology application scenarios, and accelerate the formation of industries of the future.
Chapter 10 Development of the Service Sector
In tandem with industrial transformation, and in response to increased needs of consumers, expansion of the service sector is envisaged, requiring a major increase in service delivery, as well as in the efficiency and quality of services to build a new service sector system that is optimized and competitive.
I. Integrated development of producer services
With the aim of developing high-quality manufacturing, we will promote the specialization of producer services and their movement towards the high-end of the value chain. Focusing on industrial innovation, we will accelerate the development of R&D design, industrial design, business consulting, inspection, testing, and certification services. To allocate factors of production more efficiently, we will promote the innovative development of supply chain finance, information and data, human resources, and other services. We will strengthen the complete industrial chain and improve modern logistics, procurement and distribution, production control, operation management, and after-sales service. We will promote the in-depth integration of modern services with advanced manufacturing and modern agriculture, deepen business connections, chain extension, and technology penetration, support the development of new professional organizations offering services such as intelligent manufacturing system and process re-engineering solutions, and foster internationally competitive service enterprises.
II. Development of consumer services
To enhance convenience and improve the service experience, we will push a shift of consumer services towards higher quality and greater diversity; accelerate the development of health, elderly care, child care, culture, tourism, sports, property management, and other services; strengthen the supply of basic services oriented towards public interests; expand the supply of all kinds of services covering the whole life cycle; and continue to improve the quality and expand the scale of domestic services, to integrate them into the development of smart communities, elderly care, and child care. We will encourage innovation of commercial circulation and business forms and models, promote the upgrade of digital and smart technologies and cross-border integration, and fulfillment of consumer demand through online and offline omni-channel services. We will work faster to improve the standards for elderly care, domestic services, and other services, improve the certification and accreditation system for consumer services and promote the integrity and professional development of the services.
III. Reform and opening-up in the service sector
We will further open the service sector to the domestic and international markets, relax market access, comprehensively reduce unreasonable restrictions and encourage social forces to expand the provision of diversified service at various levels. We will improve the policy system supporting the development of the service sector, and develop new policies on land, taxation, finance, and pricing, which can adapt to the needs of new service business formats and models and industrial integration. We will improve the service quality standards and systems, push the implementation and promotion of the standards, accelerate the development of regulatory catalogs, processes and standards for key service industries, and build an efficient and collaborative regulatory system for the service sector. We will improve the system for appraisal of professional titles for people in the service sector, encourage employees to participate in vocational skills training and appraisal, and push forward the comprehensive pilot reform and opening-up of the service sector.
Chapter 11 Modern Infrastructure
A holistic approach will be adopted to infrastructure development, which covers traditional and new types of infrastructure, so as to build a modern network of infrastructure that is efficient, practical, smart, eco-friendly, safe, and reliable.
I. Construction of new types of infrastructure
With the aim of strengthening the support for digital transformation, intelligent upgrade, and integrated innovation, we will build new types of infrastructure in such areas as information technology, integration, and innovation. We will build high-speed, ubiquitous, secure, and efficient information infrastructure with a space-ground integrated network and integrated interconnection, and enhance the capabilities of data sensing, transmission, storage, and computing. We will accelerate the large-scale deployment of 5G network with the user penetration rate increasing to 56%, promote the upgrade of gigabit optical network, and make arrangement for the 6G network technology reserve with foresight. We will expand the backbone network interconnection nodes, set up new international communication passageways, fully advance the commercial deployment of Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6), and implement projects for improving basic networks in small and medium-sized cities in the central and western regions. We will promote the all-round development of the Internet of Things (IoT) and build IoT access capability that supports fixed-mobile convergence with a combination of broad and narrow bands. We will accelerate the building of an integrated national system of big data centers, strengthen the overall planning and intelligent scheduling of computing power, build national hub nodes and big data center clusters as well as E-level and 10E-level supercomputing centers. We will dynamically and stably develop the Industrial Internet and Internet of Vehicles; build a highly efficient communications, navigation, and remote sensing space infrastructure network with a global coverage, as well as establish commercial space launch sites. We will accelerate the digital transformation of traditional infrastructure for transportation, energy, and urban utilities, and intensify our efforts in developing ubiquitous sensing, terminal networking, and intelligent scheduling system. We will give full play to the leading role of the market, open up diverse channels for investment, and create a system of standards for new types of infrastructure.
II. Improving transportation
China will build a modern comprehensive transportation system, promote the integrated development of various modes of transportation, and improve the network effect and operational efficiency. We will improve the comprehensive transportation corridors, intensify the construction of strategic trunk corridors with improved access to Xinjiang and Tibet, the central and western regions, and regions along the coast, rivers, and border areas, promote in an orderly manner the upgrade and expansion of corridors in congested sections, and strengthen interconnectivity with neighboring countries. We will build a network of expressways, complete the network of “eight vertical and eight horizontal” high-speed railways, improve the quality of the national highway network, and accelerate the construction of world-class port and airport clusters. We will improve the network of trunk railways, accelerate the construction of standard rail lines and the electrification of existing railways, optimize the distribution of passenger and freight railways, make progress in breaking through and upgrading bottleneck sections in normal national and provincial highways, make progress in the expansion and upgrade of high-grade inland waterways, steadily build feeder airports, general airports, and freight airports, and actively develop the general aviation industry. China will strengthen the construction of postal facilities and implement the express delivery project to ensure villages’ access to the service, promote the integration between express delivery and manufacturing, and to encourage the development of international delivery service. We will promote the integration of transportation in city clusters and metropolitan areas, accelerate the construction of intercity and suburban railways, build systems of ring expressways, and develop urban rail transit in an orderly manner. We will improve the coverage of transportation services, promote the construction of regional railways and roads along the borders and leading to border areas, continue to ensure that rural roads are well built, managed, maintained, and operated, and improve road safety facilities. China will build a multi-tier and integrated transportation hub system, optimize the hub station layout, promote intensive and comprehensive development, improve the collection and distribution system, develop intermodal passenger and cargo transport, and promote the one-stop and “one bill of lading” services for the entire trip. We will also promote the construction of China-Europe Railway Express assembly centers. In addition, reforms will be thoroughly carried out in railway enterprises, the air traffic control system, and the highway toll system and maintenance mechanism.
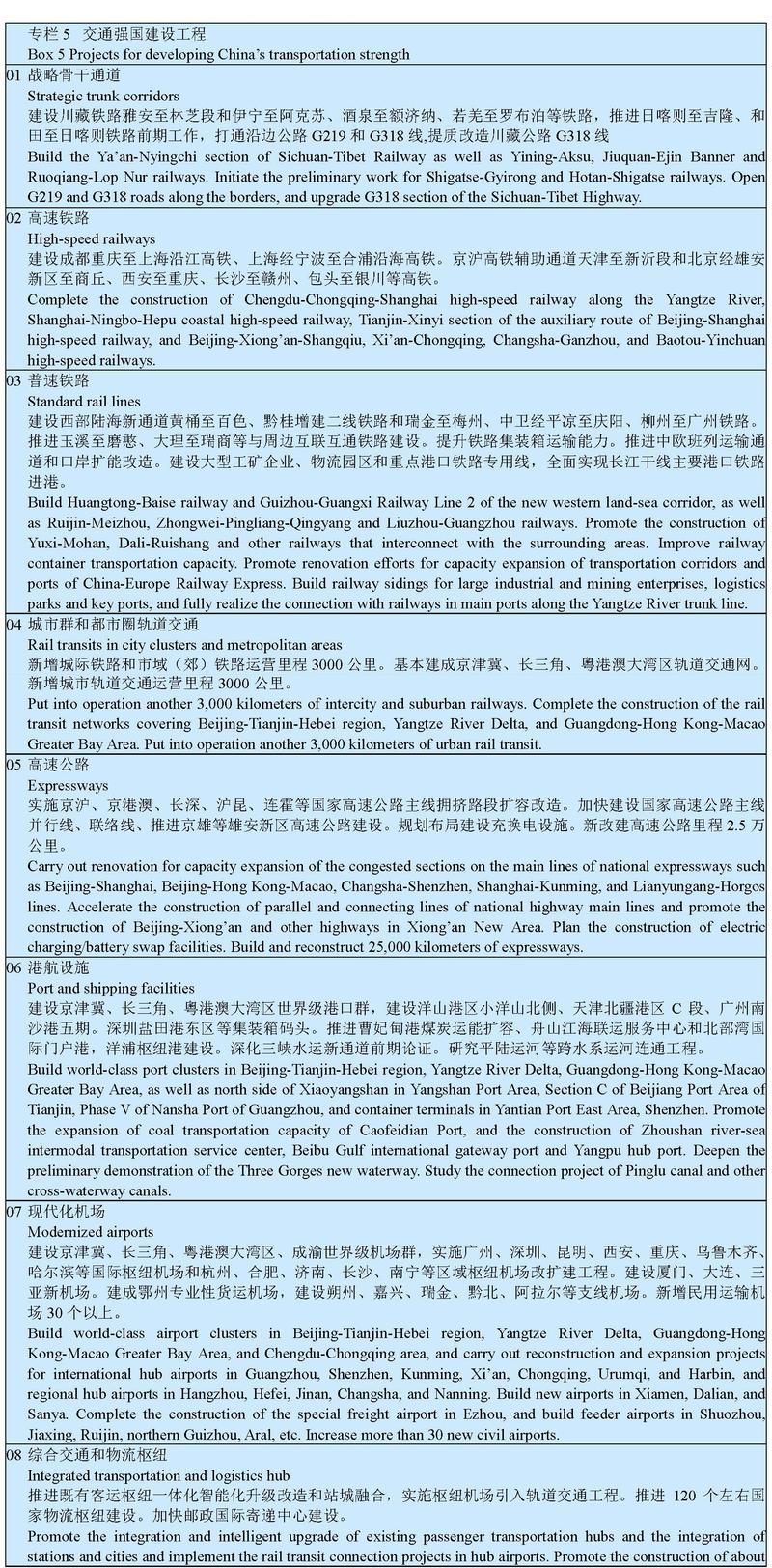
III. Building a modern energy system
We will promote the energy revolution and build a clean, low-carbon, safe, and efficient energy system to enhance energy supply capabilities. We will accelerate the development of non-fossil energy by balancing centralization and distribution, vigorously enhance the scale of wind power and photovoltaic power generation, accelerate the development of distributed energy in the central and eastern regions, ensure orderly development of offshore wind power, accelerate the construction of the southwest hydropower base, safely and steadily promote the construction of coastal nuclear power facilities, and build a number of clean energy bases featuring integrated energy development, and increase the proportion of non-fossil energy in total energy consumption to about 20%. We will promote the concentration of coal production in resource rich areas and reasonably control the scale and development pace of coal power projects to promote the replacement of coal with electricity. We will liberalize market access for petroleum and natural gas exploration and development in an orderly manner, accelerate the utilization of deep-sea, deep-seated, and unconventional petroleum and natural gas resources, and promote the increase of petroleum and natural gas reserves and production. We will develop and utilize geothermal energy according to local conditions and improve the utilization rate of UHV power transmission channels. We will accelerate the transformation of power grid infrastructure into smart infrastructure as well as the construction of smart microgrids. We will improve power system complementarity and intelligent regulation capabilities, strengthen the coordination of power source, grid, load and storage, enhance clean energy consumption and storage capabilities, and enhance transmission and distribution capacities to remote areas. We will promote flexible transformation of coal power, and accelerate the construction of pumped storage hydroelectric plants and large-scale application of new energy storage technology. We will improve cross-regional coal transportation channels and collection and distribution systems and accelerate the construction of the main natural gas pipelines and the petroleum and natural gas interconnection network.

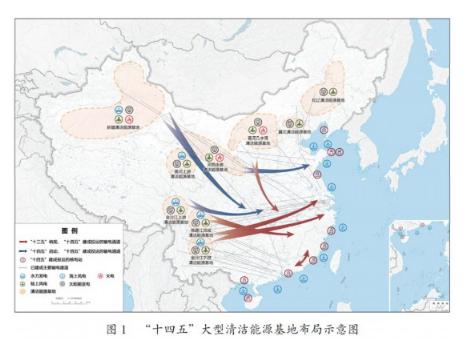
Figure 1. Distribution of large-scale clean energy bases in the 14th Five-Year Plan period
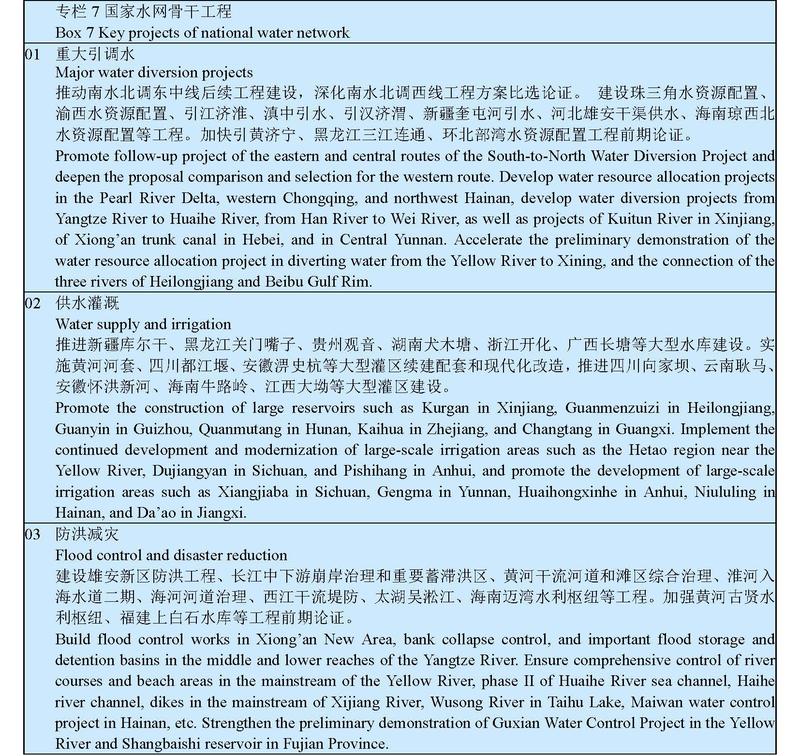
IV. Construction of water conservancy infrastructure
Based on the overall and spatially balanced allocation of water resources in the drainage basins, we will strengthen the coordination between administrative divisions in river system management and protection and key project construction, and strengthen the coordination of small, medium, and large water conservancy facilities to enhance the optimal allocation of water resources as well as flood and drought disaster prevention capabilities. By prioritizing water conservation, we will improve the water resources allocation system, build key water resource allocation projects, and strengthen the development of key water sources and urban emergency backup water projects. We will implement flood control improvement projects to solve weak links, accelerate the construction of pivotal flood control projects, enhance the management of small and medium rivers, reinforce dilapidated reservoirs, and fully advance the construction of dikes and flood storage and detention basins. We will strengthen the protection and restoration of water conservation areas and the protection and comprehensive management of key rivers and lakes and restore the water ecosystem to ensure clear waters and green shores.
Part IV A Robust Domestic Market and a New Development Paradigm
Expanding domestic demand is of strategic importance, and should occur in lockstep with supply-side structural reforms, with innovation and quality improvement driving new demand. A new “dual circulation” development paradigm will assign a central role to the domestic market, with domestic and overseas markets complementing each other.
Chapter 12 Greater Domestic Circulation
More reliance on the strong domestic market, and more seamless connection of economic processes, such as production, distribution, circulation, and consumption, will help remove impediments to rational flows of factors of production, and contribute to supply-demand equilibrium, conducive to creating a virtuous economic circle.
I. Supply chain adaptability
China will deepen the supply-side structural reform and improve the ability of supply to adapt to and lead the creation of new demand. By adapting to the customized, differentiated, and quality consumption demand, and by promoting innovation in production models and industrial organization models, the country will continue to expand the supply of high-quality consumer goods, medium and high-end products, and services in education, medical care, and elderly care, and improve product service quality and customer satisfaction to promote supply and demand coordination and matching. By optimizing and improving the supply structure, we will facilitate the coordinated development of agriculture, manufacturing, services, energy resources, and other industries; accelerate the marketization of competitive links in naturally monopolistic industries and achieve effective convergence of upstream and downstream industries in production, supply, and marketing by completing the industry support system. We will improve the long-term mechanism of marketization and the rule of law to resolve excess capacity, as well as the laws, regulations, and supporting policies for enterprise mergers and acquisitions as well as restructuring; establish and improve the quality classification system, accelerate the upgrade and iteration of standards and transformation and application of international standards; and launch the Chinese brands program, including the protection and development of China Time-Honored Brands, enhance the influence and competitiveness of our own brands, take the lead to foster a number of high-end brands in cosmetics, clothing, home textiles, electronic products, and other consumer goods.
II. Smooth flows of resources
China will remove impediments to the rational flow of the factors of production, rectify the imbalance and mismatch of resource factors, and facilitate the circulation of national economy at the source. We will improve the ability of financial services serving the real economy and the institutional arrangements for medium- and long-term capital supply in the real economy, innovate financial products and services that directly impact the real economy, and enhance the financing function of the multi-tier capital market. We will implement a long-term mechanism for the steady and healthy development of the real estate market and promote the balanced development of real estate and the real economy. We will effectively improve the skills of workers, improve the quality of employment and income level, and form a virtuous circle of human capital promotion and industrial transformation and upgrade. We will improve the mechanism of free flow of factors in urban and rural areas, build a cross-region industrial transfer pattern, and promote positive interaction between urban and rural areas.
III. Strengthening the supporting role of the circulation system
We will deepen the reform of the circulation system, improve the circulation channels of goods and services, increase the circulation efficiency, and reduce the transaction costs of the whole society. We will accelerate the development of a unified domestic market, optimize the market environment according to internationally advanced rules and best practices, promote the coordination and unification of standards, rules, and policies of different regions and industries, and effectively break down local protection, industry monopolies, and market segmentation. We will build a modern logistics system, accelerate the development of cold chain logistics, coordinate the construction of logistics hub facilities, key lines, regional distribution centers, and terminal distribution nodes, improve the facilities of national logistics hubs and key cold chain logistics bases, improve the logistics distribution system at county, township, and village levels, develop high-speed rail express and other railway express freight products, and strengthen the development of international air freight capacity and the competitiveness of international ocean shipping. We will optimize the international logistics channels and accelerate the formation of an interconnected, safe and efficient logistics network. We will improve the modern commercial circulation system, foster globally competitive modern circulation enterprises, support the transformation and upgrade of commercial circulation facilities such as convenience stores and farmers’ markets, develop contactless trading services, and strengthen the standardization and green development of commercial circulation. We will accelerate the establishment of a resilient emergency logistics system featuring sufficient reserves and rapid responses.
IV. Policies to facilitate domestic circulation
China will maintain a reasonable level of fiscal expenditure and deficit ratio, improve tax and fee reduction policies, and build a tax system that is conducive to increasing investment by enterprises, increasing R&D investment, adjusting income distribution, and reducing the burden on consumers. We will maintain reasonably adequate liquidity, ensure the increases in money supply and aggregate financing are generally in step with economic growth in nominal terms, innovate structural policy tools to guide financial institutions in increasing support for key areas and weak links, and standardize the development of consumer credit. We will develop more inclusive industry policies with a greater emphasis on functions, strengthen the fundamental role of competition policies, and support technological innovation and structural upgrade. We will improve the systems of income distribution, social security, and public services to be commensurate with the level of economic growth.
Chapter 13 Domestic and International Circulation
Greater domestic circulation creates a dynamic domestic market, spurs trade, attracts global resources, and stimulates internal and external demand, import and export, and inbound and outbound investment. It contributes to international cooperation and helps sharpen China’s competitive edge.
I. Import and export
We will improve the integrated regulatory system for internal and external trade, and better coordinate the laws and regulations, regulatory systems, business qualifications, quality standards, inspection and quarantine, certification, and accreditation in both areas. We will ensure that products sold in the home market have been produced on the same production lines, meet the same standards, and are of the same quality as those exported. We will reduce import tariffs and institutional costs, expand imports of high-quality consumer goods, advanced technology, important equipment, and energy resources, and promote the diversification of import sources; and improve export policies, optimize the quality and structure of exports, and steadily increase the added-value of exports. We will optimize the plan for the international market, guide enterprises to better explore traditional export markets, expand their presence in emerging markets and boost trade with neighboring countries, and stabilize their international market share. We will promote the transformation and upgrade of processing trade, enhance the construction of foreign trade transformation and upgrade bases, special customs supervision areas, trade promotion platforms, and international marketing service networks, accelerate the development of new models such as cross-border e-commerce and market procurement, and encourage the construction of overseas warehouses to ensure the smooth operation of the industrial and supply chains for foreign trade. We will innovatively develop service trade, promote the pilot creation of an open platform for innovative development of service trade, and improve trade digitization. We will implement trade and investment integration projects, and ensure the success of China International Import Expo, China Import and Export Fair, China International Fair for Trade in Services (CIFTIS), and other exhibitions.
II. International two-way investment
China will continue to place equal emphasis on bringing in foreign investments and going global, make efficient use of global resources and market space with high-level two-way investment, improve the industrial and supply chain support mechanism as well as industry competitiveness, make greater efforts to attract and utilize foreign investment, and promote the opening of related businesses in the fields of telecommunications, internet, education, culture, and medical care in an orderly manner. We will comprehensively optimize foreign investment services, strengthen the promotion and protection of foreign investment, give full play to the demonstration effect of major foreign investment projects, support an increase of foreign capital investment in high-end manufacturing, high-tech, traditional manufacturing transformation and upgrade, modern services, and other fields in the central and western regions, as well as support foreign-funded enterprises to set up R&D centers and participate in national science and technology projects. We will encourage foreign-funded enterprises to reinvest their profits, innovate overseas investment methods, optimize the structure and layout of overseas investment with enterprises as the main players, and improve the risk prevention capacity and income level. We will improve the overseas producer services network and circulation system, accelerate the international development of producer services in finance, consulting, accounting, and law, and promote Chinese products, services, technologies, brands, and standards to go global. We will support enterprises to integrate into the global industrial and supply chain, improve the transnational operation capacity and level, and guide enterprises to strengthen compliance management so they can prevent and resolve overseas political, economic, security, and other risks. We will promote the development of multilateral and bilateral investment cooperation mechanisms and improve policies and service systems for promoting and protecting overseas investments, as well as the legislation on overseas investment.
Chapter 14 Strategies to Boost Domestic Demand
Strategies to expand domestic demand will be implemented to enhance the role of consumption in economic growth and allow investment to play a key role in improving the supply structure. This shift is expected to lead to a stronger domestic market and stronger demand for consumption and investment.
I. Expanding consumption
In line with the public consumption upgrade trend, we will combine the expansion of consumption with the improvement in people’s living standards, promote the green, healthy, and safe development of consumption, and steadily improve people’s consumption. We will upgrade traditional consumption, accelerate the shift from purchase management to usage management for automobiles and other consumer goods, improve the mandatory end-of-life system and recycling system for used home appliances, consumer electronics, and other durables, and promote the healthy development of housing consumption. We will foster new consumption patterns, develop information consumption, digital consumption, and green consumption, and encourage the development of customization, experience, intelligence, and fashion consumption and other new business formats and models. We will develop service consumption, relax restrictions on market access in the field of service consumption, promote the improvement and expansion of consumption in education and training, medical and health care, elderly care, child care, culture, tourism, and sports, and accelerate the integration and development of online and offline consumption. We will appropriately increase public consumption and improve the efficiency of public service expenditure, and expand holiday consumption, improve the holiday system, and fully implement the paid holiday system. We will foster and build international consumption center cities, create a group of regional consumption centers, improve the integrated urban-rural consumption network, expand the coverage of e-commerce in rural areas, improve the consumption environment in counties, and promote the upgrade of rural consumption. We will improve the policy for duty-free shops in cities and build duty-free shops with Chinese characteristics. We will take measures to increase people’s income and alleviate their burdens, to continuously expand the middle-income groups and release their consumption potential. We will better safeguard consumers’ rights and interests, improve the quality standards and post evaluation system as well as the systems for defective product recall, product-related injury monitoring, and product quality guarantee, and improve the diversified consumer rights protection mechanism and dispute resolution mechanism.
II. Expanding investment opportunities
We will optimize the investment structure, improve the investment efficiency, and maintain reasonable investment growth. We will move faster to strengthen weak areas in infrastructure, urban utilities, agriculture and rural areas, public safety, ecological and environmental protection, public health, material reserves, disaster prevention and mitigation, people’s livelihood, and other fields, promote the upgrade of enterprise equipment and technological transformation, and expand investment in emerging industries of strategic importance. We will promote major projects concerning new infrastructure, new urbanization, transportation, and water conservancy that will not only boost consumption and benefit people’s livelihood, but also help adjust the structure to gain more momentum. To serve the major national strategies, we will implement major projects such as the Sichuan-Tibet Railway, the new western land-sea corridor, the national water network, hydropower development in the lower reaches of the Yarlung Zangbo River, interstellar exploration, and the industrial development of BeiDou Navigation Satellite System, and promote major research facilities and projects in the areas of ecosystem protection and restoration, public health emergency response, water diversion, flood control, disaster reduction, power and gas transmission, and transportation along the coast, rivers, and border areas, thereby providing a solid foundation, increased functions, and long-term benefits. We will deepen investment and financing reforms, leverage the government’s role in investment to stimulate private investments, and establish a market-oriented endogenous growth mechanism for investment. We will improve project planning, reserve and promotion mechanism, increase the support for capital, land, and other factors of production, and accelerate the implementation of investment projects. We will standardize and promote public-private partnership (PPP) in an orderly manner, promote the healthy development of real estate investment trusts (REITs) in infrastructure, effectively revitalize stock assets, and form a virtuous circle of stock assets and new investment.
Part V An Initiative to Build a Digital China
We will embrace the digital era, unlock the potential of big data, build China’s strength in cyberspace, accelerate the development of a digital economy, a digital society, and a digital government, and transform the pattern of production, lifestyle, and governance models through digital transformation.
Chapter 15 Pole Position in the Digital Economy
We cannot afford not to tap into the huge potential big data and its innumerable use cases. Greater integration of digital technology and the real economy will power the transformation and upgrading of traditional industries, and the development of new industries, new forms of business, and new models, which can be new drivers of economic growth.
I. Key digital technologies: innovation and application
Our focus will be on high-end chips, operating systems, key artificial intelligence algorithms, sensors, and other key fields. We will gather pace in making breakthroughs in the research and development of basic theories, basic algorithms and equipment materials and promoting their iterative application. The integrated research and development of general-purpose processors, cloud computing systems, and core software technologies will be pushed forward. Cutting-edge technologies will be developed faster, including quantum computing, quantum communications, neuro-chips, and DNA storage. Innovation will be boosted across information science, life science, materials and other basic disciplines, along with support for the development of innovation consortia including open source communities, improve open source intellectual property rights and legal systems. Enterprises will be encouraged to make available open source codes, hardware design, and application services.
II. Development of digital industries
Emerging digital industries including artificial intelligence, big data, blockchain, cloud computing, and cybersecurity will be grown stronger, and the quality of such industries as communications equipment, core electronic components, and key software will be improved. Efforts will be made to develop 5G-based application scenarios and industrial ecosystems, and carry out pilot and demonstration projects in smart transportation, smart logistics, smart energy, smart medical care, and other key fields. Enterprises will be encouraged to provide open access to search, e-commerce, social, and other data. Third-party big data services will be developed, and the healthy growth of the sharing economy and the platform economy will be boosted.
III. Digital transformation of traditional industries
We will press ahead with cloud-based big data and AI initiatives and promote the data-based collaborative transformation of the entire industrial chain. A number of industrial internet platforms and digital transformation promotion centers up to international standards will be built in key industries and regions. Digital applications will be promoted in R&D and design, manufacturing, operation and management, and market services, new models including customization and flexible manufacturing will developed, and the digital transformation of industrial parks will be accelerated. Digital transformation will be pushed through in the service sector, identify and new sources of growth will be identified, such as crowdsourcing design, smart logistics, and new retail. We will move faster in developing smart agriculture and transform agricultural production, operations, management, and services with digital technologies.
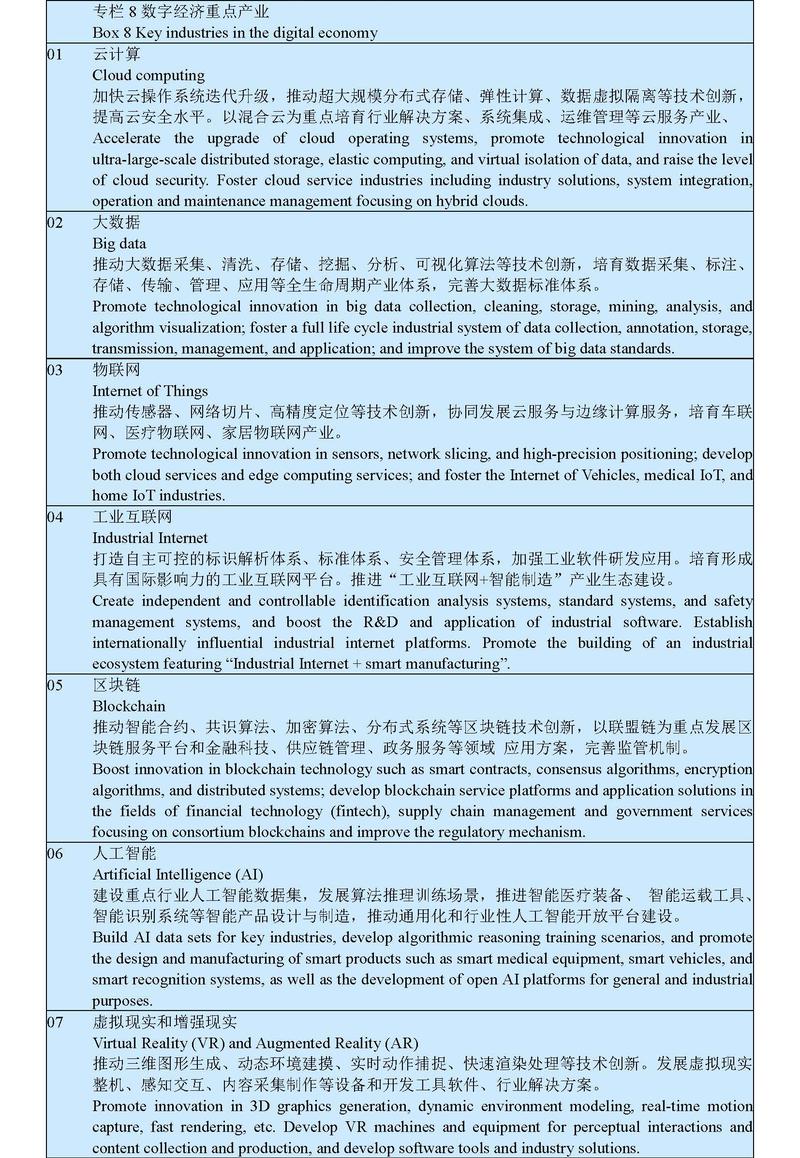
Greater integration of digital technologies into social interactions and people’s daily life calls for innovation in public services to ensure that the way our society functions better responds to the digital needs of all people.
I. Smart and easily accessible public services
Digital services will be applied widely, especially to education, healthcare, elderly care, childcare, employment, culture and sports, care for people with disabilities, and other key areas, ensuring that people have a growing sense of fulfilment. Resources in schools, hospitals, nursing homes, and other public service institutions will be digitalized to offer easier access to them and boost their application. Online and offline public services will be developed at the same time and their in-depth integration will be promoted. More efforts will be channeled into developing online classrooms, internet-based hospitals, and smart libraries. High-standard public service institutions will be encouraged to reach communities, remote areas, and underdeveloped areas. The coverage of high-quality public service resources will be expanded. Progress will be made in developing smart courts. Non-governmental actors will be encouraged to participate in the “Internet + public services” initiative, and provide innovative service models and products.
II. Smart cities and digital villages
Digital technologies will be used to help develop urban and rural areas and introduce new approaches to governance for better efficiency and livability. New smart cities in different categories will be developed, IoT sensing facilities and communications systems will be incorporated in the overall planning and development of public infrastructure, and municipal utilities and buildings will be transformed with IoT applications. Efforts will be made to improve city information modeling (CIM) platforms and service platforms, and build city data systems to develop city brains. The creation of digital twin cities will be explored and faster progress will be made in the development of digital countryside. A comprehensive information service system will be established for agriculture and rural areas, along with an inclusive agriculture-related information service mechanism, and rural management and services will be digitalized.
III. A new blueprint for digital life
We will promote the digitization of all real-life scenarios such as shopping, home life, tourism, leisure activities, and transportation to create a new digital life based on the sharing of knowledge and co-governance. Smart communities and smart service circles will be developed to benefit the people relying on digital platforms and offline community service institutions, and services online and offline will be integrated, such as community life services, community governance and public services, and smart community services. A richer diversity of digital life experiences will be introduced along with more digital homes. Digital skills education and training will be boosted to promote the digital literacy of the general public, and information accessibility will be improved to help the elderly and people with disabilities embrace the digital life.
Increased integration of digital technologies into government services will help remake governance processes, improve services, and lead to more rational decision-making and greater efficiency.
I. Open access to and sharing of public data
A sound public data resource system will be put in place to ensure the security of public data, and promote the convergence and utilization of data across departments, levels, and regions. The data resource catalogs and responsibility lists will be improved and the functions of national data sharing and exchange platforms upgraded to advance the sharing and utilization of basic information resources including national population, legal person, and geospatial data. Open access to basic public data will be expanded in a safe and orderly way, public data services will be integrated into the public service system, and an open national public data platform will be built, along with dedicated development and utilization ports. Priority will be given to high-value data sets in the fields of enterprise registration and supervision, health, transportation, and meteorology that are open to the public. Pilot projects on authorized operation of government data will be carried out and third parties will be encouraged to advance the mining and utilization of public data.
II. IT-enabled transformation of government services for all
Intensified efforts will be made to develop an IT-enabled government, improve the list of government information projects, and deepen the integration of government information systems. Major information systems will be developed, including those about governance capacity, rule of law, economic governance, market supervision, public security, and the environment. Cross-sector collaboration will be fostered in governance. China’s e-government network will be improved, and cloud platforms and data center system will be built to promote the cloud migration of government information systems which will be upgraded rapidly for a greater capacity to expand flexibly.
III. Digitalization and efficient service delivery
We will work to make sure the government functions, and delivers services in a more digital and smarter way. The “Internet + government services” initiative will be advanced to upgrade the functions of integrated online service platforms. Digital technologies will be used to facilitate government decision-making and improve the quality of accurate dynamic monitoring, prediction, and early warning based on high-frequency big data. They will also be applied widely in the response to public health emergencies, natural disasters, accidents, public safety incidents, and other public emergencies to increase the capacity for early warning and emergency response.
Chapter 18 A Healthy Digital Ecosystem
Regulatory overreach should be rolled back where it hurts business dynamism while regulation will be strengthened wherever necessary in our effort to create an open, safe, and healthy rules-based digital ecosystem.
I. Data protection regulation
A balance will be achieved between data development and utilization, privacy protection, and public security, and basic systems and standards concerning data rights, transactions, circulation, cross-border transmission, and security protection will be developed at a faster pace. Sound mechanisms for data rights trading and industry self-regulation will be put in place and well-regulated data trading platforms and business entities will be fostered. The market systems for data asset evaluation, registration and settlement, trading, dispute arbitration, etc. will be developed. The data involving national interests, trade secrets, and personal privacy will be better protected and basic legislation in the fields of data security and personal information protection will be accelerated to strengthen data security protection in the whole life cycle. The classified and multi-level data protection will be improved to adapt to the big data environment. Efforts will be made to strengthen data security assessment and promote the safe and orderly flow of data across borders.
II. An enabling policy environment
Policies and regulations favorable for the digital economy will be introduced, along with better rules for managing the sharing economy, the platform economy, and the new individual economy. Improper items requiring administrative approval and qualifications will be cancelled and platform enterprises will be supported in pursuing innovative development and building their international competitiveness. Activities on internet platforms will be overseen in accordance with laws and regulations, the positioning and regulatory rules of platform enterprises will be clarified, and the legal framework of business monopoly identification will be improved, while business monopolies and unfair competition will be fought. Efforts will also be made to explore the possibility of creating regulatory frameworks for unmanned driving, online medical services, financial technology, smart delivery service, etc., improve relevant laws, regulations and ethical review rules, and foster a better statistical monitoring system for the digital economy.
III. Cybersecurity
Efforts will be made to improve national cybersecurity laws, regulations, and standards, and intensify efforts to protect the security of data resources in important fields, important networks, and important information systems. A sound key information infrastructure protection system will be put in place to increase the capacity for security protection and political security maintenance. Cybersecurity risk assessment and review will be advanced, along with the development of cybersecurity infrastructure, cross-sector cybersecurity information sharing and collaboration, and the capacity for cybersecurity threat detection, monitoring and early warning, emergency command, and cyber attack tracing. Efforts will be stepped up to develop key technologies for cybersecurity, accelerate technological innovation in artificial intelligence for security, build the comprehensive competitiveness of the cybersecurity industry, and promote cybersecurity education and related personnel training.
IV. A global cybercommunity with a shared future
International exchanges and cooperation in cyberspace will be promoted, along with the formulation of international digital and cyber rules, and the United Nations will be considered the main channel and the Charter of the United Nations the source of basic principles. More will be done to establish a multilateral, democratic, and transparent global internet governance system and create a fairer and more reasonable cyberspace infrastructure and resource governance mechanism. We will actively participate in the development of international rules and digital technology standards including those on data security, digital currencies, and digital taxes; promote the development of global cyberspace security cooperation mechanisms, and build an international coordination and cooperation mechanism to protect data factors, handle cybersecurity incidents, and combat cybercrimes; provide digital assistance including technology, equipment, and services to less developed countries, so that all countries can share the dividends of the digital era; and actively promote cultural exchanges and mutual learning on the internet.

Part VI Comprehensive and In-depth Reform to Develop a Well-functioning Socialist Market Economy
Efforts will be ongoing to improve our socialist economic system to allow the market to play a decisive role in allocating resources while improving government regulation, so as to create synergy between an efficient market and a well-functioning government.
With the public sector as the core of our economy, the government encourages, supports, and guides the development of the non-public sector, and is committed to creating an enabling environment to allow more dynamic, creative, and competitive business entities to thrive.
I. State-owned enterprise reform
To better serve national strategies, we will make plans on where to advance and where to withdraw, what to do and what not to do, accelerate layout improvement, structural adjustment, and strategic restructuring for the state-owned sector and enhance its competitiveness, innovation, control, influence, and risk resistance capacity. We will also work to strengthen, expand, and increase the returns on state capital and enhance the strength, quality, and size of state-owned enterprises. The strategic support of the state-owned sector will be brought into full play, so that it can focus more on helping to ensure strategic security, promote industry leadership, bolster the national economy, raise people’s living standards, improve public services, and other functions. We will adjust and revitalize stock assets, improve the allocation of incremental capital, and move towards important industries concerning national security and the lifeline of the national economy, industries that provide public services and concern capacity building for emergency response, public welfare, etc. as well as emerging industries of strategic and progressive significance. For the part of the state-owned sector in fully competitive fields, we will give greater emphasis to capital gains targets and financial constraints, enhance liquidity, and improve the mechanism for optimal allocation of state capital. A long-term mechanism will be created for layout improvement and structural adjustment of the state-owned sector, and guidelines in this regard will be issued dynamically.
II. State-owned enterprise modernization with Chinese characteristics
We will uphold the Party’s leadership in all spheres of work of state-owned enterprises, balance the endeavor to strengthen the Party’s leadership and that to improve corporate governance, and accelerate the establishment of a corporate governance mechanism featuring statutorily-defined and transparent rights and responsibilities, coordinated operations, and effective checks and balances. Efforts will also be made to facilitate the establishment of boards of directors and clearly define their functions and powers, making them the main bodies of business decision-making. In accordance with the requirements of improving governance, strengthening incentives, highlighting the main business and increasing efficiency, we will push ahead with mixed-ownership reform in state-owned enterprises by radically transforming the operation mechanism, and exploring the introduction of governance mechanism and supervision system for mixed-ownership enterprises that are different from those of solely state-owned and wholly owned companies. We will put in practice a tenure system and contractual management for managers, improve the market-oriented salary distribution mechanism, and flexibly offer medium- and long-term incentives in various forms.
III. State-owned assets oversight to prevent, in particular, illegal diversion of funds
Ongoing efforts will be made to combine authorization and supervision as well as decentralization and management, and promote the transformation of state-owned asset supervision in terms of concept, focus, and modes. We will improve the approach to capital management, practice list-based management and classified authorization and decentralization, lay emphasis on performing duties through the corporate governance structure and strengthen ongoing and ex post oversight. We will deepen the reform of state capital investment and operation companies, and define the scope of rights of the government and state capital regulatory agencies, state capital investment and operation companies, and their subsidiaries in a scientific and reasonable manner. We will also improve the collaborative and efficient supervision mechanism and enforce accountability to prevent the loss of state-owned assets, and accelerate the centralized and unified supervision of for-profit state-owned assets.
IV. A favorable business environment for private enterprises
Enabling legal, policy, and market environments will be fostered for the development of private enterprises and protect their property rights and the rights and interests of entrepreneurs on an equal basis in accordance with the law. We will ensure that private enterprises have equal access to resource factors in accordance with the law, and that they can compete in an open, fair, and just manner, and enjoy equal legal protection. Market access will be expanded for private enterprises and various barriers in bidding and other fields will be broken down. New policy instruments will be developed to provide financial support for private enterprises, improve the financing and credit enhancement system, treat private enterprises as equals in their credit rating and bond issuance, and lower overall financing costs. The policy system will be improved for promoting the development of micro, small, and medium enterprises and self-employed individuals, and give more preferential tax treatment and credit support. We will build a cordial and clean relationship between government and business, establish standardized communication channels between government and enterprises, and improve the long-term mechanism for preventing and resolving payment arrears to small and medium enterprises.
V. Policy support for private-sector development with a focus on quality improvement
We will encourage the reform and innovation initiatives of private enterprises to improve their operation and management capacity, and guide qualified private enterprises to adopt a modern enterprise system. Private enterprises will be encouraged to carry out basic research and technological innovation, participate in the research and development of key and core technologies, and undertake key national science and technology projects. A better mechanism will be introduced for private enterprises to participate in the implementation of major national strategies, and they will be encouraged to operate in accordance with laws and regulations, actively fulfill their social responsibilities and participate in charitable initiatives. We will also work to foster entrepreneurship and implement the plan to promote the healthy growth of young entrepreneurs.
Chapter 20 A Unified Market that Adheres to High Standards
Proactive action will be taken to build an efficient, well-regulated, unified domestic market that adheres to high standards, with necessary institutional support in place to ensure equal access, fair competition, impartial oversight, openness, orderliness, good faith conduct, and legal compliance.
I. Protection of property rights
The modern property rights system will be improved to ensure clear ownership, well-defined rights and obligations, strict protection, and smooth transactions. With the civil code put into implementation, we will formulate laws and regulations on property rights, including real rights, creditor’s rights and stock rights, and revise them to clarify the ownership of property rights and improve the powers and functions of property rights. We will improve the property rights protection system based on the principle of fairness and give equal protection to the property rights of enterprises under all forms of ownership, including state-owned, private, and foreign-funded enterprises, in accordance with the law. Efforts will be made to improve the judicial protection system for property law enforcement and protection mechanisms such as the appeal, review, and retrial of enterprise-related property rights cases. We will make it a normal practice to screen and correct wrongful cases involving enterprises in accordance with the law and develop smooth channels for the reporting and handling of government-related property rights disputes. We will strengthen the development of the property rights system in the fields of data, knowledge, and the environment, and improve the property rights system and laws and regulations related to natural resource assets.
II. Reforms to facilitate market-based allocation of production factors
A sound unified rural-urban market will be created for land designated for construction purposes, and reforms on rural land expropriation, the marketing of rural collectively-owned land designated for business-related construction, and rural land designated for housing will be pushed forward. Efforts will also be made to reform land-use planning and management practices, grant provincial-level governments more decision-making power over the development of land, and explore the establishment of a nationwide mechanism for cross-regional trading of land for construction and newly-added cropland quotas. A mechanism will be created for the proper conversion of different types of land designated for industrial purposes and increase the supply of land for mixed industries. We will improve the unified and well-regulated human resource market, remove barriers to the flow of workforce and talents between urban and rural areas, between different regions, and between organizations of different types of ownership, and rescind excessive restrictions on personnel file management. Further progress will be made in the efforts to develop technology and data factor markets, improve the operational mechanism of the factor markets as well as trading rules and service system, and deepen the integration and sharing of public resource trading platforms.
III. A pivotal role for competition policies
Continued efforts will be made to encourage competition and guard against monopoly, improve the competition policy framework, and create a competition policy implementation mechanism covering every stage of the whole process. Conduct incremental review and stock clearance will be properly conducted, fair competition reviews will be carried out to strengthen rigid constraints while the detailed rules in this regard will be improved, and more will be done to abolish regulations and practices that impede the development of a unified market and fair competition nationwide. We will improve the market competition evaluation system and establish a complaint filing and handling mechanism. Law enforcement against monopolies and unfair competition will be stepped up and capital expansion will be regulated. We will promote market-oriented reforms in competitive operations in such sectors as energy, railways, telecommunications, and public utilities, expand market access for competitive operations, introduce more market competition mechanisms, and strengthen oversight over natural monopoly industries.
IV. Social credit system
A sound system of credit-related laws, regulations, and standards will be put in place, together with a catalog of public credit information and a list of disciplinary measures for dishonest practices, and the credit repair mechanism for defaulters will be improved. Efforts will be made to promote the credit commitment system, boost the collection, sharing, disclosure, and application of credit information, promote credit products and services that benefit people and enterprises, and establish a mechanism for the sharing and integration of public credit information and financial information. More will be done to foster internationally competitive enterprise credit reference agencies and credit rating agencies, strengthen supervision over credit investigation, and promote the healthy development of the credit service market. Intensified efforts will be made to manage the security of credit information, protect the legitimate rights and interests of entities whose credit information is gathered, and establish a sound accountability system for government administration dishonesty.
Chapter 21 Fiscal Policy, Taxation, and the Financial System
Fiscal policy should play a fundamental role in state governance. Financial services should better serve the real economy. Fiscal policy, taxation, and the financial system should respond to the need for development with a focus on quality improvement.
I. Fiscal policy
Efforts will be made to deepen reform of the budget management system, strengthen the macro guidance, review, and supervision of budget compilation, promote the overall planning of financial resources, standardization of financial expenditure, budget constraints and performance management. The multi-year budget balancing mechanism will be improved, along with medium-term financial planning management, to bolster financial support for major strategic tasks of the country. We will establish a fiscal relationship between central and local governments built on clearly defined powers and responsibilities, appropriate financial resource allocation, and greater balance between regions; appropriately strengthen the central government’s authority over intellectual property protection, pension insurance and cross-regional environmental protection; and reduce and regulate the common authority of central and local governments. We will improve the financial system at and below the provincial level and enhance the capacity to provide public services at the community level; create a better financial transfer payment system and a better transfer payment structure, and regulate the transfer payment items; improve the system for comprehensive government financial reporting based on accrual accounting; and establish a well-regulated government debt financing mechanism.
II. Taxation
We will seek to improve the structure of the tax system and the direct tax system, appropriately increase the proportion of direct taxes, create a better personal income tax system, expand the scope of comprehensive collection, and improve the tax rate structure. More will be done to improve the value-added tax (VAT) system by stabilizing the manufacturing industry and consolidating the industry and supply chains. We will also adjust and improve the scope of excise tax collection and the excise tax rate, make moves towards collecting excise tax at a point further downstream in the production-to-consumption process and hand it over to local governments in a stable way. Progress will be made in the endeavor to regulate and improve tax preferences, step up legislation on real estate taxation, improve local tax systems, and hand over more tax-related administrative powers to local governments step by step. Reforms will be deepened in the administration of tax collection and smart taxation will be developed to modernize the administration of tax collection.
III. Supply-side structural reform in the financial sector
The modern financial system that is adaptive, competitive, and inclusive will be improved and institutions and mechanisms will be put in place for the financial sector to effectively support the real economy. Efforts will be made to build a modern central bank system and improve the money supply regulation mechanism and steadily promote the research and development of digital currency. More will be done to improve the market-based interest rate mechanism and the transmission mechanism, the central bank’s policy interest rate system, and give better play to the benchmark role of the loan prime rate (LPR) mechanism. A better structure of the financial system will be defined and the reform of state-owned commercial banks will be deepened. We will move faster to improve the governance structure of small and medium-sized banks and rural credit cooperatives, regulate the development of non-banking financial institutions, and enhance the inclusiveness of financial services. Efforts will be made to reform and improve policy-backed finance, increase its capacity to serve national strategies and planning efforts, deepen the reform of insurance companies and build the ability of commercial insurance to offer protection. We will improve corporate governance in financial institutions and strengthen the oversight of shareholders’ equity and related party transactions. We will also improve the underlying systems of the capital market and the system of multi-level capital markets, make a major push to develop institutional investors, and increase the proportion of direct financing, equity financing in particular; fully implement the registration-based IPO system, make delisting a normal practice, and improve the quality of listed companies. We will deepen reform of the New Third Board, improve the market-based bond issuance mechanism, steadily expand the scale of the bond market, enrich bond varieties, and issue long-term government bonds and long-term infrastructure bonds. We will improve the investor protection system and deposit insurance system, as well as the modern financial regulatory system; shore up our weaknesses in the regulatory system; steadily advance financial innovation under the premise of prudential supervision; and improve the regulatory framework with full risk coverage and make financial regulation more transparent and more law-based. We will steadily develop financial technology and accelerate the digital transformation of financial institutions; boost the application of regulatory technology and financial innovation risk assessment; and explore the establishment of an innovative mechanism for product rectification and suspension.
Chapter 22 The Government’s Economic Governance Capacity
The transformation of government functions will be accelerated to build a rules-based governance system with clearly defined duties and responsibilities, and improve macro-level regulation and the effectiveness and efficiency of governance.
I. Macroeconomic governance
Guided by the national development plan, we will improve the macroeconomic governance system by taking fiscal and monetary policies as the main instruments, better coordinating policies on employment, industries, investment, consumption, environmental protection, specific regions, etc., setting better-defined objectives, ensuring reasonable division of functions, and boosting efficient collaboration. Efforts will be made to strengthen the role of national development planning in providing macro guidance for and coordinating public budget, land development, resource allocation, and other policies; improve the macro policy formulation and implementation mechanism; attach importance to expectation management and guidance; set proper macro-regulation targets concerning economic growth, employment, prices, balance of payments, etc.; and strengthen targeted, well-timed, and precision regulation on the basis of range-based regulation. We will improve the macro-regulation policy system, appropriately design cross-cyclical policies, improve the capacity for counter-cyclical adjustment, and promote the balance between total supply and demand, structural improvement, and internal and external balance for the economy. We will step up the development of macroeconomic governance databases, enhance the supplementary governance capacity of modern technological means including big data, and modernize the statistical system. We will improve the macroeconomic policy evaluation system as well as major risk identification and early warning mechanisms, keep the channels for participation in policy-making open, and ensure decisions are made in a sound, democratic, and law-based way.
II. A favorable business environment
Reforms will be intensified to streamline administration and delegate power, improve regulation, and upgrade services, promote the system for listing the powers and obligations of government departments across the board, and continue to improve the market-based international business environment that respects the rule of law. We will implement the negative list system across the board for market access, remove hidden barriers to market access beyond the list, and further ease access restrictions mainly in the services sector. We will reduce government permits, merge some qualification permits, cancel unnecessary registrations and annual inspections, and regulate enterprise-related inspections. We will fully carry out the reform to separate permits from business licenses and reduce permits after granting licenses, as well as the reform of the construction project approval system. We will reform the production permit system, simplify the approval procedures for industrial products, and practice list-based management for all items related to enterprises that require administrative approval. We will establish a convenient, efficient, and orderly exit system for market entities, simplify ordinary deregistration procedures, and establish a sound bankruptcy system for enterprises and natural persons. We will develop new ways to deliver government services and streamline the approval services for the convenience of the people. We will promote the application of single-window document processing for international trade and improve the business environment assessment system.
III. Better regulation
We will improve the new regulatory mechanism featuring the random selection of both inspectors and inspection targets, the prompt release of results and the Internet Plus Oversight initiative, focusing on key targets and credit supervision to promote the integration of online and offline supervision. We will strengthen market supervision, quality supervision, safety supervision, the supervision of food and drugs, special equipment, online transactions, tourism, advertising, intermediaries, property management, etc., as well as the supervision of factor market transactions, and implement accommodative and prudent regulation of new industries and new forms of business. We will deepen the reform of coordinated law enforcement by government departments in market oversight and improve cross-sector law enforcement and collaborative supervision mechanisms. We will deepen the reform of trade associations, chambers of commerce, and intermediary agencies, and facilitate supervision by the public and the press.
Part VII Agricultural and Rural Development and Rural Revitalization
A uniquely Chinese approach to rural revitalization will be adopted with strategies that encourage the manufacturing sector and urban entities to support agriculture and rural development, a move that will help create industry-agriculture and urban-rural synergies, beneficial to both urban and rural areas and allow coordinated development leading to shared prosperity and accelerated modernization of agriculture and rural areas.
Chapter 23 Quality Issues and Competitiveness in the Agricultural Sector
The fundamental role of agriculture should never be underestimated. Supply-side structural reform in the agricultural sector is necessary to spur the growth of rural industries, with special attention to improving the quality of their products.
I. Boosting the overall agricultural production capacity
We will consolidate the foundation of grain production capacity and ensure the supply of important agricultural products such as grain, cotton, cooking oil, sugar, meat, and milk. We will enforce the strictest possible system for protecting farmland, strengthen the protection of farmland quantity and enhance its quality, ensure the total area of China’s farmland stay above the red line of 120 million hectares, prevent the use of farmland for non-agricultural and non-grain purposes, regulate the balance between the occupation and replenishment of farmland, and strictly prohibit the replacement of superior land with inferior land and irrigable land with to non-irrigable land. Focusing on functional zones for grain production and protective areas for the production of major agricultural products, we will build a national food security industrial belt, implement high-quality farmland development projects, and build contiguous high-quality farmland of more than 71.67 million hectares. We will carry out chernozem soil conservation projects and strengthen the conservation of chernozem soils and restoration of soil fertility in northeast China. We will promote water-saving transformation and lean management in large and medium-sized irrigation areas and build key water-saving irrigation projects while promoting comprehensive water pricing reform. We will step up the research, development and application of large and medium-sized, smart and multifunctional agricultural machinery so that the overall level of mechanization in plowing, sowing, and harvesting can be increased to 75%. We will boost the protection and utilization of germplasm resources and the development of seed banks to ensure the security of seed sources; step up efforts to break bottlenecks in developing technology to improve agricultural varieties; steadily advance the industrial application of biological breeding; and foster leading enterprises in the seed industry with international competitiveness. We will improve the agricultural science and technology innovation system, employ new ways to promote agricultural technologies, and develop smart agriculture. We will channel more efforts into animal epidemic prevention and control of crop diseases and insect pests, as well as agrometeorological services.
Figure 2. Layout of functional zones for grain production and protective areas for the production of major agricultural products
II. Structural adjustment in the agricultural sector
We will improve the distribution of agricultural production, and build industrial belts for advantageous agricultural products and advantageous areas of featured agricultural products. We will promote the overall planning of grain, cash crops, and feed, as well as the coordination of agriculture, forestry, animal husbandry, and fishery; improve the farming structure; vigorously develop modern animal husbandry and healthy aquaculture; and actively develop protected agriculture as well as forestry and fruit industry according to local conditions. We will further promote high-quality grain projects, drive the green transformation of agriculture, boost environmental protection in production areas, develop water-saving and dry-farming techniques, advance the initiative of reducing pesticides and fertilizers, control agricultural film pollution by improving its recovery and utilization rate, and promote the comprehensive utilization of straw and the utilization of livestock manure as resources. We will improve the green agriculture standard system and the certification of green food, organic agricultural products, and agricultural products with geographical indications; intensify whole-process quality and safety supervision over agricultural products and improve the traceability system; and build industrial parks of modern agriculture and agricultural modernization demonstration zones.
III. Diversification of the rural economy
We will develop county economy, promote the integrated development of primary, secondary, and tertiary industries in rural areas, extend the agricultural industrial chain, and develop featured modern industries to ensure rural prosperity. We will boost the combination of farming, breeding, and processing and the reengineering of industrial chain, advance the development of agricultural products processing industry and agricultural producer service industry, and expand characteristic industries such as leisure agriculture, rural tourism, and homestay economy. We will step up the development of storage and preservation as well as cold chain logistics facilities for agricultural products, improve rural property rights trading, commercial circulation, inspection, testing, and certification platforms, as well as smart standard plants and other facilities, and encourage the development of clusters in rural secondary and tertiary industries. We will improve the interest linkage mechanism, and ensure farmers share more benefits from the growth of industries by “turning resources into assets, funds into shares, and farmers into shareholders”.
Chapter 24 Rural Development Initiatives
Rural development is high on our socialist modernization agenda. Rural development initiatives aim to increase production, conserve and protect ecosystems, and improve the living environment.
I. Rural development planning
We will coordinate the planning and development of towns and villages in counties while considering all relevant factors, including land use, industrial development, development of residential areas, improvement of the living environment, ecological conservation, disaster prevention and reduction, and conservation of cultural heritage. We will design sound layout plans for villages in counties, develop villages of different categories according to different local conditions, regulate the comprehensive improvement of land in the whole region, protect traditional villages, ethnic villages, and rural styles and features, and strictly prohibit the willful removal and merger of villages to build large communities or large-scale demolition and construction against the wishes of farmers. We will improve the layout of rural living spaces, strictly preserve the spaces for agricultural production and rural ecological conservation, and delineate suitable, restrained, and forbidden areas for breeding industry. We will also encourage areas to draw up practical village plans, where conditions permit.
II. Upgrading infrastructure and public services in rural areas
We will drive the integrated development of urban and rural areas by taking counties as the basic units, and enhance counties’ capacity to provide comprehensive services and townships’ functions to serve farmers. We will improve the mechanism for unified planning, development, management, and protection of urban and rural infrastructure, promote the extension of municipal utilities to suburban villages and large-scale central towns, improve rural infrastructure relating to water, electricity, roads, gas, postal communications, radio and television, and logistics, as well as the quality of rural housing construction. We will promote the adoption of the same standards for basic public services and the same systems in urban and rural areas; increase the provision of services in education, healthcare, old-age care, culture, and other fields in rural areas; promote the exchange and job rotation of teachers and doctors in counties; and encourage non-governmental actors to launch charitable initiatives in rural areas. We will improve farmers’ literacy in science, technology, and culture, and promote the revitalization of rural talents.
III. Better living environment in rural areas
We will work on redeveloping the rural living environment, and steadily resolve outstanding environmental issues such as the “villages surrounded by garbage” and dirty and odorous water bodies in rural areas. We will promote the on-site sorting and recycling of household waste and steadily advance household sewage treatment in rural areas, while focusing on seats of township governments and central villages. We will promote the toilet revolution in line with local conditions, boost comprehensive improvement of rural water systems, and organize in-depth village cleaning and greening activities to make public spaces, courtyards, and houses in villages, as well as their surrounding areas clean and tidy.
Chapter 25 Integrated Urban-Rural Development
Favorable policies will be rolled out to facilitate two-way flows of urban and rural production factors, and encourage, in particular, channeling more resources towards rural areas to boost rural dynamism.
I. Agricultural and rural reforms
We will consolidate and improve the basic rural management system, implement the policy of extending the second round of land contracts for another 30 years upon expiration, improve the system of separating the ownership right, contract right, and management right of rural contracted land, and further reduce restrictions on the management right. We will develop various types of appropriately scaled agribusiness operations, accelerate the fostering of new agricultural business entities such as family farms and farmers’ cooperatives, improve the system of specialized and commercial services for agriculture, and introduce small rural households to modern agriculture. We will further carry out trial reforms on rural land designated for housing, accelerate the confirmation and certification of both land and house rights, and explore the approach to achieving the separation of ownership, entitlement, and right to use of rural land designated for housing. We will vigorously explore and implement a system for putting rural collective land for development purposes on the market, allow rural collectives to convert idled land designated for housing that has been recovered after paying compensation, and disused collective land designated for public good into collective land for development purposes and put the land on the market according to law based on the premise of farmers’ willingness. We will establish a mechanism for determining public interests in rural land requisition and narrow the scope of requisitioned land. We will deepen the reform of the rural collective property rights system, improve the powers and functions of property rights, quantify for-profit assets for the members of the collective economic organizations, and develop a new rural collective economy to effectively alleviate the burden of village-level organizations. We will give play to the exemplary role of national pilot zones for integrated urban-rural development and rural reform pilot zones.
II. Supply of production factors for agricultural and rural development
We will improve the system for guaranteeing government funding for agriculture and rural areas and increase support to them from the central government’s financial transfer payments, proceeds from sale of land-use rights, and local government bonds. We will improve the agricultural support and protection system, as well as the interest compensation mechanism for major grain-producing areas, develop a new system of agricultural subsidy policies, and refine the policy for setting minimum prices for state grain purchases. We will deepen the reform of supply and marketing cooperatives and improve the support mechanism for rural land use, to ensure that the reasonable land-use needs in developing protected agriculture and rural industries are met. We will improve the rural financial service system and the incentive mechanism of financial support to agriculture, expand the scope of financing guaranteed by rural asset collateral, and develop agricultural insurance. We will allow people who seek employment or who want to start businesses in the countryside to register their household and enjoy relevant rights and interests in their native places or the locations of their jobs or businesses, and establish a system for scientific researchers to engage in secondary jobs and off-post entrepreneurship in rural areas.
Chapter 26 Rural Revitalization to Be Pursued by Building on Success in Poverty Alleviation
Support will continue to be provided to rural low-income groups and underdeveloped areas. The level of government funding for this purpose will stay stable and assistance programs will continue to be implemented even after the target communities have been lifted out of poverty, a move that is intended to keep the momentum going and prevent the vulnerable from slipping back into poverty.
I. Building on poverty alleviation achievements
We will work to meet the requirements of “continuing poverty alleviation responsibility, policies, and assistance and oversight for areas that have been removed from the poverty list”, and establish a robust long-term mechanism for consolidating and expanding poverty alleviation achievements. We will improve the dynamic monitoring and targeted assistance mechanisms for preventing people from falling back into poverty, regularly monitor groups who are liable to return to or fall into poverty, establish a sound mechanism for rapid detection and response, and bring people who can potentially return to poverty into the scope of assistance policies in a timely manner, considering different types at different levels. We will improve the social security and assistance system in rural areas, and improve the mechanism for regular assistance of low-income rural residents. For areas that have been lifted out of poverty, we will continue to implement the policy for intra-provincial trading of the surplus quotas under the policy of linking newly-added cropland quotas with the amount of land used for urban and rural construction, and adjust and improve the policy of inter-provincial trading of the same. We will step up the management and supervision of funds and assets in poverty alleviation projects, and promote the sustainable development of characteristic industries. By rolling out work-relief programs, we will drive low-income population to get jobs locally or in nearby regions. We will effectively provide follow-up support for people relocated from inhospitable areas, and promote a new type of urbanization in large-scale resettlement areas.
II. A continued upward trajectory for communities recently out of poverty
We will encourage the areas that have got rid of poverty to develop featured farming and breeding industries, extensively organize activities to ensure better linkage between production and sales of agricultural products, and expand the assistance by boosting the consumption of goods produced by the areas lifted out of poverty. A number of counties lifted out of poverty in western China will be designated as key counties for receiving assistance for rural revitalization and receive focused support in terms of government funding, financial services, land, manpower, infrastructure, and public services, so as to increase their capacity to consolidate their achievements in poverty alleviation and boost internal forces driving development. We will carry on and improve the mechanisms for collaboration between the eastern and western regions, for providing paired assistance, for designated assistance by central departments and organizations, and for the participation of non-governmental entities. We will adjust and improve the collaboration between eastern and western regions in offering paired assistance and the way of offering such assistance and give greater emphasis to industrial and labor service cooperation.
Part VIII New Urbanization Strategy with a Focus on Quality Development
A uniquely Chinese approach to urbanization will continue to guide the new urbanization process. The process should be people-centered. It aims to promote coordinated development of large, medium-sized, and small cities and small towns that make up urban clusters and metropolitan areas, while helping local cultural traditions and industries and services with local characteristics thrive. The goal is to allow more people to enjoy better city life.
Chapter 27 Urban Residency Status for Rural Residents
The household registration system will undergo an overhaul to ensure full access to basic urban public services for all urban residents, and allow rural residents who have moved to urban areas, especially those who have been living for a long time in cities to gain urban residency, so as to facilitate their integration into city life.
I. Reform of the household registration system
We will lift or reduce the restrictions on household registration, except in certain mega cities, and pilot the household registration system based on places of one’s habitual residence. We will lift all restrictions on household registration in cities with a permanent urban population of less than 3 million, and ensure that the people who have moved from other and local rural areas enjoy equal treatment with respect to urban household registration. For Type-I large cities with a permanent urban population of 3 to 5 million, we will fully relax the conditions for granting urban residency. For mega cities with a permanent urban population of more than 5 million, we will improve the points-based household registration policy by streamlining the points categories, to ensure that the number of years of social insurance payment and the number of years of residence carry the most weight, and we will encourage the cancellation of the annual quota for household registration. We will improve the mechanism for providing basic public services based on the residence permit and linked to the length of residence and other conditions, encourage local governments to provide more basic public services and more convenient access to government services, and improve the urban compulsory education, housing, and other services actually enjoyed by residence permit holders.
II. Urban residency status for rural migrants
We will improve the policies related to the linkage between the fiscal transfer payments and the granting of urban residency to the people with rural household registration living in urban areas, raise the conversion ratio of the permanent population in the balanced distribution of the transfer payments, and determine the distribution of the central fiscal incentive funds for urban residency primarily based on the number of the people who have moved from other provinces. For cities that have taken in a large number of people who have relocated from rural areas, we will set up a mechanism for subsidizing their infrastructure construction with part of fiscal construction funds, and increase central funding budgetary support. We will adjust the basis for the annual allotment of land designated for construction in urban areas, and establish a mechanism to link the allotment with the number of people with rural household registration living in urban areas granted with urban residency and the scale of government-subsidized housing. We will adjust the quota of teachers and doctors and the layout of basic public service facilities for areas with inflow and outflow population according to the actual population flow. We will protect the rights of rural migrants who have settled in cities in accordance with the law with respect to farmland contracting, residential land use, and proceeds from rural collective undertakings, establish a market system for transferring rural property rights, and improve the mechanism and supporting policies for market-based abdication from the abovementioned “three rights” of rural households.
Chapter 28 Spatial Distribution of Urban Centers
With the expansion of urban clusters and metropolitan areas, better coordination is essential for the development of large, medium-sized, and small cities that make up clusters, each with its own priorities and areas of focus, taking into account the need for proper density, coordination in service delivery, and rational distribution of services and amenities.
I. Integrated development of urban clusters
We will take promoting the development of urban clusters as the starting point to all-roundly form a strategic pattern of urbanization featuring “two horizontal and three vertical axes”, by upgrading the urban clusters of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, Yangtze River Delta, Pearl River Delta, Chengdu-Chongqing region, and the middle reaches of Yangtze River; developing the urban clusters of Shandong Peninsula, the coastal areas of Guangdong, Fujian, and Zhejiang, the Central Plains, the Guanzhong Plain, and the Beibu Gulf; and fostering the urban clusters of Harbin-Changchun, Central and Southern Liaoning, Central Shanxi, Central Guizhou, Central Yunnan, Huhhot-Baotou-Ordos-Yulin, Lanzhou-Xining, Ningxia along the Yellow River, and the north slope of Tianshan Mountains. We will establish and improve the mechanisms for integrated and coordinated development of urban clusters and for cost and benefit sharing, and comprehensively promote the coordinated layout of infrastructure, industrial division of labor and cooperation, public service sharing, ecological co-construction, and environmental co-governance. We will also optimize the internal spatial structure of urban clusters and build them into a multi-center, multi-level, and multi-nodal network with improved ecological and security shields.
II. Modern metropolitan areas
We will improve the coordinated development of one-hour commute circles by relying on the central cities with strong capacity to facilitate the development of surrounding areas, and foster several modern metropolitan areas with a high degree of urban integration. With intercity railways, suburban railways, and other rail transits as the backbone, we will eliminate all kinds of “dead end roads” and “bottleneck roads”, promote effective connection of intra-city and inter-city traffic and integration of “the four networks” - trunk, intercity, suburban, and urban railways, and improve the connectivity of infrastructure in metropolitan areas. We will encourage mutual recognition of social security and household registration points, sharing of educational and medical resources in metropolitan areas, and promote the exchange and circulation of scientific and technological innovation coupons as well as the co-construction of industrial parks and scientific research platforms. Where conditions permit, metropolitan areas will be encouraged to establish unified planning committees to achieve unified formulation and implementation of plans, and ways will be sought to promote unified management of land and population.
III. Functions of the central areas in mega cities reimagined
We will take into account the multiple needs of economy, life, ecology, and security to transform the development model of mega cities, and strengthen their risk prevention and control in terms of governance, so as to promote their high-quality and sustainable development. In order to appropriately reduce the development intensity and population density in central urban areas of mega cities, we will relieve in an orderly manner the areas of general manufacturing industries, regional logistics bases and professional markets as well as related functions and facilities, and avoid excessive concentration of public service resources including medical services and higher education. We will enhance the roles of mega cities in global resource allocation, in driving scientific and technological innovation, and in leading the development of high-end industries, ensure that mega cities take the lead in forming an industrial structure with modern service industry as the mainstay and advanced manufacturing as the prop, and enhance their overall capacity and international competitiveness. We will continue the integration of urban areas and industries and improve the functions of new suburban cities to realize multi-center and cluster development.
IV. Livability and better working conditions in large and medium-sized cities
We will make full use of the relatively low comprehensive cost advantages of large and medium-sized cities, and actively undertake the transfer of industries and functions of mega cities, to lay a solid foundation for the development of the real economy. Based on these cities’ featured resources and industrial foundation, we will have differentiated positioning in manufacturing to promote the development of the manufacturing sector on a large scale or in clusters, and build advanced manufacturing bases, commercial and trading logistics centers, and regional professional service centers according to local conditions. We will improve the layout and functions of municipal public facilities, support the presence of tertiary hospitals and universities in large and medium-sized cities, increase the supply of cultural and sports resources, and create a modern and fashionable consumption environment, to make cities better places for living.
V. County-level urbanization
We will step up efforts to shore up weak links in counties, upgrade and expand their public services, environmental sanitation, municipal utilities, and industrial supporting facilities, and enhance their overall carrying capacity and governance capacity. We will support the development of the counties with a good foundation in the eastern regions, focus on the development of counties in the urbanized areas of central and western regions as well as northeastern regions, and appropriately support the development of counties in major production areas of agricultural products and key eco-function zones. We will improve the funding and financing mechanism for development of counties, to give better play to the role of fiscal funds, and guide financial and non-governmental capital to increase funding. We will steadily and in an orderly manner promote the conversion of qualified counties and super-large towns with a permanent population of over 200,000 into cities, develop small towns according to the local conditions, resource endowment and development basis, and promote the standardized and healthy development of characteristic towns.
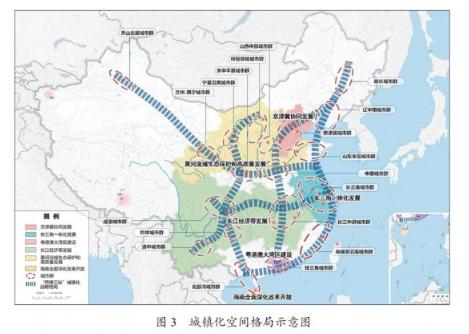
Figure 3. Schematic diagram of the urbanization spatial layout
Chapter 29 Quality of Urban Living
A paradigm shift in urban development is necessary to better coordinate urban planning and city development management, including initiatives for urban renewal and for more rational use of urban space, with a view to improving the quality of urban living.
I. A paradigm shift in urban development
We will logically determine the scale and spatial structure of cities in accordance with the carrying capacity of resources and the environment and make overall arrangements for urban construction, industrial development, ecological conservation, infrastructure, and public services. We will adopt an intensive and compact development model that enables multi-functional, three-dimensional, and transit-oriented development, coordinate the utilization of above-ground and underground space, increase greening nodes and public open space, and promote the block system for new residential buildings. We will promote management and control of urban design and landscape, put into effect guidelines for building applicable, economic, green, and beautiful cityscape in the new era, and strengthen control over new high-rise buildings. We will accelerate urban renewal by redeveloping and upgrading the functions of old residential areas, old factory areas, old blocks and urban villages among other idle zones, promote the renovation of old buildings, and actively expand new parking lots and charging piles.
II. New city centers
In line with the new vision and trend of urban development, we will carry out pilot and demonstration projects to modernize cities, and make them livable, innovative, smart, green, civil, and resilient. We will build smarter cities and practice the “one map” digital management of urban buildings, public space, and underground pipe network as well as the unified network management of urban operations. We will make sound plans for developing the green ring, green corridor, green wedge, and green lane in urban areas, promote ecological restoration and functional improvement, prioritize the development of urban transit, develop a slow-traffic network of bicycle lanes and pedestrian paths, develop smart construction, and build low-carbon cities by popularizing the use of eco-friendly building materials, prefabricated buildings, and steel structure housing. We will keep cultural heritage alive and put an end to large-scale demolition and construction so that cities can evoke the nostalgia of residents. We will build an urban flood control and drainage system featuring combination of storage and drainage for the source emission reduction, elimination of the waterlogging risk and emergency response, so as to achieve substantial results in promoting urban waterlogging control. We will enhance the ability of public facilities to cope with storms, droughts, and geological disasters, and improve the functions of public facilities and buildings as emergency shelters. We will strengthen the building of an accessible environment, expand the sources of urban construction funds, and establish a financially sustainable financing mechanism that involves appropriate terms and supports diversified channels.
III. Urban governance
We will uphold Party building measures, shift the focus downward, and ensure empowerment by science and technology, continue to make urban governance more effective, meticulous, and intelligent, and promote the modernization of social governance in urban areas. We will reform and improve the urban management system, promote the experience of community-level management mechanisms as represented by “all departments responding to the call of the sub-district and township governments to process public complaints without delay”, channel more resources, management, and services down to sub-districts and communities, and accelerate the building of modern communities. We will promote innovation in urban management methodology, model, and concept with digital technology and meet the exact needs of the people with high efficiency. We will strengthen property service oversight and improve the coverage, quality, and standardization of property services.
IV. Housing market and housing support
We will uphold the principle that housing is for living rather than for speculation, and accelerate the establishment of a housing system with diverse suppliers, multiple channels of support, and combined renting and purchase, to ensure access to housing and balanced job and housing provisions for all people. We will implement a host of measures based on local conditions and ensure that urban governments have the primary responsibility for keeping land and housing prices and expectations stable. We will establish a linkage mechanism between housing and land, strengthen financial regulation of real estate, give full play to the regulatory role of housing tax, support reasonable demand for owner-occupied housing, and curb speculative and investment-related demand for housing. We will work faster to foster and develop the housing rental market, effectively revitalize idle housing resources, expand the supply of urban rental housing in an effective and orderly manner, improve the long-term rental housing policy, and gradually endow renters and purchasers of housing with equal rights in terms of access to public services. We will step up the development of housing rental laws and regulations and strengthen the supervision of the rental market to protect the legitimate rights and interests of lessees and lessors. We will effectively increase the supply of government-subsidized housing and improve the basic system and supporting policies for guaranteeing access to housing. We will expand the supply of government-subsidized rental housing with a focus put on cities with large population inflows and high housing prices, and step up efforts to solve the housing problems of people in difficulties and new residents. We will formulate a separate land use plan for rental housing, explore the use of collective construction land and idle land owned by enterprises and public institutions to build rental housing, and support the conversion of non-residential housing into affordable rental housing. We will improve the mechanism for distribution of income from land transfer, and increase fiscal, taxation, and financial support. We will develop shared ownership housing in line with local conditions, properly handle the relationship between basic guarantee and non-basic guarantee and improve the way of housing guarantee and the policies on the targets, threshold, and exit management concerning housing guarantee. We will reform and improve the housing provident fund system in terms of mechanisms for deposit, use, management, and operation.
Part IX Improving Regional Economic Structures and Promoting Coordinated Regional Development
A strategic approach to coordinated regional development will guide major initiatives to strengthen coordination at the regional level, rationalize land use planning through functional zoning, and improve institutional support for an integrated regional economic structure conducive to coordinated development with a focus on quality improvement.
Chapter 30 Land Use Planning and Environmental Protection
Land use planning will be based on the carrying capacity of a particular environment in question, the comparative advantages of various regions, and the need for environmental protection, in a way that promotes rational flows and efficient concentration of production factors, conducive to creating synergy by leveraging complementary strengths while enhancing distinctive main functions of each area. The goal of land use planning is to promote development with quality improvement top of mind.
I. Functional zoning
In line with the changing trend of the spatial structure, we will optimize the layout of major infrastructure, major productive forces, and public resources, improve the development of urbanized areas by category, promote the agglomeration of agricultural production to functional zones for grain production, protected areas for the production of major agricultural products, and advantageous areas of featured agricultural products, and optimize the system of defense for ecological security, to gradually form a spatial pattern consisting of three major areas—urbanized zones, main agricultural production zones, and ecosystem service zones. We will classify policies into units according to different functional orientations, and introduce differentiated policies for key development areas, ecologically fragile areas, and areas rich in energy resources, so as to adopt targeted policies for different areas. We will strengthen the overall planning and coordination of space development and ensure the implementation of national major development strategies.
II. Key drivers of quality-oriented development
Focusing on areas that possess economic development advantages, such as central cities and city clusters, we will enhance the economic and population carrying capacity and drive the overall improvement of national economic efficiency. With the focus laid on the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, Yangtze River Delta, and Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, we will enhance the capacity of driving innovation and allocating resources at a global level, and move faster to build the top echelon to lead high-quality development. In the central and western regions, where conditions permit, we will improve the functions of city clusters, accelerate industrialization and urbanization, and build key areas for high-quality development, with the central cities as the driving force. We will remove the obstacles of resource flow, improve administrative divisions, and enhance the comprehensive carrying capacity and the ability of optimal resource allocation of central cities so as to give better play to their roles in driving regional development.
III. Key functional zones: capacity upgrading
Supported by zones that are undertaking strategic functions, such as the main agricultural production zones, key ecosystem service zones, areas rich in energy resources, and border areas, we will safeguard the national food security, ecological security, energy security, and border security, and work together with areas with impetus for growth to build a power engine driving high-quality development. We will support main agricultural production zones to enhance their agricultural production capacity, eco-functional zones to lay their focus on protecting the ecological environment and providing ecological products, and the population in the eco-functional zones to relocate and settle in urbanized areas in a gradual and orderly manner. We will improve the energy development and transportation layout, strengthen the construction of bases for comprehensive development and utilization of energy resources, and improve domestic energy supply support. We will strengthen the development capacity of border areas, offer them more support in terms of population and economy, and promote national unity and border stability in these areas. We will improve the public resource allocation mechanism and provide effective transfer payments for key eco-functional zones, major agricultural production zones, and border areas.
Chapter 31 Major Regional Development Strategies
Major regional development strategies focus on strategic objectives that are likely to have spillover effects and will spur action or drive growth in neighboring areas or in related fields. These strategies promote regional integration, interaction, connectivity, and complementarity.
I. Coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region
We will prioritize relieving Beijing of functions that are non-essential to its role as the capital city, structure a corresponding policy system, and implement several landmark projects to relieve the city of such non-essential functions. We will ensure Xiong’an New Area is developed up to the highest standards, accelerate the construction of the Pilot Area and the Initial Development Zone, and promote innovation of the management system. We will ensure high-quality development of Beijing Municipality’s administrative center in Tongzhou and promote integrated development of Tongzhou with Sanhe, Xianghe, and Dachang in Hebei Province. We will promote the high-quality development of Tianjin Binhai New Area and support the development in Zhangjiakou of the water conservation functional zone and the ecological buffer zone for the capital. We will improve the basic research and original innovation capacity of Beijing Science and Technology Innovation Center, give full play to the role of Zhongguancun National Independent Innovation Demonstration Zone in piloting and testing new initiatives, and promote the in-depth integration of the industrial chain and innovation chain in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. We will ensure the basic completion of the highly connected rail transit in the region and improve the coordination among airport and port clusters. We will enhance the joint efforts for prevention, control, and treatment of air pollution, and strengthen the comprehensive treatment of groundwater overexploitation and land subsidence in North China.
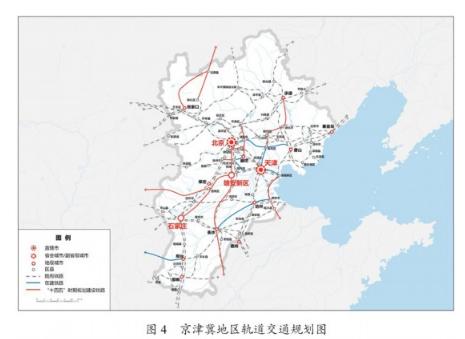
Figure 4. Map of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region rail transit plan
II. The Yangtze River Economic Belt
We will consistently prioritize ecological conservation, boost green development, ensure well-coordinated environmental protection, prevent overdevelopment, and adopt a holistic approach to pursue both ecological and environmental protection and economic development, to create a model of Beautiful China where humanity and nature harmoniously co-exist. We will continue to promote the rectification of prominent problems in the ecological environment, promote meticulous region-specific management and control of the Yangtze River Basin and implement projects for urban sewage and garbage treatment, industrial pollution control, agricultural non-point source pollution control, ship pollution control, tailing pond pollution control, etc. We will carry out demonstrative projects for green development and promote ecological conservation and environmental protection in Chishui River Basin. We will enforce a 10-year fishing ban in the waters of the Yangtze River. Focusing on the construction of the Yangtze River artery, we will design a comprehensive transportation system to ease the bottleneck of the Three Gorges Project and accelerate the construction of high-speed railway and freight railway along the Yangtze River. We will give full play to the overall advantages of industrial coordination and connectivity to build a green industrial system, and make every effort to protect the cultural relics and heritage of the Yangtze River.
III. Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area
We will strengthen collaborative development among enterprises, universities, and research institutions in Guangdong, Hong Kong, and Macao, improve the framework system consisting of “two corridors” (Guangzhou-Shenzhen-Hong Kong and Guangzhou-Zhuhai-Macao) and “two pivots” (Shenzhen-Hong Kong Science and Technology Innovation Cooperation Zone in Hetao and Guangdong-Macao Cooperation Area in Hengqin) for science and technology innovation, to promote the development of comprehensive national science centers and facilitate the cross-border flow of innovation factors. We will accelerate the construction of intercity railways, coordinate the functional layout of ports and airports, and optimize the allocation of shipping and aviation resources. We will deepen the reform of customs clearance models, and promote the convenient and efficient flow of personnel, goods, and vehicles. We will expand the scope of professional qualifications of mutual recognition between the Mainland and Hong Kong and Macao, and further promote the convergence of rules and mechanisms in key areas. We will facilitate the youth from Hong Kong and Macao to study, work, and start business in Mainland cities of the Greater Bay Area (GBA), and create top-notch youth exchange brands among Guangdong, Hong Kong, and Macao.
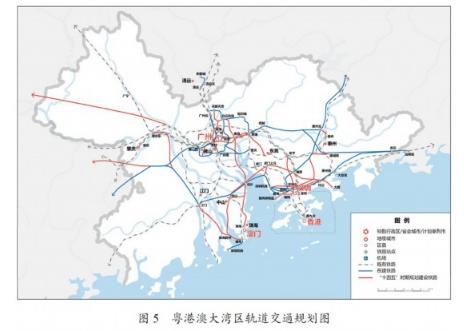
Figure 5. Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area rail transit plan map
IV. Integrated development in the Yangtze River Delta
With the aim to build internationally advanced scientific and technological innovation capacity and an industrial system, we will accelerate the development of the G60 Science and Technology Innovation Corridor and the industrial innovation belt along Shanghai and Nanjing in the Yangtze River Delta, to improve the Yangtze River Delta’s capacity of allocating global resources and driving national development. We will accelerate infrastructure interconnection, achieve full coverage of high-speed rail in the cities at the prefecture level and above in the Yangtze River Delta and promote the integrated governance of port clusters. We will develop the Hongqiao International Airport as an opening hub, strengthen the role of Lingang New Area of the Shanghai Pilot Free Trade Zone (FTZ) in intensive development of an open economy, and deepen the joint development of the pilot FTZs in Shanghai, Jiangsu, Zhejiang, and Anhui. We will accelerate the sharing of public services and optimize the distribution of high-quality education and healthcare resources. We will promote the joint protection and governance of the ecological environment and build a high-level demonstration zone for integrated ecological and green development in the Yangtze River Delta.

Figure 6. Yangtze River Delta rail transit plan map
V. Ecological protection and quality-oriented development in the Yellow River Basin
We will intensify the protection and restoration of key ecosystems in the upper reaches of the Yellow River, take appropriate steps to protect Sanjiangyuan (Source of Yangtze, Yellow, and Lancang rivers) as “China’s Water Tower”, and enhance the water conservation capacity of Gannan, Ruoergai (Zoige), and other areas. We will seek new methods for addressing soil erosion in the middle reaches of the river in the Loess Plateau, and actively carry out comprehensive management of small watersheds, and construction of dry land terraces and silt dams. In the lower reaches, we will advance efforts to comprehensively address secondary suspended rivers and floodplains, and strengthen the protection and restoration of wetlands in the Yellow River Delta. We will tackle agricultural pollution from non-point sources in the Fen-Wei Plains and Hetao Irrigation Area, check up and rectify industrial enterprises along the Yellow River shoreline, and strengthen the construction of urban sewage treatment facilities and supporting pipe networks along the Yellow River. We will implement intensive water conservation and control initiatives to reduce the intensity of water resource development and utilization, rationally control the intensity of coal development, and promote integrated development and utilization of energy resources and the ecological restoration of mines. We will improve the development pattern of central cities and city clusters, and coordinate the development of counties and villages along the Yellow River. We will also implement systematic conservation projects related to the Yellow River cultural heritage, create an internationally influential Yellow River cultural tourism belt, and build a pilot area for ecological protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River Basin.
Chapter 32 Coordinated Regional Development Strategies
The focus of coordinated regional development is on relative balance and coordination. Development efforts in the western region will be in full swing. Revitalization of the northeast remains an ongoing process. The central region is expected to witness a new takeoff. The eastern region will lead the charge. Development support will be provided to areas with special features.
I. A new stage of development in the western region
We will intensify efforts and implement more targeted and effective policies to promote large-scale development in the western region. We will implement several major ecological projects in key areas, actively integrate the regional development into the pursuit of the Belt and Road Initiative, strengthen the development of the large opening-up corridors, and build multi-level platforms for opening up interior areas. We will increase investment in infrastructure construction in the western region, support the development of competitive industries that take advantage of local strengths, pool efforts to consolidate the achievements of poverty alleviation, and shore up the weaknesses in the fields of education, health care, and people’s livelihood. We will promote the development of Chengdu-Chongqing economic circle and make it an economic center, a center for science and technology innovation, a new highland of reform and opening-up, and a livable place for high-quality life of national influence. We will upgrade the city clusters in the Central Shaanxi Plain to promote cooperation and interaction between the northwest and southwest regions. We will support Xinjiang in building “three bases and one corridor” (national bases for large-scale oil and gas production and storage, for coal production, thermal power generation and coal chemical industry, and for wind power generation, as well as the national energy and resources corridor) and we will support Tibet in building an important corridor that opens to South Asia. We will promote the protection and development of the areas west of the 400 mm precipitation line.
II. Revitalization of northeast China
From the strategic perspective of safeguarding national defense, food, ecology, energy, and industrial security, we will strengthen efforts to coordinate policies to achieve breakthroughs in prioritized areas. We will quicken our pace in shifting government functions, deepen reform of state-owned enterprises, step up efforts to improve the business environment, and vigorously develop the private economy. We will build Liaoning Coastal Economic Belt and Changchun-Jilin-Tumen Development and Opening-up Pilot Zone and improve Harbin’s cooperation with and opening-up to Russia. We will accelerate the development of modern agriculture and make it a “ballast” to ensure national food security. We will intensify the protection of ecological resources and build a strong ecological security shield in northern China. We will transform and upgrade traditionally competitive industries such as equipment manufacturing, foster and develop emerging industries, vigorously develop characteristic industries including ice and snow and eco-tourism in cold regions, and build an internationally influential ice and snow tourism belt, so as to develop a new industrial structure for balanced development and competitive advantages. We will implement measures more attractive to talents, and deepen paired cooperation with the eastern region.
III. The rise of the central region
We will step up efforts to build important and advanced manufacturing bases, improve the ability of independent innovation in key areas, build a highland for opening-up of interior areas, consolidate the ecological and green development model, and promote the rapid growth of central China. We will strive for bigger and stronger advanced manufacturing, build mid-to-high-end industrial clusters along the Yangtze River and along the Beijing-Guangzhou, Lanzhou-Lianyungang, and Beijing-Kowloon railway lines, and actively undertake the deployment and transfer of emerging industries. We will promote the coordinated development of city clusters in the middle reaches of the Yangtze River, accelerate the development of Wuhan and Changsha-Zhuzhou-Xiangtan metropolitan areas, and make them important growth poles in China. We will build up the foundation for grain production, keep up efforts to improve the comprehensive benefits and competitiveness of agriculture, and accelerate the development of modern agriculture. We will enhance joint protection and governance of the ecosystem and environment and strive to build protective barriers for eco-security. We will support the inter-connected development of the upper and lower reaches of the Huaihe River and Hanjiang River ecological economic belts, accelerate the construction of corridors for opening-up, and build high-level platforms for opening up interior areas. We will improve public service support, and especially the ability to respond to public health and other major emergencies.
IV. Accelerated pace of modernization in the eastern region
We will give full play to the advantages of the eastern region in bringing together innovative factors, help the region to make faster breakthroughs in innovation, and push the region to take the lead in achieving high-quality development. We will move faster to foster world-class advanced manufacturing clusters, spearhead the development of emerging industries and modern service sectors, improve the output efficiency of production factors, and take the lead in upgrading industries. We will ensure the region can participate in international economic cooperation and competition at a higher level, create new advantages in opening-up, and take the lead in establishing a system for an all-round open economy. We will support Shenzhen to build a leading demonstration zone of socialism with Chinese characteristics, Pudong to build a leading zone of socialist modernization, and Zhejiang to build a demonstration zone of common prosperity and high-quality development. We will further promote the development of the comprehensive pilot zone to replace the old growth drivers in Shandong Province.
V. Support for development in areas with special features
We will coordinate and promote the revitalization of the old revolutionary base areas, develop characteristic industries according to local conditions, inherit and carry forward the “red” culture, support the demonstration of high-quality development in the former Central Soviet Area of Jiangxi, Fujian, and Guangdong, and promote the green innovation and development of the old revolutionary base areas of Shaanxi-Gansu-Ningxia, Dabie Mountains, Zuoyoujiang, Sichuan-Shaanxi, Yimeng, etc. We will comprehensively address ecologically degraded areas, protect and restore ecologically fragile areas, and support the development of the Bijie pilot area. We will promote the development of demonstration areas for sustainable development and pilot zones for transformation and innovation in resource-based areas, comprehensively address subsidence in coal mining areas, and implement projects to upgrade independent industrial and mining areas. We will reshape the competitive advantages of manufacturing in the old industrial bases and build demonstration areas for industrial transformation and upgrade. We will improve the infrastructure of state-owned forest farms and forest regions and implement multiple measures to solve production and living difficulties faced by the people living in high altitude areas. We will vigorously boost development in border areas, improve the living standards and maintain stability and security in the region; to this end, we will improve the conditions for production and living in border areas and the urban system along the borders, support the construction of border ports, and accelerate the construction of villages and towns on the border and roads leading to border areas. We will promote innovative development of the border trade and increase targeted support for the development of key border areas.

VI. Coordinated regional development
We will establish and improve mechanisms for regional strategic planning, market-based integrated development, regional cooperation and mutual assistance, and interregional interest compensation, to better boost the common growth of developed and underdeveloped regions, eastern, central, and western regions, and the northeast of the country. We will raise the level and standards of regional cooperation, and support the provincial border areas to establish new cooperation mechanisms characterized by unified planning and management, co-construction, and benefit sharing. We will improve the mechanism of financial transfer payments to support underdeveloped areas, gradually realize equal access to basic public services, and guide talent flow to the western regions and the border and remote areas facing hardships. We will improve the regional cooperation and benefit adjustment mechanism, support various forms of benefit compensation between the upper and lower reaches of the river basins, the main grain producing and marketing areas, and the resource exporting and importing areas, and encourage the exploration of benefit sharing models via co-construction parks and enclave economy. We will foster a strong sense of community for the Chinese nation, increase support for the development of areas with concentrations of ethnic minorities, and carry out comprehensive, in-depth, and sustained publicity and education on ethnic unity and progress, to promote exchanges and interaction among all ethnic groups.
Chapter 33 Development of the Marine Economy
Coordinated development is the key. Coordination is required for activities on land and at sea to protect the health and integrity of marine ecosystems and the harmony between people and the sea while developing the marine economy. International cooperation is important in the search for win-win solutions. We will not falter in our efforts to protect our maritime rights and interests, and to build China into a strong maritime country.
I. Development of marine industries
We will make several breakthroughs in core technologies related to marine engineering, marine resources, and marine environment. We will foster and expand marine engineering equipment and marine biomedical industry, promote seawater desalination and large-scale utilization of marine energy, and enhance the development of marine cultural tourism. We will optimize the distribution of green aquaculture in coastal areas, build marine pastures, and develop sustainable pelagic fisheries. We will build several demonstration zones for high-quality development of marine economy and characteristic marine industrial clusters, and comprehensively boost the development of the three major marine economic circles in the north, east, and south. We will deepen sea-related cooperation with neighboring countries based on coastal economic belts.
II. Sustainability of marine ecosystems and habitats
We will explore the establishment of a coordinated system for comprehensive management that covers coastal areas, river basins, and sea areas. We will impose stricter management and control on sea reclamation, and step up comprehensive management of coastal zones and coastal wetland protection. We will expand the control range of total discharge volume of pollutants into the sea to ensure good water quality of the sections of the rivers flowing into the sea. We will accelerate comprehensive treatment of key sea areas, build a mechanism for coordinated pollution prevention and control of river basins, estuaries, and coastal waters, and promote the protection and construction of beautiful bays. We will guard against major environmental risks such as oil spills and hazardous chemical leakage and improve our ability to cope with maritime natural disasters and environmental emergencies. We will improve the systems for coastline protection and paid use of sea areas and uninhabited islands, and explore the regulation of the retraction line of coastal buildings and compensation for damages to marine ecosystem and environment, to ensure the natural coastline retention rate is no less than 35%.
III. Participation in global marine governance
We will actively develop the blue partnership, fully participate in the formulation and implementation of mechanisms and rules for international maritime governance, and promote the building of a just and equitable international maritime order and development of a marine community with a shared future. We will increase practical cooperation with coastal countries in the fields of marine environmental monitoring and protection, scientific research and maritime search and rescue, and intensify the investigation and evaluation of deep-sea strategic resources and biodiversity. We will join in practical cooperation in the Arctic and build the “Silk Road on Ice”. We will enhance our ability to participate in the Antarctic conservation and utilization. We will step up efforts to study and evaluate situations, prevent risks, and handle legal issues, and strengthen maritime judicial system building, to resolutely safeguard China’s maritime rights and interests and promote the formulation of the basic marine law in an orderly manner.
Part X Socialist Cultural Development and China’s Soft Power
Marxism guides all activities in our ideological space. Reflecting confidence in our culture, cultural development informed by our core socialist values promotes moral ideals, forges cohesion, helps the younger generation grow and thrive, enriches tradition, and shapes our national image. It helps meet the people’s cultural needs and provides emotional support. It is therefore essential to enhance socialist cultural development.
Efforts will be ongoing to promote ethical standards informed by core socialist values in response to the needs in the new era. Character development is especially relevant in this respect to foster a positive ethos, civility, and ethical behavior.
I. Moral education as a regular activity
We will strengthen efforts to carry out education in Xi Jinping Thought on Socialism with Chinese Characteristics for a New Era and improve the work system of arming the whole Party and educating people with the Party’s innovation theory. We will establish and improve the system and long-term mechanism of “remaining true to our original intention and keeping our mission firmly in mind”, strengthen and improve our ideological and political work, continue the publicity and education on socialism with Chinese characteristics and the Chinese Dream, intensify education on the history of the Party, the history of new China, the history of reform and opening-up, and the history of socialist development, as well as the education on patriotism, collectivism, and socialism. We will strengthen research, interpretation, publicity, and education on revolutionary heritage and carry forward the great spirit of the Party and the people that was formed during various historical struggles. We will improve the legal and policy system for promoting the socialist core values, incorporate the requirements of the socialist core values into the improvement of the rule of law and social governance, and embody them in the whole process of national education, improvement of public civility, as well as the creation and production of cultural products. We will improve the mechanism for coordination and cooperation in the education of young people on ideals and convictions.
II. Philosophical studies and social sciences with Chinese characteristics
We will strengthen comprehensive and systematic research, publication, dissemination, publicity, and interpretation of Xi Jinping Thought on Socialism with Chinese Characteristics for a New Era, and work to adapt Marxism to China’s conditions, keep it up-to-date, and enhance its popular appeal. We will carry out the Marxist Theory Research and Development Project, build centers (institutions) for the study of Xi Jinping Thought on Socialism with Chinese Characteristics for a New Era and the theories of Socialism with Chinese Characteristics, and establish and make good use of learning platforms such as “xuexi.cn”. We will build a discipline system, academic system, and discourse system of philosophy and social sciences with Chinese characteristics, further implement philosophy and social science innovation projects, and step up efforts to build new think tanks with Chinese characteristics.
III. Building on fine traditional Chinese culture
We will implement programs to carry on the best of Chinese cultural traditions and heritage, improve the systematic protection of important cultural and natural heritage and intangible cultural heritage, and promote the creative conversion and development of fine traditional Chinese culture. We will strengthen scientific and technological innovation related to cultural relics, implement projects that explore the origin of Chinese civilization and archaeology in China, carry out general surveys of Chinese cultural resources, strengthen the conservation, research, and utilization of cultural relics and ancient books, promote the protection of revolutionary cultural relics and “red” sites, and improve the system of recourse and retrieval of lost cultural relics. We will build national cultural parks themed on the Great Wall, the Grand Canal, the Long March, the Yellow River, and so on, and better conserve world cultural heritage, cultural relics protection units, archaeological site parks, as well as China’s renowned historic and cultural cities, towns, and villages. We will improve the system for conservation and inheritance of intangible cultural heritage and better protect and inherit the excellent traditional handicrafts of all ethnic groups.
IV. Ethical values and civility
We will advance civic morality and vigorously promote social morality, professional ethics, family values, and integrity of individuals. We will publicize and learn from the winners of national medals and national honorary titles, models of the times, models of high morality, the most beautiful people, and good people around us. We will implement initiatives to improve public etiquette and ethical standards, build more Chinese cultural centers in the new era, do a good job in the election and commendation of exemplary cities, villages, towns, entities, campuses, and families in a sound and standardized manner, and further raise the intellectual and moral standards of children and the youth. We will improve social norms including civic conventions, village regulations and agreements, student rules and regulations, as well as provisions of organizations, and establish a mechanism for punishing immoral behavior. We will promote the culture of integrity throughout the society; extensively carry out volunteer services campaigns to help those in need; encourage hard work, diligence, and frugality; and carry out publicity and education on the theme of creating happiness through work. We will also improve ethical standards and advance civility in cyberspace and develop a positive and healthy cyberspace culture.
Chapter 35 Public Cultural Services
Culture should serve the needs of the people and contribute to the socialist cause. Through cultural activities, we “let a hundred flowers bloom and a hundred schools of thought contend”. Public cultural services and the institutional framework for these services should be strengthened in an innovative manner to better protect the people’s cultural rights and interests, help disseminate Chinese cultural products, and facilitate cultural exchanges.
I. Creation, production, and dissemination of quality cultural products
We will take quality improvement as the lifeline of literary and artistic works and improve our ability to create original literature and arts. To this end we will carry out projects to improve the quality of literary and artistic works, improve the planning and organization mechanism for the creation of works on major realistic, revolutionary, and historical themes, strengthen the creation of works on rural and children’s themes, and continue to launch high-quality literary and artistic works that reflect the new ethos of the times and eulogize the innovation and creativity of the people. We will establish and improve the incentive mechanism and evaluation system for the conception, production, dissemination, guidance, and promotion of cultural products, and promote the formation of a healthy and clean literary and artistic ecosystem. We will strengthen the building of cultural teams, and train high-level creative talents, and promote eminent figures of moral integrity and outstanding artistic competence.
II. Public cultural services
We will optimize the allocation of urban and rural cultural resources, and promote integrated development of urban and rural public cultural services. We will launch new public cultural projects, improve the functions of community-level multipurpose cultural service centers, and extensively carry out mass cultural activities. We will promote the free admission and digital development of public libraries, cultural centers, art galleries, museums, and other public cultural venues. We will boost the in-depth integration of media and improve new mainstream media. We will improve the emergency broadcast system and implement projects to enhance the functions of smart radio and television in maintaining social order in the border and rural areas. We will develop archiving systems, further promote nationwide reading to build China into a nation of avid readers, and upgrade film screening facilities in rural areas. We will develop new operation mechanisms for public cultural services and encourage social forces to participate in the supply of public cultural services and the construction and operation of relevant facilities.
III. International appeal of Chinese culture
We will strengthen cultural exchanges with foreign countries and multi-level dialogue with global civilizations, innovate and promote international communication to share China’s stories, spread China’s voice, and promote people-to-people connectivity through both online and offline channels. We will carry out activities such as “Reading China”, “Journey around China”, and “See and Hear China”, and make every effort to hold the Chinese Culture Year (Festival) and China Tourism Year (Festival). We will establish platforms for Chinese language communication and develop a global communication system for Chinese language and culture and an international standard system for Chinese language education.
Chapter 36 Cultural Industries
Social benefits are always the top consideration. Pursuit of economic returns should be aligned with the delivery of social benefits, a requirement that underpins the development of cultural industries and markets.
I. The supply of high-quality cultural products
We will implement the strategy of digitizing cultural industries, accelerate the development of new types of cultural enterprises, forms of cultural business, and modes of cultural consumption, and strengthen digital creativity, online audio-video, digital publishing, digital entertainment, and online broadcasting industries. We will step up efforts to improve the production and broadcasting capacity of ultra-high-definition TV programs, upgrade TV channels for high-definition broadcasting and promote the application of immersive video and cloud broadcasting. We will implement cultural branding strategies and create influential and representative cultural brands, develop leading cultural enterprises, standardize the development of cultural industrial parks, and promote the construction of regional cultural industrial belts. We will vigorously develop foreign cultural trade, open up overseas cultural markets, encourage excellent traditional cultural products and digital cultural products such as films, TV dramas, and games to “go global”, and strengthen the construction of national cultural export bases.
II. Integrated development of culture and tourism
We will offer a unique Chinese cultural tourism experience by shaping tourism through culture and highlighting culture through tourism. We will further develop mass tourism and smart tourism, innovate tourism products, and offer better tourism consumption experience. We will strengthen the integration of regional tourism brands and services and build world-class tourist attractions and resorts with rich cultural connotations as well as national tourism and leisure cities and blocks with distinctive cultural characteristics. We will promote the innovative development of “red” tourism, cultural heritage tourism, and tourism performance, improve the quality of services for holiday recreation and rural tourism, and adopt better policies for the development of cruises, yachts, and low-altitude tourism. We will improve the tourism infrastructure and distribution system, promote a revolution of public toilets in tourist attractions, and construct smart scenic spots. We will establish a system for evaluating the quality of tourism services, and regulate online tourism business services.
III. Reforms in the cultural sector
We will improve the cultural management system and the mechanism of cultural production and operation, as well as the efficiency of cultural governance. We will improve the institutions and mechanisms for managing state-owned cultural assets, deepen reforms of cultural institutions for public benefit, and promote the reform of public cultural institutions’ corporate governance structure. We will advance the reform of different types of state-owned cultural enterprises, and promote the reform of state-owned literature and art troupes, as well as cinema reform. We will improve the system of comprehensive law enforcement in cultural markets and formulate laws and regulations for protection of minors when it comes to Internet, online information communication and transmission and other fields.
Part XI Green Development and Harmonious Co-existence between Humanity and Nature
We will stay true to the principle that lucid waters and lush mountains are invaluable assets by respecting nature, conforming to nature, and protecting nature. We will prioritize conservation, protection, and natural recovery, implement the sustainable development strategy, improve the overall coordination mechanism in the field of ecological civilization, build an ecological civilization system, and promote comprehensive transformation towards green economic and social development to build a beautiful China.
Chapter 37 Improving the Ecosystem
We will continue the systematic governance of mountains, rivers, forests, farmland, lakes, and grassland, strive to improve the self-rehabilitation ability and stability of ecosystems, make sure that the red line of ecological security is not crossed, and improve the overall quality of natural ecosystems.
I. Improving the eco-security shield system
We will strengthen the planning of territorial space and control over its use, draw red lines for ecological protection, boundary lines for permanent basic cropland and land for urban development, and protection lines for all types of sea areas, and ensure that these lines are not crossed. Focusing on the national key ecological areas and red lines for ecological protection, national nature reserves, etc., we will implement major projects for the protection and restoration of important ecosystems, and accelerate the construction of protective barriers for eco-security in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, the important ecological areas along the Yellow River and the Yangtze River, the northeast forest belts, the sand control belts in the north, the hilly and mountainous areas in the south, and the coastal zones. We will strengthen ecological protection and governance of the Yangtze River, the Yellow River, and other major rivers, as well as important lakes and wetlands, and put more efforts towards building and protecting important ecological corridors. We will comprehensively strengthen the protection of natural forests and wetlands and increase the wetland protection rate to 55%. We will make solid efforts to comprehensively control soil erosion, desertification, and stony desertification, carry out large-scale land afforestation, and introduce the forest-chief system. We will carry out weather modification initiatives based on science; promote the rehabilitation of grasslands, forests, rivers, and lakes; improve the rotation and fallow system of cultivated land; and consolidate the achievements of converting cropland to forests and grasslands, converting farmland to lakes and wetlands and embankments into part of beaches and seas.
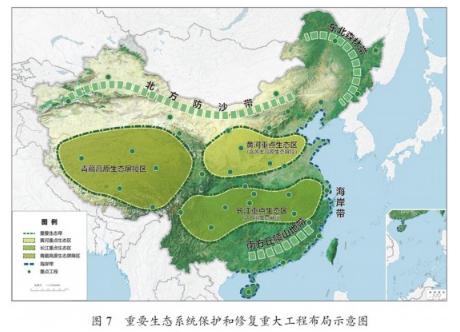
Figure 7. Layout of major ecosystem protection and restoration projects
II. The nature reserve system
We will appropriately delimit the scope and functional zones of nature reserves, accelerate their integration and optimization, and build a nature reserve system with national parks as the mainstay, nature reserves as the basis, and nature parks as the supplement. We will strictly control non-ecological activities within nature reserves, and steadily promote the orderly withdrawal of residents, cultivated land, and mining rights from the core areas. We will improve the management institutions and operation mechanisms of national parks and integrate and set up several national parks. We will implement major biodiversity conservation projects, build a biodiversity conservation network, strengthen the protection and restoration of species on the national key list of protected wild plants and animals and rare and endangered wildlife as well as their habitats, and intensify the control of alien species. We will improve policies on land and sea use for ecological protection and restoration as well as the regulatory system of nature reserves and ecological protection red lines, and monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of ecosystem protection.
III. The mechanism of compensation for ecological conservation
We will increase transfer payments to key ecological areas, source areas of important rivers, and nature reserves, and encourage horizontal ecological compensation between benefited areas and protected areas, and between the upper and lower reaches of river basins through various forms including financial compensation and business-driven development support. We will improve market-oriented and diversified ecological compensation and encourage all kinds of private capital to participate in ecological conservation and restoration. We will improve the ecological compensation system for forests, grasslands, and wetlands. We will promote the establishment of a basin-wide ecological compensation mechanism along the Yangtze River, the Yellow River, and other important rivers. We will establish a mechanism to realize the value of ecological products, carry out pilot projects in the Yangtze River Basin and Sanjiangyuan National Park, and formulate and implement regulations on compensation for ecological conservation.
Chapter 38 Continuous Environmental Improvement
We will increase efforts to prevent and control pollution, establish and improve the environmental governance system, promote accurate, scientific, law-based and systematic pollution control, work together to reduce pollution and carbon emissions, consistently improve air and water environment quality, and effectively control soil pollution risk.
I. Furthering pollution prevention and control
We will continue to prevent and control pollutants at sources, and adopt a comprehensive approach to strengthen coordinated control of multiple pollutants and coordinated treatment among regions. We will improve the management for meeting required air quality standards in urban areas, promote coordinated control of fine particulate matter (PM2.5) and ozone (O3), reduce the PM2.5 concentration in cities at and above the prefectural level by 10%, effectively curb the increase in O3 concentration, and basically eliminate heavy air pollution. We will continue to improve the air quality in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region and its surrounding areas, as well as Fen-Wei Plains and Yangtze River Delta; promote clean heating in northern China based on local conditions, promote industrial furnace treatment and transformation of non-electric industries towards ultra-low emission, and accelerate the comprehensive treatment of volatile organic compound (VOCs) emissions, with the total emissions of nitrogen oxides (NOx) and VOCs reduced by more than 10%. We will improve the coordination mechanism for water pollution prevention and control in river basins, intensify the comprehensive treatment of key river basins, key lakes, urban water bodies, and offshore areas, promote the protection and construction of beautiful rivers and lakes by reducing the total chemical oxygen demand (COD) and ammonia nitrogen emissions by 8%, and basically eliminate substandard Grade V surface water sections controlled at the national level and urban black and malodorous water bodies. We will carry out standardized construction of sources of urban drinking water, and promote the relocation and transformation of heavy pollution enterprises in key river basins. We will promote the control and restoration of contaminated land for farming and for construction, and implement coordinated prevention and control of water and soil environmental risks. We will improve the prevention and control against plastic pollution throughout the chain, better control environmental noise pollution, and at the same time, attach importance to the treatment of new pollutants.
II. Comprehensive improvement of environmental infrastructure
We will build a system of environmental infrastructure that integrates sewage, garbage, solid waste, hazardous waste, and medical waste treatment and disposal facilities and monitoring and supervising capabilities, and form an environmental infrastructure network extending from cities to towns and villages. We will promote complete coverage of the urban sewage pipe network, carry out differential and accurate upgrade of sewage treatment, and promote centralized incineration of sludge for harmless treatment, so that the 90% of urban sludge is harmlessly treated and over 25% of sewage is recycled in water-deficient cities at the prefecture level and above. We will set up a household waste treatment system with separate dumping, collection, transportation, and treatment of different types of waste based on waste sorting. We will deploy facilities for centralized recycling and disposal of hazardous waste with emphasis put on major industrial bases. We will accelerate the construction of centralized treatment facilities for medical waste in cities that are at and above the prefecture level, and improve the system for collection, transportation, and disposal of medical waste in counties.
III. Environmental risk prevention and controls
We will establish and improve the mechanism for evaluation and early warning of and emergency response to key risk sources. We will comprehensively rectify illegal stockpiling of solid waste and improve the regulation and risk prevention capabilities for hazardous waste. We will strengthen the monitoring and early warning of heavy metal pollution in key areas and industries. We will improve the system for managing environmental risks from toxic and hazardous chemicals and complete the relocation and transformation of hazardous chemical production enterprises in key areas. We will rigorously supervise nuclear and radiation safety and promote the prevention and control of radioactive pollution. In terms of ecological and environmental emergencies, we will establish a post-event assessment mechanism and a public health impact assessment system. In high-risk sectors, we will promote compulsory environmental pollution liability insurance.
V. Coping with climate change
We will make sustained efforts to achieve the objectives of China’s Intended Nationally Determined Contributions 2030 and formulate an action plan to reach the peak of carbon emissions by 2030. We will improve the double control system of total energy consumption and intensity with a focus put on controlling fossil energy consumption. We will implement a system that focuses on carbon intensity control supplemented by total carbon emission control, and support the key industries and enterprises in the places where conditions permit to take the lead in reaching the peak of carbon emissions. We will promote clean, low-carbon, safe and efficient use of energy, and further promote the transformation of industries, construction, transportation, and other sectors towards low-carbon development. We will increase efforts to control methane, hydrofluorocarbons, perfluorocarbons, and other greenhouse gases, increase the carbon sink capacity of ecosystems, and anchor efforts to achieve carbon neutrality by 2060 by adopting even more robust policies and measures. We will intensify the observation and assessment of the impact of global warming on vulnerable areas in China, and enhance the capacity of urban and rural construction, agricultural production, and infrastructure, to adapt to climate change. We will exert more efforts on comprehensive scientific research on the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. On the basis of equity and in accordance with the common but differentiated responsibilities and respective capabilities of all countries, we will play a constructive role and lead international cooperation in responding to climate change, promote the implementation of the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change and its Paris Agreement, and actively carry out South-South cooperation on climate change.
V. Modern environmental governance system
We will establish a system for coordinated above-ground and underground ecological and environmental governance on land and at sea. We will implement the emission permit system across the board, ensure that emission permits cover all fixed pollution sources, ensure industrial polluters comply with emission standards within a specified time limit, and facilitate market-based trading of emission rights, energy consumption rights, water use rights, and carbon emission rights. We will improve the management of obligatory targets for environmental protection, energy conservation, and emission reduction, improve the management and protection mechanism of rivers and lakes, and strengthen the river-chief and lake-chief system. We will strengthen audit of natural resource assets at the end of the tenure of leading officials. We will improve the central supervision system for ecological environment protection, as well as the vertical management system for monitoring, supervision, and law enforcement of eco-environmental institutions that are at and below the provincial level, promote the reform of comprehensive law enforcement with respect to eco-environmental protection, and improve the system of eco-environmental public interest litigation. We will increase environmental protection information publicity, step up efforts to build up the environmental governance corporate responsibility system, and improve the mechanisms for public supervision and feedback on complaints, to guide non-governmental organizations and the public to participate in environmental governance. (To be continued)
(Note: PM2.5 refers to PM2.5 and O3 refers to O3)
Chapter 39 Faster Transformation for Green Development
We will prioritize the ecology and pursue green development, promote overall resource management, scientific allocation, comprehensive conservation, and recycling, and coordinate efforts to drive high-quality economic development and high-level ecological environment protection.
I. Higher resource utilization efficiency
We will prioritize and pursue the policy of energy conservation to improve energy conservation in industry, construction, transportation, and public institutions; raise energy use efficiency in emerging fields such as 5G and big data centers; strengthen energy-saving management of key energy users; implement energy system optimization and energy-saving technology transformation and other key projects; and accelerate the formulation and revision of mandatory national standards for energy consumption quota and energy efficiency of products and equipment. By implementing a national water-saving initiative, establishing a rigid constraint system for water resources, strengthening agricultural water conservation for greater use efficiency, industrial water conservation, emission reduction, urban water conservation, and loss reduction, and encouraging the use of recycled water, we will reduce water consumption per unit of GDP by about 16%. We will pursue more economical and intensive use of land, increase efforts to handle the unused and idle land, put inefficiently used land in cities and towns to good use, support the recovery and utilization of abandoned industrial and mining land, improve the policies to support composite use and multi-dimensional development of land, and control the increase of land designated for construction by less than 1.97 million hectares, to drive the steady decline of construction land use area per unit GDP. We will enhance the development and protection of mineral resources, develop green mining, and build green mines.
II. The resource recycling system
We will comprehensively implement the concept of a circular economy and build a multi-tiered system for efficient resource recycling. We will further promote the transformation of industrial parks towards recycling, improve and extend the industrial chain, and boost the graded utilization of energy and resources, waste recycling, and concentrated disposal of pollutants. We will strengthen the comprehensive utilization of bulk solid waste and standardize the development of remanufacturing industry. We will accelerate the development of circular agriculture that organically combines planting and breeding, enhance the planning and construction of waste recycling facilities, and improve the urban waste recycling and sorting system. We will put in practice “reverse recovery” and other measures for production enterprises, and establish and improve an online-offline integrated resource recovery system where the flow of resources can be controlled. We will expand the coverage of the system for extending producers’ responsibilities; and drive the minimization, standardization, and recycling of delivery packaging.
III. Vigorously developing green economy
We will resolutely curb blind development of high energy consumption and high emission projects, and boost transformation towards green development, to achieve positive growth. We will expand the industries covering energy conservation and environmental protection, clean production, clean energy, ecological environment, infrastructure upgrade towards eco-friendliness, and green services, and promote service models such as contract-based energy management, contract-based water conservation, and the third-party treatment of environmental pollution. We will drive the clean and efficient use of fossil fuels such as coal, promote the transformation of industries such as iron and steel, petrochemical, and building materials towards green development, and accelerate the shift in the transportation of bulk goods and medium and long-distance freight transportation, from highways to railways and waterways. We will boost the electrification of urban public transit and logistics distribution vehicles. We will build a system for market-oriented innovation in green technology, implement initiatives to make breakthroughs in green technology innovation, and carry out benchmarking campaigns to improve the resource use efficiency of key industries and key products. We will establish a unified set of standards for the green product certification and identification system, improve the mechanism for promotion of energy-saving household appliances, efficient lighting products, and water-saving appliances and intensify efforts to promote green living.
IV. A policy system for green development
We will enhance the law and policy support for green development, and implement tax policies conducive to energy conservation, environmental protection, and comprehensive utilization of resources. We will vigorously develop green finance; improve the system of paid use of natural resources; and innovate and improve pricing mechanisms in the fields of natural resources, sewage and garbage treatment, and water and energy use. We will strengthen energy-saving review and supervision over fixed asset investment projects and promote reform of the management system for key energy users, improve the “pacesetter” system for energy and water efficiency, and intensify the water quota management in high water consumption industries. We will further develop ecological civilization experimental sites, and further promote the construction of a national pilot area of comprehensive reform for the transformation of resource-based economy in Shanxi and the pilot project for the comprehensive reform of the energy revolution.
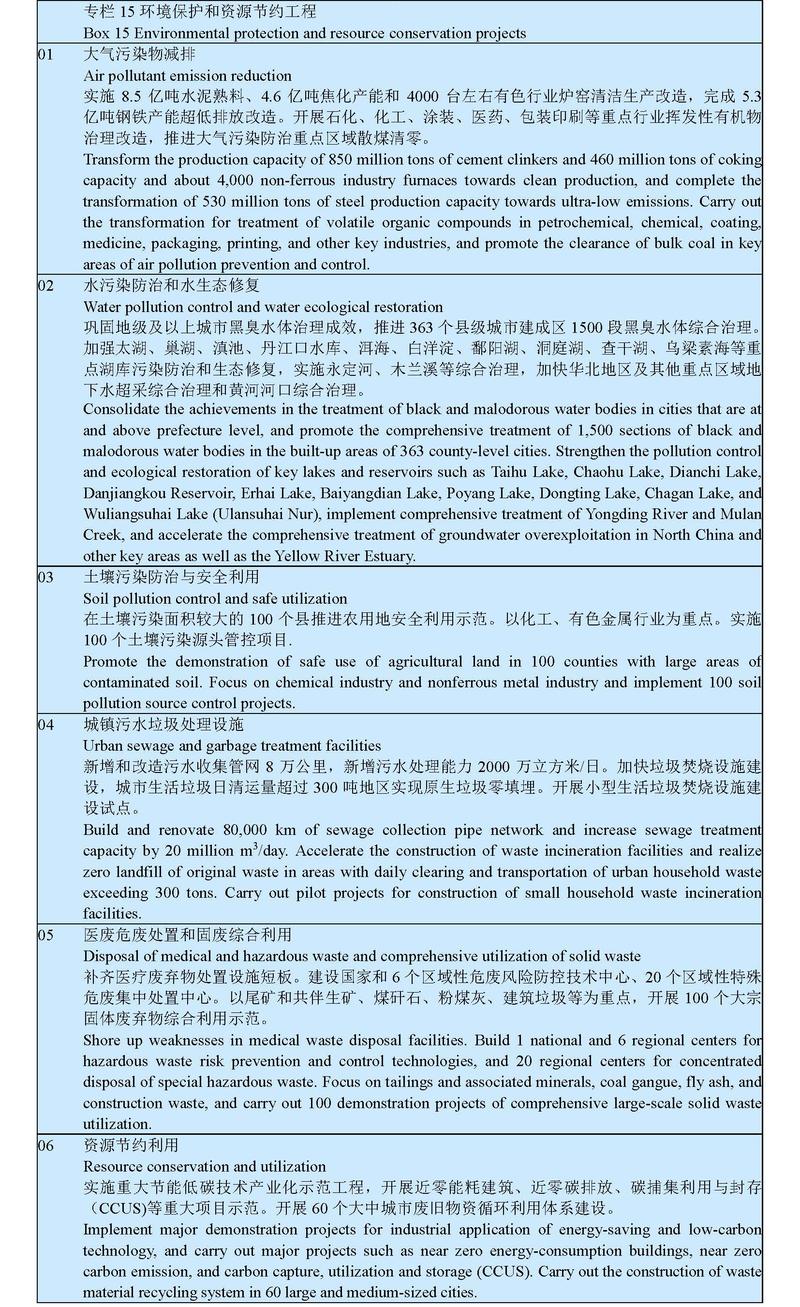
Part XII Further Opening-up for Win-Win Cooperation
We will continue to open up more sectors, increase the breadth and depth of opening-up, leverage the ultra-large-scale domestic market to promote international cooperation for mutual benefit and win-win outcome, and advance the stable and sustained joint pursuit of the Belt and Road Initiative and the co-building of a community with a shared future for mankind.
Chapter 40 A New Open Economy System
We will comprehensively improve the level of opening to the outside world, promote liberalization and facilitation of trade and investment, continue to deepen opening-up based on the flow of goods and production factors, and steadily expand institutional opening-up based on rules, regulations, management, and standards.
I. Accelerating institutional opening-up
We will build an institutional system and supervision model in line with the general practice of international trade. We will improve the management system for pre-access national treatment plus a negative list, further shorten the negative list for foreign investment, and implement post-access national treatment, to promote fair competition between domestic and foreign-funded enterprises. We will establish and improve the negative list management system for cross-border trade in services and improve the technology trade promotion system. We will steadily promote the opening of banking, securities, insurance, funds, futures, and other financial sectors, deepen the interconnection of domestic and foreign capital markets, and improve the system of qualified foreign investors. We will steadily promote the internationalization of RMB in a prudent manner, adhere to market-driven operation and independent choice of enterprises, and create a new type of mutually beneficial cooperative relationship based on the free use of RMB. We will improve the management of entry-exit, customs, foreign exchange, tax revenue, and other regulations and services.
II. Upgrading the opening-up platforms
We will promote the development of various open platforms across the board and create a new highland of opening-up with a higher level of opening, better business environment, and stronger impact. We will improve the structure of pilot free trade zones, grant them greater decision making power for reforms, further explore innovative, integrated, and differentiated reform, and proactively replicate and promote the results of institutional innovation. We will steadily promote the development of Hainan Free Trade Port, and liberalize and facilitate trade in the direction of “zero tariff” for trade in goods and “allow firms in and let them do business” for trade in services. We will greatly ease market access; comprehensively implement the minimum approval investment administration system; carry out pilot projects for reforms in cross-border securities investment and financing and security management of cross-border data transmission; adopt more open polices for talents, entry-exit, and transportation; formulate and promulgate Hainan Free Trade Port law; and basically establish policies and systems of free trade ports with Chinese characteristics. We will make innovations to upgrade state-level new areas and development zones, promote high-standard opening-up of comprehensive bonded zones, improve the functions of key pilot zones for development and opening-up along border areas, border economic cooperation zones, and cross-border economic cooperation zones, and support the efforts of Ningxia, Guizhou, and Jiangxi in developing inland opening-up pilot economic zones.
III. Improving the regional opening-up structure
We will encourage all regions to expand opening-up to the outside world based on their comparative advantages; boost inter-regional connectivity in opening-up; and bring about a new pattern of all-round two-way opening-up with links running eastward and westward over land and sea. We will consolidate the leading position of the eastern coastal areas and mega cities in opening-up, so that they can take the lead in promoting all-round and high-standard opening-up. We will accelerate the pace of opening-up in the central and western regions and the northeast, support them to undertake domestic and foreign industrial transfer, foster major global processing and manufacturing bases and new growth poles, and consider the establishment of national first-class ports in inland areas, to fuel the development of inland areas and push them to the forefront of opening-up. We will promote high-quality border development and opening-up, accelerate the innovative development of border trade and give better play to the role of key ports and border cities as links between domestic and foreign areas. We will support Guangxi in developing itself into a highland of opening-up and cooperation with ASEAN, and Yunnan into a center of opening-up towards South and Southeast Asia and the Indian Ocean Rim.
IV. Improving the opening-up security system
We will build a regulatory and risk resistance system in line with a higher standard of openness, properly cope with economic and trade frictions by improving the early warning system for industrial damage, and enrich policy instruments covering trade adjustment assistance and trade relief. We will improve the foreign investment national security review system, anti-monopoly review system, national technical security list management, and unreliable entity list. We will establish an early warning system for global supply chain risk for important resources and products and strengthen cooperation in international supply chain support. We will intensify the monitoring of the international balance of payments to maintain its basic equilibrium and the basic stability of foreign exchange reserves. We will intensify the monitoring of external assets and liabilities and establish and improve the system of unified supervision of external debts. We will improve the classified and graded supervision system for overseas investment and build a system for overseas interest protection, risk early warning, and risk resistance. We will enhance the infrastructure support capacity of overseas diplomatic agencies and improve the institutions and mechanisms for consular protection, to safeguard the security and legitimate rights and interests of Chinese citizens and institutions overseas.
Chapter 41 Joint Pursuit of the Belt and Road Initiative
We will follow the principle of extensive consultation, joint contributions, and shared benefits, adhere to a vision of green development, openness, and clean governance, and step up efforts for practical cooperation, security assurance, and common development.
I. Development strategy and policy alignment
We will promote alignment between strategies, plans, and mechanisms, as well as connectivity between policies, rules, and standards. We will explore new alignment methods, promote the effective implementation of signed documents and negotiate and sign agreements on investment protection, double taxation avoidance, and other affairs with more countries, enhance cooperation in customs, taxation, and regulation, and promote the implementation of a higher-standard integrated customs clearance. We will expand the areas of policy connectivity and strengthen cooperation for policy alignment in financing, trade, energy, digital information, agriculture, and other sectors. We will enhance complementarity and synergy between the BRI and regional and international development agendas.
II. Infrastructure interconnectivity
We will promote integrated connectivity that comprises land, sea, air, and cyber links, build a connectivity framework featuring "six corridors, six routes, and multiple countries and ports”, and on this basis, develop a connectivity network dominated by the New Eurasian Land Bridge and other economic corridors, propped up by the China-Europe Railway Express, the new land-sea corridor, and other large corridors and information highways, and supported by railways, ports, and pipe networks, and we will create a new international land-sea trade corridor. Focusing on key corridors and cities, we will promote the construction of major cooperation projects in an orderly manner, and comprehensively integrate high quality, sustainability, risk-resistance, reasonable pricing, inclusiveness, and accessibility goals into the projects. We will improve the operation of China-Europe Railway Express and promote the formulation of rules on international land transportation and trade. We will expand the influence of the “Maritime Silk Road” as a brand, advance the building of Fujian and Xinjiang into the core areas of the Belt and Road, develop the space information corridor of the BRI, and build the “Air Silk Road”.
III. Further practical cooperation in economy, trade, and investment
We will enhance trade and investment cooperation with countries within the framework of the BRI and actively develop Silk Road e-commerce. We will deepen international cooperation on production capacity, expand the third-party market cooperation, build a system for win-win cooperation on industry and supply chains, and expand two-way trade and investment. We will continue the enterprise-based and market-oriented development and follow international practices and the principle of debt sustainability to improve a diversified investment and financing system. We will explore a new framework for financing cooperation and leverage the roles of special loans and Silk Road Fund for the joint pursuit of the BRI. We will establish and improve the BRI financial cooperation network, promote the interconnectivity of financial infrastructure, and support multilateral and international financial institutions to participate in investment and financing. We will improve the risk resistance and security support system of the BRI and enhance legal service support to effectively prevent and defuse various risks.
IV. Building a bridge for exchanges and mutual learning among civilizations
We will deepen cultural and people-to-people exchanges in public health, digital economy, green development, science and technology, education, culture and arts, and other fields. We will enhance exchanges among parliaments, political parties, and non-governmental organizations, bring about close communication among women, the youth, people with disabilities, and other groups, to form a pattern of multi-dimensional and interactive people-to-people exchanges. We will advance the implementation of the BRI Science, Technology, and Innovation Cooperation Action Plan, and build the digital Silk Road and the innovative Silk Road. We will strengthen exchanges and cooperation in addressing climate change, marine cooperation, wildlife protection, and desertification control, and develop the green Silk Road. We will vigorously cooperate with countries in the framework of the BRI in healthcare and the prevention and control of infectious diseases and build a healthy Silk Road.
Chapter 42 Participating in the Reform and Development of the Global Governance System
We will uphold the principles of peace, development, cooperation, and mutual benefit, remain firm in pursuing an independent foreign policy of peace, promote the development of a new type of international relations, and make the global governance system more just and reasonable.
I. Multilateral economic governance mechanism
We will maintain the multilateral trade system, actively participate in the reform of the World Trade Organization (WTO), and resolutely safeguard the status of the would-be members of the organizations. We will push the G20 to play its role in international economic cooperation, and we will play a constructive role in cooperation on economic governance among APEC, BRICS, and other mechanisms, and put forward more China initiatives and China programs. We will promote the deepening of governance reform in major multilateral financial institutions, support the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank and the New Development Bank to play a better role, and enhance their ability to participate in international financial governance. We will promote communication and coordination of international macroeconomic policies, build a platform for international cooperation, work together to maintain the stability of global industry and supply chains and global financial markets, and join forces to promote world economic growth. We will promote the formulation of rules on economic governance in emerging sectors.
II. A network of high-standard free trade zones
We will implement the strategy of upgrading free trade zones and build a global network of high-standard free trade zones. We will optimize the layout of the FTZs, promote the implementation of the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) Agreement, accelerate the negotiation process of the Free Trade Agreement (FTA) between China, Japan, and ROK, and steadily promote the building of the Free Trade Area of the Asia-Pacific (FTAAP). We will raise the standards of the development of FTZs, consider joining the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) and promote the negotiation and signing of agreements on even more high-level FTAs and regional trade.
III. A sound external environment
We will proactively develop global partnership, promote coordination and cooperation among major countries, strengthen relations with neighboring countries, and advance unity and cooperation with developing countries. We will adhere to multilateralism and the principle of extensive consultation, joint contributions and shared benefits, and safeguard the international system with the United Nations as the core and the international order based on international law, to jointly cope with global challenges. We will actively participate in international cooperation in the prevention and control of major infectious diseases and promote the building of a global health community. We will expand efforts to reform the institutions and mechanisms of foreign aid, improve the distribution of foreign aid, do our best to aid developing countries, especially the least developed countries, and strengthen foreign cooperation and assistance in the fields of healthcare, science, technology, education, green development, poverty alleviation, human resource development, and emergency humanitarian assistance. We will actively implement the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development of the United Nations.
Part XIII Promotion of Human Development
Promoting human development is a top priority. To this end, it is crucial to improve the quality of education and healthcare for all. Also important is how to guide the evolvement of the population structure with the aim of maximizing the human development dividend and boosting human capital in an overall effort to improve the people’s wellbeing.
Chapter 43 Quality Education for All
Guided by the Party’s education policy, development of education remains high on our agenda. Education includes character education and civil education that cultivates a sense of social responsibility in addition to practical skills to pave the way for moral, intellectual, and physical growth, so that our students will grow into effective contributors to socialist prosperity.
I. Equitable access to basic public education
Building on what has been achieved in balanced compulsory education is an imperative, which calls for improving education standards, with a focus on developing high-quality, well-balanced, and integrated compulsory education in both urban and rural areas. Urban schools need to expand capacity to ensure access to basic public education for children who have moved with their parents from rural to urban areas. Efforts will be ongoing to improve conditions in small rural schools and boarding schools in towns and townships, build a large team of competent rural teachers dedicated to helping rural children move ahead, and continue to reduce dropout rates. Universal access to high-school education is another area of focus. Special attention will be paid to the need to diversify education at the high-school level and to raise the gross enrollment ratio to over 92%. Regulation of after-school academic programs will be strengthened. More support will be provided to publicly accessible preschool education, and a goal of raising the gross preschool enrollment ratio to over 90% is envisaged. Support will also be provided to special education and special programs for children who have run-ins with the law. Efforts will be stepped up to improve the quality and effectiveness of education in ethnic minority areas to enhance the mastery of the national official language.
II. Adaptable vocational and technical education
Reform and innovation are needed to improve different types of vocational and technical education by leveraging the special strengths of each program and better structuring the vocational and technical education services and through more rational deployment of resources in this field with a view to better training technicians and skilled workers. Revision of national standards for vocational and technical education is necessary to complement academic certification with vocational certification. Innovative approaches should be explored to better align classroom education with real world needs, expand cooperation between businesses and education institutions, encourage involvement of businesses in providing high-quality vocational and technical education, and develop apprenticeship programs that suit China’s needs. Improving the quality of modern vocational and technical education will be an ongoing focus with plans to build a group of top-notch vocational and technical colleges and programs and steadily develop career-focused undergraduate education in a move to further integrate vocational and general education, encourage mutual recognition of vocational qualifications and academic degrees, and provide opportunities for students in vocational education to receive general education.
III. Quality higher education
Category-based management is needed for higher education and comprehensive reform is needed for higher education institutions, so as to diversify the higher education system with an aim of seeing the gross enrollment ratio rise to 60%. First-class universities and academic disciplines will be built on a categorized basis. Support will be provided for developing top-notch research universities. Quality of undergraduate education will be improved by encouraging a number of regular undergraduate institutions to become applied colleges. Reform of high-level talent training in basic academic disciplines will be facilitated by adjusting academic disciplines and programs that suit the needs and giving play to their strengths to provide more targeted disciplines, so that the gaps in scientific, engineering, agricultural, and medical personnel can be filled. Efforts will be made to better manage and improve postgraduate program, as well as admit more applicants for professional postgraduate degrees. Higher education in the central and western regions will be revived by optimizing the distribution of higher education resources.
IV. Teacher competencies
A high-standard modern teachers education system is needed, focusing on strengthening the professional ethics and competence of teachers, improving the policies for teacher management and development, and enhancing teachers’ capacity to impart knowledge and cultivate students. Priority will be given to establish a batch of teachers education bases, support quality comprehensive universities to carry out teachers education programs, improve the government-paid education for normal school students, and exempt graduate students of education programs and government-funded normal school students from applying teacher certificates through examinations. Support will be provided to top-notch engineering universities to train teachers for vocational and technical education. And universities, vocational schools, and enterprises will be encouraged to jointly train teachers qualified both in delivering theoretical knowledge and guiding practice. Measures will be taken to deepen the management of teachers in primary and secondary schools and kindergartens, including making plans for the overall and regional distribution of budgeted posts, ensure that teachers working in compulsory education are regulated by county-level authorities and employed by schools, and appropriately raise the proportion of middle-ranking and senior teachers.
V. Education reform
To enhance students’ well-rounded development, with a focus on patriotism, sense of innovation, and healthy personality, it is needed to deepen education evaluation reform in the new era by establishing sound education evaluation systems and mechanisms. Remained as a not-for-profit cause, education will see more funds, an improved system for fund management and fund use, and an increase in fund use efficiency. Action related to school running include ensuring that schools have a greater say, improving internal governance structure, and guiding the private sector to participate running school in an orderly manner. Comprehensive reform is needed for examination and enrollment, with the focus on supporting and regulating private education and encouraging high-standard learning institutions and programs jointly run by Chinese and overseas institutions. The advantageous online education will be integrated into the lifelong learning system, and help build a learning society. Other education related measures include encouraging top-notch universities to provide open access to their educational resources, providing opportunities for registered learning and flexible learning, and smoothing the channels of mutual recognition and conversion of different types of learning achievements.
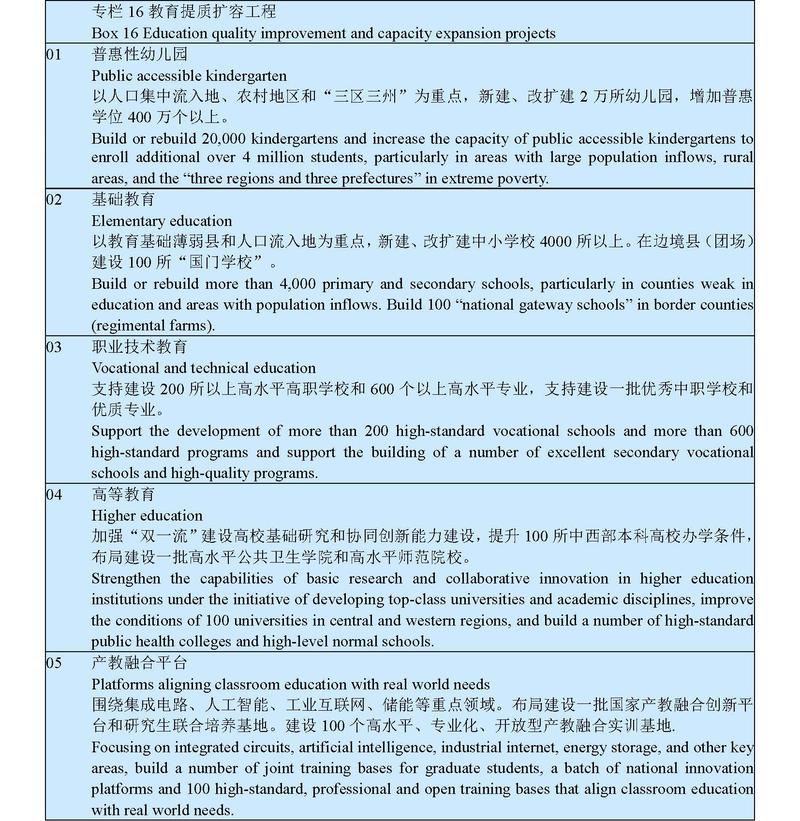
In a strategic move to improve health and wellbeing for all, the Healthy China Initiative has been rolled out with an emphasis on prevention. As a national health policy, it aims to strengthen national public health network and provide healthcare for all.
I. A robust public health system
Healthcare reform aims to improve disease prevention and control and strengthen, in particular, a system for health monitoring and early warning, risk assessment, epidemiological investigation, inspection and detection, and emergency response. More predictable public funding for healthcare is envisaged to enhance essential disease control measures and community-level public healthcare. Public accountability for medical institutions will also be enhanced. Innovative approaches to integrating prevention and treatment are encouraged. Efforts to strengthen public health emergency monitoring, early warning, and response mechanisms are ongoing, including measures to build a robust laboratory testing network, and improve patient care, technological support, and logistics support. A tired, multi-level, and referral-based infectious disease treatment network will be built, so will a unified national system of reserves of essential supplies for public health emergencies. Modifications to large public buildings are underway to better accommodate the needs for epidemic control. Infectious disease screening at ports of entry has been stepped up. Other measures in this connection include more support for public health colleges and talent development; expansion of national vaccination plans; chronic disease prevention, early screening, and comprehensive intervention; and mental health services and psychosocial support.
II. Healthcare reform
Efforts will be made to continue to provide non-for-profit healthcare. With a focus on improving medical treatment quality and efficiency, more resources will flow to medical services, mainly in public medical institutions followed by non-public ones. A modern hospital management system is imperative for public medical institutions, which calls for reform in governance structure, staffing and remuneration, budgeted posts management, and performance appraisal. National and regional medical centers will be built to accelerate the expansion and balanced regional distribution of quality medical resources. Special attention will be paid to developing community-level healthcare workforce, especially in urban and rural communities, border and port cities, and county-level hospitals to improve the medical services network in urban and rural areas. Medical consortia are needed for tired diagnosis and treatment, as well as ensuring the coordination of prevention, treatment, nursing, and rehabilitation. Reform will be rolled out in state-organized centralized procurement and use of medicines and medical consumables, in particular high-end medical equipment. The rapid evaluation and approval mechanism will be improved for innovative medicines, vaccines, medical devices, and targeting medicines and medical devices in urgent need for clinical use and for treating rare diseases, allowing for as quickly as possible the domestic marketing of those that are already available in overseas markets. Measures will be taken to improve the quality and scale of healthcare personnel, including addressing the gaps in pediatricians, general physicians, and other physicians; increasing the number of registered nurses per 1,000 people to 3.8; implementing a regional registration system for physicians which can make it convenient for them to provide services in multiple institutions; expanding the coverage and improving the quality of contracted family doctor services in urban and rural areas; supporting private hospitals and encouraging experienced physicians to run clinics.
III. Universal medical insurance
Efforts will continue to ensure stable and sustainable funding for basic medical insurance and adjust medical benefits by revising payment policies for medical insurance premiums and developing lists for medical benefits. Overall planning of basic medical insurance shall be made at the municipal and provincial levels. Improvement measures are needed for the general support mechanism for covering outpatient medical bills under employee basic medical insurance and the system of medical insurance and aid for treating serious diseases. It is necessary to make timely adjustments to the catalogue of medicines covered by medical insurance. A diversified, compound medical insurance payment model based on disease-related payment is under way. Qualified internet-based medical services will be made reimbursable under the medical insurance plan. Medical bills incurred in any locality will be settled through basic insurance accounts. Solid progress will be made in setting standards for medical insurance and applying information technology, so as to improve insurance services. Efforts are ongoing to better supervise medical insurance funds to ensure a long-term care insurance system. Commercial medical insurance will be encouraged.
IV. Development of and innovation in traditional Chinese medicine
Equal importance will be attached to traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and Western medicine. While making good use of their complementary advantages, special support will be provided to TCM. A sound TCM service system is needed to give full play to TCM’s unique strengths in disease prevention, treatment, and rehabilitation. TCM and Western medicine will be better integrated. And efforts will be made to develop medicine of ethnic minority groups. In this regard, measures aiming to develop and protect new medicines include conducting research on the essence of Chinese medical classics, building scientific and technological support platforms for TCM, reforming and revising the TCM evaluation and approval mechanisms. A stronger supervision system is important for quality Chinese medicines. Efforts are ongoing to foster specialists in TCM to better inherit and innovate TCM culture. With all these endeavors, TCM will go global.
V. A country strong in sports
The nationwide fitness-for-all campaign is needed to improve the people’s health. Efforts on health maintenance and disease prevention will be initiated at earlier stages through integrating sports and education, sports and healthcare, and sports and tourism. A sound public service system for fitness and sports requires more publicly accessible sports venues and facilities as well as school stadiums, for example, more fitness trails and other easily accessible fitness facilities, sports parks that suit local conditions, and public sports facilities on river fronts that do not affect flood control. A national physique monitoring and intervention program is underway, particularly among teenagers to ensure physical education classes on campus and extracurricular exercise hours. Regarding competitive sports, equal emphasis will be put on both academic education and professional training, and efforts will be made to increase the talent reserve for competitive sports, improve the competitive strength of athletes in key events, and maintain China’s dominance in sports it traditionally does well in. Other measures in this connection include exploring pathways for the development of football, basketball, and volleyball with Chinese characteristics, continuing to promote winter sports, and organizing internationally influential professional sports events. Fitness, recreation, outdoor sports, and other sports industries will be developed to encourage sports consumption. Works will be done to ensure the success of the 2022 Winter Olympics and Paralympics in Beijing, and the 19th Asian Games in Hangzhou.
VI. Patriotic health campaigns
More diversified patriotic health campaigns will be carried out to encourage the public to lead a positive and healthy lifestyle. More support will be provided for infrastructure construction to ensure a good public health environment in urban and rural areas that meets hygiene standards and vector control requirements. Efforts will be ongoing to foster healthy towns. Health education and health knowledge will be more accessible, with a focus on encouraging good eating habits, opposing food and beverage waste, facilitating tobacco and alcohol control, putting an end to bad habits such as eating wild animals, and promoting the practice to order single portions of food in restaurants, use serving chopsticks, and conduct garbage sorting.
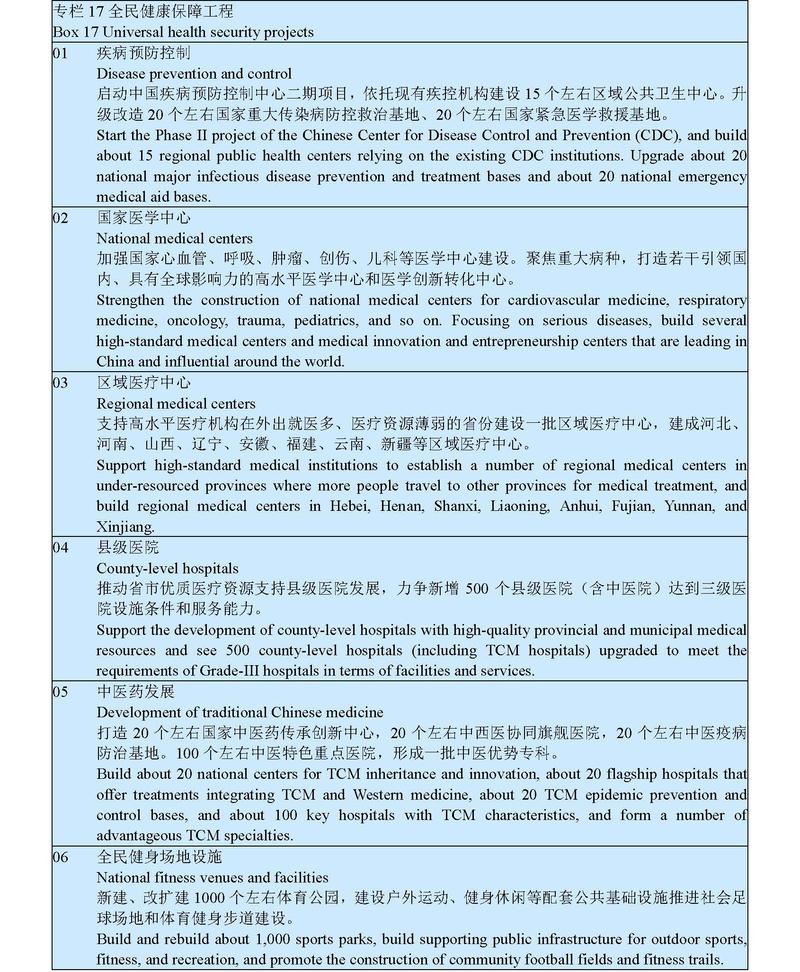
Chapter 45 A National Strategy in Response to Population Aging
A long-term population strategy will be developed, including revised childbirth policies, to promote long-term and balanced population development and improve population services with a focus on elderly care and child care.
I. An appropriate birth rate
Revised childbirth policies are more inclusive and will be implemented in tandem with economic and social policies to reduce the burden of child bearing, upbringing, and education on families, with potential spillover benefits. At the same time, efforts will continue to improve infant care, youth development, support for the elderly, and care for the sick and disabled, implement the maternity leave policy, and explore the possibility of mandating parental leave. A full range of services for maternal care, including preconception and postnatal care, and child development will be made available and easily accessible, to improve the health and wellbeing of the newborn population. Support will be provided to families facing special difficulties for the loss or disability of their only children. Related actions include improving population data collection and analysis, monitoring population trends, especially birth rate changes, and conducting research on population issues from a strategic perspective to inform decision-making with regard to population and development.
II. Infant development policies
Child care services will be made publicly accessible relying on improved policies for infant and child care services and childhood education. More support and guidance will be provided to at-home care and community services, with an aim to enhance scientific parenting. Supporting kindergartens will be set up in urban communities, as part of the effort to diversify infant and child care service institutions. Other measures include encouraging capable employers to provide infant and child care services, supporting enterprises, public institutions, social organizations, and other non-governmental forces to provide public accessible child care services, and encouraging kindergartens to incorporate child care services into their service system. Also important is to provide professional and standardized infant and child care services so as to ensure the quality and competence of care and education.
III. Elderly care
Efforts will be made to coordinate elderly care programs and elderly care industries, improve the basic elderly care service system, make elderly care services more publicly accessible, and support at-home elderly care, so as to build an elderly care service system that coordinates home care and community services and integrates medical care and health care. The network of community-based, at-home elderly care services will be improved, supported by elderly-friendly public facilities, services from professional institutions, and idle resources for community-embedded elderly care. Subsistence allowances will be provided for disabled and partially disabled elderly people in extreme poverty. Rural happiness homes and other forms of mutual-aid elderly care will be developed. Reform will be rolled out in state-run elderly care institutions to improve their service capacity and quality. The government-enterprise joint campaign for public accessible elderly care will be launched, among which the private sector are encouraged to run government-funded elderly care institutions, training and recuperation institutions are welcomed to reorient to offer elderly care services, and policy support will provided for private nursing care institutions for the elderly. Medical care and health care will be better integrated to improve health services for the elderly. Talent training for elderly nursing will be intensified. The supply of nursing beds in elderly care institutions will be increased, with an aim to raise the proportion to 55%, so as to better meet the nursing service needs of the elderly with disability and dementia. Steadily, the welfare of the elderly will be improved, with a sound subsidy system for the disabled elderly with financial difficulties, and the visit and care system for the disabled elderly with special difficulties left behind in rural areas. The comprehensive regulatory system for elderly care services is needed for a social environment in which the elderly are respected and cared for, and live happily, and in which their rights and interests are ensured. By taking into account the increase in life expectancy per capita, the accelerated population aging trend, the increased education years, the change of labor force structure, and other factors, and in accordance with the principles of implementing flexible, tailored policies for different groups, considering all factors, and making overall plans, the statutory retirement age will be raised in a phased manner to give full play to the potential of human resources. The silver economy is emerging, requiring elderly-friendly technologies and products and smart elderly care services and other new business models.

Part XIV A Focus on the People's Wellbeing: a Participatory Approach
Basic public services are essential to improving the wellbeing of our people. Best efforts will be made within the limits of the available resources to upgrade and expand these services to ensure universal access and inclusiveness, so that the people's essential needs are met and no one is left behind. Public participation in governance will be encouraged to promote collaboration and synergy in building shared prosperity. An action plan for shared prosperity will focus on narrowing the development gap between different regions and between urban and rural areas, as well as the income gap between rich and poor households, so that development gains will benefit everyone in a fair manner, and help create a greater sense of fulfillment, happiness, and security.
Chapter 46 National Public Services
It is crucial to improve the quality and standards of public services by addressing weaknesses in both basic and non-basic public services.
I. Equitable access to basic public services
Efforts will be made to ensure that comparable quality basic public services are provided in both urban and rural areas and across regions. National standards and benchmarks will be developed and/or readjusted, wherever and whenever necessary, against which provision of public services, including public education, employment and entrepreneurship development services, social insurance, healthcare, social services, housing, culture and sports, veteran services, and disability services, among others, is evaluated to ensure the uniformity of standards being applied and equity in service delivery in urban and rural areas and across different regions. Deployment of basic public services will be based on the area and number of residents to be covered. More resources will be made available at the community level and deployed to rural areas and remote areas to help, in particular, disadvantaged groups and individuals.
II. Innovative public service delivery
By distinguishing basic public services from non-basic public services, it is crucial to highlight the government’s dominant role in guaranteeing the supply of basic public services and welcome diverse providers and methods of non-basic public services. In child care, elderly care, and other services that see the prominent imbalance between supply and demand, support will be provided for the private sector to supply more public accessible and standardized services by various means, including running government-funded institutions, government procurement of services, and public-private partnership, and ensure that all providers of such services enjoy equal preferential policies. Deepened reform is needed for public institutions to provide public services, so they could compete in the market with the private sector in a fair manner.
III. Policies to support public services
An optimized structure of government spending will give priority to the funding for addressing weaknesses in basic public services. In the field of public services, the respective fiscal powers and expenditure responsibilities of central and local governments will be defined, with increasing financial support from the central and provincial governments to local governments in providing basic public services. More public service programs will be included in the list that guides government procurement of services, to encourage an increase in government procurement and improved preferential policies on fiscal funding, financing, and land use. Private and public institutions will enjoy fair treatment in qualification access, professional title appraisal, land supply, financial support, government procurement, and supervision and management, among other aspects.
Chapter 47 An Employment-First Strategy
Effective measures will be taken to create more employment opportunities, especially high-quality jobs, and overcome any structural barriers to job creation.
I. Policies to encourage employment creation
Economic development must be employment-oriented. Mechanisms will be established to assess whether employment targets are met and how employment is impacted. Employment support for college graduates, veterans, migrant workers, and other key groups will remain a priority. Policies will be devised to encourage businesses to create employment opportunities, provide support for businesses that employ a large number of people, such as service industries, MSMEs, and labor-intensive enterprises, and expand job opportunities in community supermarkets, convenience stores, and community services. Measures will be taken to promote equal employment, increase high-quality employment, support the growth of skill-intensive industries and the development of new forms of employment, expand government procurement in areas such as primary-level education, medical care, and specialized social services, encourage entrepreneurship as a way to create jobs, bolster flexible employment through multiple channels, remove any restrictive policies that hinder job creation, and make the labor market more inclusive. Urban and rural employment policies will be better aligned to ensure mutual complementarity, and more support will be available to rural workers in their search for jobs. More public welfare jobs will be created and special support will be provided to people having difficulty finding employment, especially people with disabilities and members of families without a single bread earner.
II. Public employment services
More support will be provided to the community-level public employment and entrepreneurship service platforms which offer free policy consultation, job introduction, and employment guidance for employees and enterprises, so as to improve the public employment service system covering both urban and rural areas. A regular mechanism assisting enterprises to stabilize employment will be established by making good use of employment subsidies and unemployment insurance funds. Efforts will be made to coordinate both ends of labor transfer to realize cross-regional connectivity. Measures to protect labor rights and interests include improving the labor contract system, the labor relations coordination mechanism, the long-term mechanism for controlling arrears of wages, and the labor dispute mediation and arbitration system, and exploring ways to protect the labor rights and interests of employees under new business models. Progress will be made in the employment demand survey and unemployment monitoring and early warning mechanism.
III. Development of employability skills and entrepreneurship
As part of the effort of the lifelong skills training system, continuous vocational skills training will be carried out on a large scale, including campaigns to improve vocational skills, targeted training programs for key groups, extensive skills training for employees working in new forms and models of business, with a focus on improving training quality. Funds will be coordinated and used in innovative ways for vocational skills training programs at all levels and of all types, with the aim to ensure that training subsidies are channeled directly to enterprises and participants. Through improved policy on pre-tax deductions for training funds, enterprises will be encouraged to launch training programs to improve the skills of their employees. Other measures in this connection include supporting demand-based and customized training, establishing a batch of public training bases and bases that align classroom education with real world needs to promote the contribution and sharing of training resources, and ensuring the success of national competitions on vocational skills.
Chapter 48 Improving the Income Distribution Structure
It is important to ensure that personal income grows in step with economic growth and that workers’ compensation rises in tandem with the increase in labor productivity. It is also important to continue to increase the income of low-income groups while expanding the size of the middle-income group in an effort to bring prosperity to all.
I. More opportunities to increase income
The system in which distribution according to work is dominant and a variety of modes of distribution coexist will see an increase in the proportion of labor remuneration in the primary distribution. To better decide and increase wages, as well as secure the payment, it is needed to improve the mechanism for developing the minimum wage standard and wage guidelines, and determining wages through collective discussion. Efforts will be made to improve the mechanism whereby remuneration for various factors of production is determined by the market, and explore ways to increase the income of low-and-middle-income groups through their rights to use and benefit from land, capital, and other production factors, so as to improve distribution policies and systems based on production factors. In state-owned enterprises, the market-oriented salary distribution mechanism will be improved, and the performance-based evaluation system of employees will be implemented across the board. In public institutions, reform aims to improve the salary system to reflect job performance, position level, and job category. Standards will be set for labor dispatch and employment to ensure equal pay for equal work. More channels will be opened to increase the property income of urban and rural residents, including raising the proportion of farmers’ share in land value-added revenue, improving the dividend system of listed companies, and developing more innovative financial products to meet the needs of family wealth management. The system by which state capital gains are turned over to public finance will be improved so as to increase public spending in people’s wellbeing.
II. Expanding the rank of middle-income earners
An initiative to expand the rank of the middle-income earners and consistently increase its proportion will be launched, with the focus on graduates from regular universities and vocational schools, skilled workers, and migrant workers. Support will be provided for graduates from universities and vocational schools to help them find jobs, in particular those suiting their academic background. Efforts will be made to offer more opportunities for skilled workers, especially those in non-public economic organizations, social organizations, and freelance professionals and technicians, to apply for professional titles and qualification certificates for promotion, raising their benefits and social status. A program to develop competent farmers will be launched to help them use agricultural and rural resources and modern operation methods to increase their income. Policies will be devised to support small and micro startups, and support groups such as self-employed individuals and workers in flexible employment, to embark on the journey of prosperity through hard work.
III. A more rational wealth and income redistribution mechanism
The distribution pattern of income and wealth will be improved, benefiting from more intense and accurate adjustments to taxation, social security, and transfer payments, and the role of charity in the third distribution. Measures will be taken to advance the direct tax system by improving the system for taxing personal income on the basis of both adjusted gross income and specific types of income, and strengthening tax regulation and supervision of high-income individuals. With dynamically adjusted standards in response to the basic needs, social security benefits and services will become fairer and more accessible. The income distribution order will be well-regulated to protect legitimate income, regulate excessive income in a reasonable manner, ban illegal income, and curb income obtained by means of monopoly and unfair competition. A sound system of information on personal income and property will be established and the modern payment and income monitoring system will be perfected.
Chapter 49 A Multi-Tiered Social Security System
Our bottom line is to protect the most vulnerable, expand social security coverage, and improve protection mechanisms to prevent anyone from being left behind. To this end, it is essential to build a sustainable, multi-tiered universal social security system with integrated urban and rural coverage, and with clearly defined rights and responsibilities for all actors involved.
I. Social insurance
The old-age insurance system will be improved to ensure the long-term balance of basic insurance funds. The coordinated national management of basic old-age insurance funds will be achieved. Restrictions preventing workers in flexible employment from participating in the insurance system will be reduced. Social insurance will cover the entire legally eligible population. The system for transferring state capital to increase social security funds will be improved to upgrade and strengthen social security strategic reserve fund. Adjustments to the basic pension for urban workers will be more reasonable, leading to a raising pension standard for urban and rural residents. A multi-tiered and multi-pillar old-age insurance system will take shape, which will see an increase in the coverage ratio of enterprise annuity, and the well-regulated private pensions as the third pillar. The coverage of unemployment insurance and work-related injury insurance for professional workers will be expanded, and relevant plans will be made at the provincial level. Efforts will be made to promote the transfer and continuation of social security and improve the unified national platform on social insurance public services.
II. Social assistance and charity
The tiered and classified social assistance system will be perfected, with the focus on urban and rural recipients of minimum subsistence allowances, people in special difficulties, and low-income families, so as to form a comprehensive pattern of assistance. A sound basic living assistance system and the special assistance system for medical treatment, education, housing, employment, and disaster victims, will be established, based on dynamic adjustments to criteria for assistance and the list of aid recipients. Temporary relief policies and measures will be taken to strengthen the functions of emergency social relief. We will coordinate the urban and rural relief systems, gradually allowing applicants to apply for and receive relief from the local governments of their permanent residence. Active actions will be taken to provide service-oriented social assistance and boost the government procurement of social assistance services. Philanthropy will be encouraged. Fiscal and taxation incentive policies will be improved, and standards will be set for online charity platforms to better management lottery and public welfare funds.
III. Veteran services and support
Regarding veteran affairs, efforts will be made to improve the organization and management system, work operation system, and policy system, so as to enhance the service and support for veterans. Further reform will be rolled out in the employment service system for veterans to help them find better jobs by providing greater support in terms of education, training, and employment assistance as well as by offering job opportunities in more diversified sectors. A new type of system for ensuring benefits to eligible groups will be established to improve and implement preferential treatment policies, appropriately raise the standards of benefits for veterans and other entitled groups, and make great efforts in job arrangement, household registration and education of their spouses and children. Measures will be taken to improve transfer, resettlement, treatment, and recuperation of veterans and disabled veterans, including developing service centers (stations) for demobilized veterans and improving the services and facilities of special care hospitals, glory hospitals, and military supply stations. Other related actions include strengthening convergence of the insurance system for ex-service members, carrying forward the spirit of martyrs, enhancing the construction, management, protecting memorial facilities for martyrs, building military cemeteries, and forming model cities (counties) of mutual support between the civilians and the military.
Chapter 50 Basic Rights and Interests of Women, Children, and People with Disabilities
Gender equality, child development, and disability care, among others, are key components of our national policy to protect the rights of disadvantaged groups, including women, children, and people with disabilities, and give them opportunities to thrive.
I. Gender equality and development of women
The Program for the Development of Chinese Women will be implemented for a continuously improved environment for women’s development, in which women are able to exercise their rights, participate in economic and social development, and benefit from the development outcomes on an equal basis in accordance with the law. Women’s access to health services will be ensured, in particular to comprehensive prevention and treatment of cervical and breast cancers and relevant relief policies. Women will be guaranteed to have equal right to education and see an increase in their number of years of schooling as well as their overall ability and quality. Women will be guaranteed to enjoy equal economic rights and interests, be free from gender discrimination in employment, and enjoy law-based maternity leave and maternity allowance. Rural women’s land rights and interests will be protected. Women will be guaranteed to enjoy equal political rights and largely participate in social affairs and democratic management. Mechanisms for assessing gender equality in laws and policies will be implemented. And the gender-specific data collection system will be improved. Efforts will be made to ensure quality care services for women left behind in rural areas, and crack down on illegal and criminal acts infringing upon the personal rights of women and girls.
II. Child development services and support
The China National Program for Child Development will be implemented for an enabling environment for children’s development, ensuring children’s rights to survival, development, protection, and participation. Improvements will be made to the children’s health service system, so as to prevent and control children’s diseases, reduce the incidence of children’s death and serious birth defects, control children’s obesity and myopia, and implement the nutrition improvement plan for preschool children. Measures will be taken to safeguard children’s right to equal access to education and strengthen education and services for children’s psychological health. Children suffering from difficulties will be under protection on a categorized basis, among whom the left behind children in rural areas will be under the care service system, and orphans and de facto unattended children under another protection mechanism. Other measures include implementing and improving the guardianship system for children, combating illegal and criminal acts that infringe on the rights and interests of children, and improving the comprehensive children protection system. With regard to the youth, the Youth Development Program will be implemented to promote the all-round development of young people, and build a platform for their growth and success to release their potential in innovation and starting businesses.
III. Family support services
The Happy Family program will be implemented, focusing on building civilized families, implementing scientific tutoring, and inheriting good family traditions. A legal and policy system to support family development will be built to promote the process of family education legislation, strengthen the implementation of the Anti-Domestic Violence Law, improve marriage and family counseling services, and prevent and resolve marriage and family conflicts and disputes. Family education guidance will be provided in urban and rural areas, and the mechanism of school-family-community cooperative education will be improved. Diversified family services will be provided. The role of families, family education, and family traditions in social governance at the community level will be given full play.
IV. Support for people with disabilities
The assistance system for people with disabilities will be improved to help them participate in the system of basic medical care and basic old-age insurance, and make dynamic adjustments to the standards of living allowances for the disabled in need and nursing subsidies for the severely disabled. Employment support will be offered to the disabled, including better protecting their labor rights and interests, prioritizing vocational skills training, and supporting them to start their own businesses. Full coverage of education for school-age disabled children and adolescents will be achieved with higher education quality. With regard to rehabilitation, efforts will be made to build universities, promote the market-oriented development of rehabilitation services, raise the application rate of rehabilitation assistive devices, and improve the quality of rehabilitation services. Care services will be offered for the severely disabled. Measures will be taken to provide the disabled with quality services and service facilities, including improving the policy system for the building and maintenance of accessible environment, and equipping families with disabled people with accessible facilities.
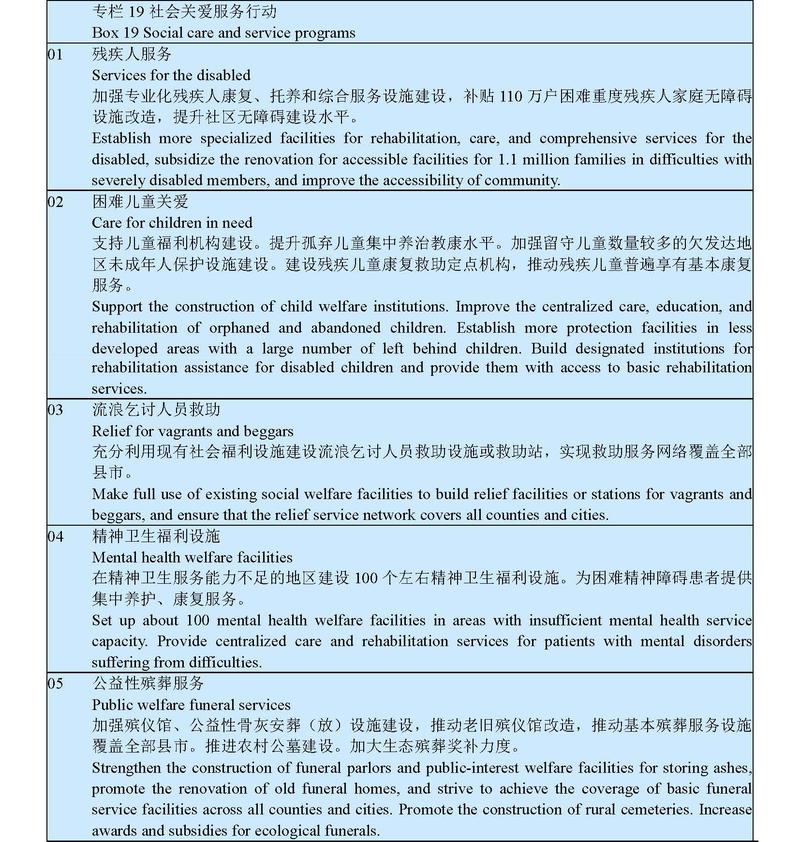
Chapter 51 Community-Level Participatory Governance
Community-level participatory governance will continue to be improved in urban and rural areas under the leadership of Party organizations with an emphasis on self-governance, rule of law, and ethical standards to facilitate public participation and community-level democratic consultation, so as to empower everyone to take ownership to contribute to the common good.
I. A framework for community-level participatory governance
The framework of community-level participatory governance will continue to be improved under the leadership of Party organizations, with village (neighborhood) committees playing the leading role and the people as the main participants. Efforts will be made to reduce the burden on the community-level, especially village-level organizations, i.e., clarifying the powers and responsibilities of local governments and community-level self-governing organizations in accordance with the law and including the clarified powers and responsibilities in urban and rural community governance in a list for functional departments of counties (districts) and townships (sub-districts) so that they can have a better idea of what they need or need not to do. The community-level self-governing organizations will be better regulated with reasonably defined functions, scale, and responsibilities. Mechanisms of community-level self-governance will be enhanced by improving the vehicles for self-governance such as village (neighborhood) people’s meetings, councils, and oversight committees to better organize and provide institutional channels for village (neighborhood) people to participate in the governance.
II. Community development and services
Efforts will be made to realize the downward shift of focus of participatory governance and services and channel resources down to the community level to provide well-targeted and refined services for the urban and rural community development. The community level will be allowed to have approval authority and address public service items, thus giving rise to an open and information-based system providing a gridded management model and better services for everyone. The system will achieve the integration and connectivity of the service scenarios for the convenience of residents, including employment and social security, elderly care, child care, disability assistance, health care, domestic services, logistics, supermarkets, public security and law enforcement, dispute mediation, and psychological assistance. With regard to building a team of full-time, professional community workers in urban and rural areas, the functions of neighborhood committees in urban communities will be improved, and owner committees and property service enterprises will be urged to perform their duties, so as to improve community property services and management.
III. Participation of non-governmental actors in community-level governance
The role of people’s organizations and social organizations, including market entities, new social strata, social workers, and volunteers in participatory governance will be given full play, through more smooth and well-regulated participatory channels. In this way, the vitality of community-level participatory governance is released across the board. Standards will be set for industry associations, chambers of commerce, public welfare organizations, and social organizations in urban and rural communities, accompanied with policy support and on-going and ex-post oversight on financial subsidies, service procurement, tax incentives, and talent protection. Support will be given to develop social work service institutions and volunteering organizations to expand the volunteer teams, build more platforms for voluntary services, and improve the voluntary service system.
Part XV An Integrated Approach to Development and Security
A holistic approach to national security calls for the integration of national security imperatives into every aspect of national development, so as to be better able to implement our national security strategy, safeguard national security, respond effectively to both traditional and non-traditional threats, and forestall any challenges to China’s modernization.
Chapter 52 National Security and Capacity-building
As part of the effort to protect our national interests, strengthening national security requires a holistic look at a full spectrum of security issues, ranging from political security, which is of overarching importance, the security of the people, which is the ultimate concern, and economic security, which underpins all other considerations, to military, scientific and technological, cultural, and social perspectives, which reinforce efforts in other areas. A centralized, unified, efficient, and authoritative leadership structure is indispensable in this connection, based on applicable laws, and supported by related strategies and policies, including those on talent development, as well as implementation mechanisms. National security legislation, systems and policies in key areas have to be strengthened. It is also important to strengthen the people’s line of defense against threats to national security, raise public awareness of national security issues, and improve mechanisms for assessing national security risks, and coordinating efforts to prevent, control, forestall, and fend off these risks. National security oversight will be enhanced, so will law enforcement in related areas. Challenges to state power, our political system, and our values will be confronted resolutely. Cyber security and capacity building in this field are a top priority. Robust measures will be taken to prevent and respond to infiltration, sabotage, and subversion by hostile forces.
Chapter 53 National Economic Security
Mechanisms for economic security risk early warning and prevention and control and related capacity building will be strengthened to keep under control risks to key industries, including food production, energy, and financial services, as well as critical infrastructure, strategic resources, and major technology facilities.
I. Food security
The supply of agricultural products will be ensured based on crop varieties. It is essential to improve the systems to guarantee the supply of major agricultural products and to the production, purchase, storage, marketing, and sale of grain, so as to ensure absolute security of staple food, basic self-sufficiency of grain, and adequate supply of major agricultural and sideline products. Efforts will continue to develop grain production, further implement the strategy of sustainable farmland use and innovative application of agricultural technology for national food security, break through the bottleneck of technologies in superior seed sources, and keep independent production of improved varieties under control. It is of great significance to guard against the red line of 120 million hectares of farmland and the control line of permanent basic farmland, which allows for stable and increased grain acreage and yield. It is also necessary to create an appropriate layout of regional emergency supply bases for agricultural products. In order to better regulate and control grain reserves, it is needed to deepen reforms for the purchase and storage of agricultural products, step up to diversify market participants, and reform and improve the central grain reserve management system. Provincial governors should assume responsibility for food security and mayors assume responsibility for the “vegetable basket”. Both Party and government leaders should take responsibilities. The grain conservation campaign will be ongoing to reduce the losses in grain production, storage, transportation, and processing. International cooperation on major agricultural products will be carried out to improve the mechanism for managing importing agricultural products, and diversify sources of import, thus creating an enabling environment for domestic large international grain merchants and agricultural conglomerate companies. The food security law will be enacted.
II. Energy and resource security
By focusing on domestic demand, addressing weaknesses, carrying out diversified guarantee measures, and strengthening reserves, we will improve the production, supply, storage, and marketing systems and enhance the ability of sustainable and stable energy supply and risk management and control, with the aim to ensure that basic coal supply is secure, that core oil and gas demand is met by domestic supply, and that power supply is stable and reliable. Building on domestic output, China will see a high and steady yield of crude oil and natural gas, and move ahead with the planned distribution and control of strategic coal-to-liquid and coal gas bases. Efforts will be made to expand the scale of oil and gas reserves and improve the oil and gas reserve system in which government reserves and corporate reserves for social responsibilities are combined and complementary to each other. The coal reserve capacity will be built. A system for energy emergencies management and control is needed to guarantee electric power supply for key cities and users, and better protect major energy facilities and networks. Diversified sources of importing oil and gas will secure the strategic channels and key nodes. A China-centric trading center and pricing mechanism will be established to promote home currency settlement. More support will be provided for the planning and control of strategic mineral resources to better secure reserves and put into effect a new round of strategic actions for breakthroughs in prospecting.
III. Financial security
The systems of financial risk prevention, early warning, disposal, and accountability will be established to ensure that the regulatory responsibilities and due responsibilities in places within jurisdiction are fulfilled, that we have zero tolerance towards violation of laws and rules, and that no systemic risks arise. Improvements will be made to the macro-prudential regulation system in order to keep the macro leverage ratio stable with a slight decline. Supervision of systemically significant financial institutions and financial holding companies will be enhanced, to reinforce the identification and disposal of non-performing assets, forestall and fend off shadow banking risks, dispose high-risk financial institutions in an orderly manner, crack down on illegal financial activities, and improve the long-term regulatory mechanism of internet finance. Efforts will be made to improve the mechanisms for identification, assessment, early warning, and effective prevention and control of debt risks, improve the mechanism for handling defaults in the bond market, promote unified law enforcement in the bond market, steadily resolve the implicit debt of local governments, and severely punish debt evasion and abandonment. A sound management framework of cross-border capital flow will be established to strengthen regulatory cooperation and enhance the ability of risk prevention and control as well as response under open conditions. By strengthening the RMB cross-border payment system, it is possible to ensure the security and controllability of core information technologies in the financial sector, and safeguard the financial infrastructure security.
The institutional mechanisms for public security will be improved, building on the principle that the people and their lives are above everything else, to implement the accountability and regulation systems for public security, and secure the people’s lives.
I. Workplace safety
It is needed for a sound workplace safety responsibility system to establish systems for the investigation of potential public safety hazards and for safety-oriented prevention and control. An accountability system for all-staff workplace safety in enterprises will be built, with an emphasis on ensuring enterprises to shoulder due responsibilities for workplace safety. Monitoring, early warning, supervision, and law enforcement concerning workplace safety are needed for campaigns to promote safety in key sectors such as hazardous chemicals, mines, construction, transportation, fire control, industrial explosives, and special equipment, and for the level-by-level supervision of the major hidden dangers treatment and effectiveness evaluation. Standards will be set for workplace safety in enterprises to strengthen safety management in industrial parks and other key areas. Innovative and advanced technologies and equipment will be applied in the fields such as deep mining and major disaster prevention. For example, workers doing dangerous jobs will be replaced by robots. Key areas will be under full coverage of workplace safety liability insurance.
II. Food and drug safety oversight
Efforts will be made to strengthen and improve the food and drug safety oversight system, including improving the food and drug safety laws, regulations, and standards, and exploring the establishment of a system of punitive compensation system for civil public interest lawsuits over food safety. The food safety strategy will be further implemented to strengthen oversight over the quality and safety of the entire food chain, advance the food safety assurance projects, and intensify joint efforts to address food safety issues in key areas. Measures need to be taken to prevent and control drug safety risks, including building the mechanism for lifecycle management of drugs and vaccines, improving the electronic drug tracing system, and realizing the whole-process traceability of drugs under key categories. Steady progress will be made to promote the system for unique labelling of medical devices. Stronger actions are needed for risk monitoring, random inspection, regulation, law enforcement, and rapid notification and response for food and drug safety.
III. Biosafety risk prevention and control
The system for biosafety risk prevention, control, and governance will be established to enhance national capacity of biosafety governance. The national systems for risk monitoring and early warning and for emergency plan on risk prevention and control concerning biosafety need improvements so as to release information in a unified manner for major biosafety incidents. Stronger prevention and control measures need to be taken for animal and plant epidemics and alien invasive species at ports. Overall planning for biosafety infrastructure will be made, including building a system of national biosafety data centers, and better developing and managing the system of high-level biosafety laboratories. Regulation on biosafety resources will be intensified by formulating and improving the catalog of human genetic resources and biological resources, and establishing a sound risk assessment mechanism of biotechnology research and development. The biosafety law will be put into practice. China will strengthen international cooperation on biosafety and take an active part in the development of international biosafety rules.
IV. National emergency management system
An emergency management system will be put into practice, featuring unified command, both specialized and regular operations, quick response, and coordination between the upper and lower levels, to systematically improve the national emergency management capacity and enhance the ability of disaster prevention, mitigation, resistance, and relief. Actions will be taken to improve the graded response mechanism at the central and local levels based on shared responsibilities with the local governments as main responsibility takers, and strengthen inter-regional and cross-basin coordination in disaster and incident emergency response. Based on investigation of potential risks and hidden dangers of disasters and incidents, we will implement public infrastructure safety and reinforcement projects and projects for enhancing the capacity of natural disaster prevention and control, and raise the standard for preventing and protecting against natural disasters including floods and droughts, bush fires and grassland fires, geological disasters, meteorological disasters, earthquakes, and so on. It is needed to build stronger national comprehensive fire brigades with enhanced rescue capacity for all types of disasters, and strengthen and improve the aviation emergency rescue system and capacity. Science-based adjustments will be made to the type, size, and structure of emergency supply reserves to improve the capacity of rapid deployment and emergency transportation. The system of information networks and comprehensive monitoring and early warning for emergency command will be built to ensure communication support for emergency rescue under extreme conditions. Catastrophe insurance are encouraged.
Chapter 55 Social Stability and Security
Contradictions among the people under the new situation will be properly handled to better maintain public order, and weave an all-round, three-dimensional, and intelligent social security net.
I. Resolution of social conflicts
Building on the “Fengqiao Experience” and its connotations in the new era, a comprehensive mechanism for social conflict resolution will be established, featuring prevention and control at the source, troubleshooting, dispute resolution, and emergency response. Smooth and regulated channels will be provided for people to express their needs, coordinate their interests, and protect their rights and interests. Improvements will be made to the joint work system of people’s mediation, administrative mediation, and judicial mediation. Diversified resolutions will be provided for conflicts and disputes, giving full play to the role of mediation, arbitration, administrative adjudication, administrative reconsideration, and litigation in preventing and resolving social disputes. A sound petition system will be implemented to provide law-based solutions to the people’s reasonable demands on the spot in a timely manner. Prevention and control of social risks and disputes will be better integrated. The social psychological service system and crisis intervention mechanism will be improved.
II. Crime prevention and control
The three-dimensional, law-based, specialized, and intelligent measures will be taken to maintain public order by combining the efforts of both professionals and the people, and preventing and controlling crimes through public participation. A working mechanism will be put into place to jointly tackle problems, work together, and put in efforts to create “Peaceful China”. In this way, a sound crime prevention and control system will take shape. Efforts will continue to carry out the people’s war against drugs and terrorism, combat organized crime and root out local criminal gangs on an ongoing basis, fight against all illegal and criminal activities, and enhance our ability to crack down on emerging cybercrimes and transnational and cross-regional crimes. Actions will be taken to identify and tackle potential problems in key areas for maintaining public order and improving the mechanism for coordinating crime prevention and control, by combining punishment and prevention, as well as integrating prevention and control. A intelligent big data platforms on public security will be built. Efforts are needed to improve the mechanism for checks and oversight over the exercise of law enforcement and judicial power, and improve the mechanism for safeguarding the rights and interests of law enforcement and judicial personnel. The crime prevention and control systems at ports will be established. And international practical cooperation on law enforcement and security will be deepened.
Part XVI Modernization of National Defense and the Armed Forces as We Build National Prosperity
Our efforts to strengthen national defense and the armed forces are guided by Xi Jinping’s instructions and the military strategy for the new era. The Party’s absolute leadership over the armed forces is of paramount importance. It is also important to raise political awareness among service members, implement necessary reforms, expand the use of new technologies, cultivate and harness talent, and create a rules-based culture. The modernization process involves mechanization, digitization, and the use of smart technologies, in addition to more rigorous and systematic military training to boost combat readiness. The process aims to enhance the ability of the armed forces to safeguard China’s sovereignty, security, and national interests, and ensure that the centenary goal of strengthening the armed forces is achieved by 2027.
Chapter 56 Modernization of National Defense and the Military
More will be done to accelerate the modernization of military theories and introduce new warfare and strategic guidance to keep abreast with the times, improve the military’s strategic system in the new era, and develop advanced combat theory. Efforts will be made to modernize our military’s organizational structure, deepen the reform of national defense and the armed forces, promote the revolution of military management, accelerate the transformation of military branches and armed police forces, expand the strategic forces and combat forces in new domains with new types of military personnel, build a high-standard strategic deterrence and joint operation system, and strengthen the joint training, joint support, and joint application of military forces. Steps will be taken to accelerate the modernization of military personnel, implement a military education policy that is suitable for the new era, improve the three-pronged training system for new military personnel, and forge a new array of high-quality and professional military personnel. We will also gather pace in the modernization of weaponry by focusing on independent and original innovation in defense-related science and technology, as well as the development of strategic, innovative and disruptive technologies, and accelerate the upgrade of weaponry and equipment as well as the development of smart weaponry and equipment.
Chapter 57 Strengthening National Defense in Tandem with Economic Growth
In coordination with the modernization drive of the country, we will build an integrated national strategic system and capacity by stepping up strategic planning efforts, promoting the sharing of resources and factors, coordinating policies and institutions, and improving organizational management, task fulfillment, policies and institutions, personnel training, and the risk control system. We will do better in balancing the development of key regions, key sectors, and emerging sectors, and focus on the implementation of major projects in the field of national defense. The planning of military development and that of regional economic development will be well coordinated to better serve the strategic needs for national security and development. We will boost military-civilian collaborative innovation in science and technology; advance both military and civilian development in the fields of ocean, aerospace, cyberspace, biology, new energy, artificial intelligence, and quantum science and technology; promote the resource sharing of military and civilian scientific research facilities; and facilitate the two-way application of military and civilian scientific research achievements and the development of key industries. We will boost the co-development and sharing of infrastructure, intensify efforts to plan for and develop new types of infrastructure, and do better in meeting national defense needs in economic development projects. Efforts will be made to speed up the development of a modern military logistics system and asset management system, intensify the joint training of people competent in both military and civilian services, and improve the systems for their exchange, employment, and qualification certification. We will improve the structure of defense-related science, technology, and industry, and accelerate the process of standardization and generalization. We will promote the reforms of market access for weaponry and equipment and air traffic management; improve the national defense mobilization system; coordinate efforts to respond to emergencies and meet challenges in wartime; improve the mechanism for strengthening the border defense; promote national defense education for all people; and consolidate the unity of the military, the government, and the people. We will safeguard the legitimate rights and interests of service members and their families and make serviceman a profession respected by the whole society.
Part XVII Socialist Democracy, the Rule of Law, and Party and State Oversight Mechanisms
We will uphold the unity of the leadership of the Communist Party of China (CPC), the running of the country by the people, and the rule of law, and push the socialist political system with Chinese characteristics to improve and develop.
Chapter 58 Socialist Democracy
Continued efforts will be made to improve the system where the CPC exercises overall leadership and coordinates the efforts of all involved, and ensure the CPC’s leadership in all fields and aspects of the country’s development. We will also uphold and improve the system of people’s congresses, strengthen the system for the people’s congresses to oversee the governments, the supervisory commissions, the people’s courts, and the people’s procuratorates, and ensure that the people engage in the management of state , economic, cultural, and social affairs through various channels and in various forms in accordance with the law. We will uphold and improve the system of multiparty cooperation and political consultation under the leadership of the CPC, promote the development of other political parties participating in state governance under Chinese socialism, further build the CPPCC as a special consultative body, leverage the unique advantages of socialist consultative democracy, and give better play to its role in offering advice to the government and building consensus. We will fully implement the the CPC’s policies concerning ethnic groups, uphold and improve the system of regional ethnic autonomy, create a strong sense of community for the Chinese nation, and encourage all ethnic groups to unite closely and work in concert for common prosperity and development. We will fully implement the CPC’s basic policy on religious affairs, uphold the principle of developing religions in the Chinese context, and actively guide religions to adapt themselves to the socialist society. We will improve the system of community-level self-governance, and increase the people’s capacity to manage their own affairs, serve and educate themselves, and exercise public scrutiny. We will give full play to the role of trade unions, Communist Youth League organizations, women’s federations, and other people’s organizations as bridges linking the CPC with the people. We will improve the united front with extensive participation of all political parties, promote harmony between political parties, between ethnic groups, between religions, between social strata, and between Chinese at home and overseas, and consolidate and develop greater unity and solidarity. We will fully implement the CPC’s policy on overseas Chinese affairs and pool the support of overseas Chinese to serve the big-picture interests.
Chapter 59 Promotion of the Rule of Law
We are fully committed to promoting socialist rule of law with Chinese characteristics. Efforts will be made to pursue parallel progress in the rule of law for national governance, exercise of state power, and government administration, promote the efforts to build a country, government, and society based on the rule of law, and implement the plan for promoting the rule of law in the country. Institutions and mechanisms will be improved to fully implement the Constitution, boost the implementation of the Constitution and oversight of constitutional compliance, put in place a mechanism for constitutional interpretation, and promote constitutionality review. We will improve the legislative institutions and mechanisms, advance legislation in key areas, emerging areas, and areas related to foreign affairs, lay equal emphasis on legislation, amendment, abolishment, interpretation, and compilation, and improve the socialist legal system with Chinese characteristics with the Constitution as the core. We will implement the outline for building a government based on the rule of law, uphold and improve the system of procedures for major administrative decision-making, deepen the reform of the administrative law enforcement system, see that law is enforced in a strict, standardized, fair, and civil way, regulate the use of discretionary powers in law enforcement, and promote reform of the administrative review system. We will deepen integrated, complete reform for the judicial system to improve the systems of judicial trials, of procuratorates, of punishment enforcement, and of lawyers, fully implement the judicial responsibility system, enhance the supervision over judicial activities, deepen reform of the enforcement system, and promote judicial justice. We will implement the outline for building a society based on the rule of law, foster a culture of socialist rule of law, promote publicity and education on the rule of law, implement the eighth five-year plan for increasing public knowledge of the law, and improve the public legal service system, legal aid, and national judicial assistance system. We will strengthen the judicial protection of human rights across the board and promote the all-round development of the cause of human rights. We will intensify efforts to build the legal system concerning foreign affairs and better train legal personnel on foreign affairs.
Chapter 60 Party and State Oversight Mechanisms
We will seek to improve the oversight system that features the CPC’s overall leadership, full coverage, and authoritative and efficient oversight and create a mechanism for exercising power that ensures sound decision-making, resolute enforcement, and effective oversight. We will ensure that leadership and oversight responsibilities for strict self-governance are properly assumed, enhance political oversight, advance political inspections, and intensify rectification efforts. More will be done to promote the coordination of oversight via disciplinary action, supervisory mechanism, dispatched resident teams, and inspections, and form a long-standing supervision synergy by leveraging the leading role of the intra-Party supervision and driving the coordination of all types of supervision, to better integrate the oversight systems into the national governance system. We will deepen the reform of the discipline inspection and supervision system, strengthen the leadership of the discipline inspection and supervision commissions at higher levels over those at lower levels, promote well-regulated and law-based discipline inspection and supervision activities, and give full play to the role of oversight in ensuring implementation and promoting improvement and development. We will improve the power allocation and operation restriction mechanisms, as well as the systems for exercising power by matter, setting power by post, delegating power in a graded manner and regular job rotation. We will improve the system of disclosures on Party affairs, government affairs, judicial affairs, and other fields; improve the mechanisms for finding problems, correcting deviations, and ensuring accurate accountability; and build full-coverage accountability and oversight systems. We will continue to ensure that there are no no-oversight zones, no ground is left unturned, and no tolerance is shown for corruption. We will strengthen deterrence so that officials do not dare to be corrupt, strengthen the oversight of institutions so they are unable to be corrupt, and strengthen their vigilance so they have no desire to be corrupt. We will put in every effort to ensure that our political atmosphere and development environment are clean and free of corruption. We will deepen international cooperation against corruption. We will make steady efforts to implement the central Party leadership’s eight-point decision on improving Party and government conduct, create a better long-term mechanism for improving conduct, continue to rectify the practice of formalities for formalities’ sake and bureaucratism, effectively prevent the resurgence of hedonism and extravagance, and resolutely combat corruption and unhealthy tendencies among people.
Part XVIII The Principle of "One Country, Two Systems" and National Reunification
We stay committed to lasting prosperity and stability in Hong Kong and Macao, and peaceful development of cross-Straits relations and national reunification, on our journey towards the great renewal of the Chinese nation.
Chapter 61 Lasting Prosperity and Stability in Hong Kong and Macao
We will stay true to the letter and spirit of the principle of “One Country, Two Systems”, which allows the people of Hong Kong and Macao to administer their own affairs with a high degree of autonomy. Rule of law must be maintained in Hong Kong and Macao, the two Special Administrative Regions (SARs), in accordance with the Constitution and the basic laws. The central authorities’ overall jurisdiction over the SARs cannot be challenged. The legal system and enforcement mechanisms for the SARs to safeguard national security must be implemented effectively to protect national sovereignty, security, national interests, and overall social stability in the SARs. Resolute actions will be taken to guard against and deter external interference in the affairs of Hong Kong and Macao. Support will be provided to the SARs in their efforts to enhance their competitive advantages and better integrate into the overall process of national development.
I. Support for the SARs’ endeavor to enhance their competitive advantages
We will support Hong Kong in enhancing its status as an international financial, shipping, and trade center and an international aviation hub, and strengthen its functions as a global offshore RMB business hub and an international center for asset management and risk management. We will support Hong Kong in building itself into an international center for innovation and technology, a center in the Asia-Pacific region for international legal and dispute resolution services, and a regional center for intellectual property trade. We will support Hong Kong’s endeavor to make its service sector more competitive in high-end markets and creating greater value, and its effort to develop itself into a center for cultural and art exchanges with other countries. We will support Macao in enriching its significance as a world tourism and leisure center, support Guangdong-Macao cooperation on developing the Hengqin region, and help Macao expand its functions as a service platform for business cooperation between China and Portuguese-speaking countries, and build itself into a center for exchanges and cooperation where Chinese culture is the mainstream and diverse cultures coexist. We will support Macao in boosting the research, development and manufacturing of traditional Chinese medicine and developing characteristic finance, high technology, convention and exhibition, commerce and trade, and other industries, and help Macao appropriately diversify its economy.
II. Support for the SARs’ endeavor to better integrate into the overall process of national development
We will improve the mechanism for integrating the SARs into the overall development of the country and coordinating the development of the two regions and the mainland based on their complementary advantages. We will support the SARs in participating in and facilitating China’s endeavor to open up fully and develop a modern economic system and build a functional platform for joint pursuit of the Belt and Road Initiative. We will deepen the economic, trade, and technological cooperation between the mainland and the SARs, and expand the connectivity of their financial markets. We will build a high-quality Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, further the cooperation between Guangdong, Hong Kong, and Macao as well as the Pan-Pearl River Delta regional cooperation, and promote the development of major cooperation platforms between Guangdong, Hong Kong, and Macao, such as Qianhai in Shenzhen, Hengqin in Zhuhai, Nansha in Guangzhou, and Shenzhen-Hong Kong Science and Technology Innovation Cooperation Zone. We will boost exchanges and cooperation between the mainland and the SARs in all fields, improve the policies and measures for helping residents of the SARs live and work better in the mainland, and promote education on the Constitution, the basic laws, and national conditions, to enhance the national awareness and patriotism of residents of the SARs. We will support the SARs in carrying out exchanges and cooperation with foreign countries and regions.
Chapter 62 Peaceful Development of Cross-Straits Relations and National Reunification
We will stay committed to the one-China principle and the 1992 Consensus, and peaceful and integrated development of cross-Straits relations with the wellbeing of the people on both sides of the Straits top of mind. We will remain vigilant against and resolutely confront any separatist activity seeking “Taiwan independence”.
I. Integrated cross-Straits development
Efforts will be made to improve systems and policies for safeguarding the wellbeing of our Taiwan compatriots and ensuring they enjoy the same treatment in the mainland as local residents. We will continue to introduce and implement policies and measures that benefit Taiwan and the people, so that our Taiwan compatriots can share development opportunities and participate in the mainland’s economic and social development. Taiwan’s business people and enterprises will be encouraged to participate in the BRI and the implementation of the country’s coordinated regional development strategy. We will promote cross-Straits financial cooperation and support qualified Taiwan-invested enterprises in going public in the mainland. We will promote the development of platforms for cross-Straits cooperation, such as the Cross-Straits Industrial Cooperation Zone, the Pingtan Comprehensive Experimental Zone, and the Kunshan Experimental Zone for Deepening Cross-Straits Industrial Cooperation. We will support Fujian in exploring a new path for integrated development across the Straits, and accelerate the development of demonstration zones for such integrated development. We will strengthen cross-Straits industrial cooperation and build a cross-Straits common market to grow a stronger Chinese economy.
II. People-to-people exchanges across the Straits
We will actively promote exchanges, cooperation, and people-to-people interactions across the Straits, to boost their mutual understanding, trust, and recognition. More will be done to advance cross-Straits exchanges and cooperation in culture, education, healthcare, and other areas, promote the sharing of social security and public resources, and support equal access to inclusive and convenient basic public services in areas adjacent to each other or with comparable conditions across the Straits. People on both sides of the Straits will be encouraged to carry forward and develop the fine traditional Chinese culture through innovation. We will strengthen cross-Straits exchanges between community-level organizations and young people and encourage young people from Taiwan to pursue and fulfill their dreams in the mainland. We will unite all the Taiwan compatriots to oppose separatist activities seeking “Taiwan independence”, safeguard the peaceful development of relations across the Straits and strive for the great rejuvenation of the Chinese nation.
Part XIX Implementation of This Plan
This Plan will be implemented under the CPC’s overall leadership. Implementation mechanisms will be strengthened to ensure that the government fulfils its responsibilities, and to spur dynamism and creativity across society in our join effort to build a socialist modern country.
Chapter 63 The Overall Leadership Role of the CPC Central Committee
We will see that the CPC charts the direction, exercises overall governance, formulates policies and facilitates reform, and thoroughly study and implement Xi Jinping Thought on Socialism with Chinese Characteristics for a New Era. We will be keenly aware of the need to maintain political integrity, think in big-picture terms, follow the leadership core, remain aligned with the central Party leadership, stay confident in the path, theory, system, and culture of socialism with Chinese characteristics, uphold General Secretary Xi Jinping’s core position on the Party Central Committee and in the Party as a whole, and uphold the Party Central Committee’s authority and its centralized, unified leadership. We will keep improving our capacity for political judgement, thinking, and implementation, and ensure the Party’s leadership over all fields and processes of plan implementation. With these efforts we will ensure the implementation of major decisions and plans of the Party Central Committee. We will give full play to the guiding role of full and strict governance over the Party and integrate the improvement of Party and state oversight systems into plan implementation. We will improve the organizational system that links governments at all levels with effective execution and build the political competence and professionalism of leadership bodies and officials at all levels in carrying out reform, promoting development, and maintaining stability, in line with the new demands of the new era.
We will arouse the enthusiasm of all sectors to participate in plan implementation, encourage trade unions, Communist Youth League organizations, and women’s federations to function well, give full play to the role of other political parties, industry and commerce federations and public figures without party affiliation, and galvanize consensus and strength of the whole society to the greatest extent. We will build a mechanism for internal driving forces to meet the requirements of high-quality development, improve the incentive-oriented performance evaluation mechanism and the mechanism to ensure that those who have fulfilled their duties are not held accountable, and mobilize the enthusiasm, initiative, and creativity of officials, especially those at the community level.
A national planning system will be established, comprising national development planning, spatial planning, and special and regional planning. Planning is done at the national, provincial, municipal, and county levels. It sets clear goals, defines tasks to achieve those goals and the scope within which the tasks are to be implemented, and determines the way in which the tasks are mutually reinforcing and aligned with objectives outlined in national plans.
I. The central role of national development planning
We will make better use of the strategic guiding role of national development plans, and strengthen the support of spatial, special, and regional plans for the implementation of this Plan. In accordance with the requirements and key tasks for territorial space development and protection set out in this Plan, we will formulate and implement a national territorial space plan to provide territorial space support for the implementation of major strategic tasks. Focusing on the strategic priorities and main tasks specified in this Plan, we will formulate and implement several national key special plans in the fields of scientific and technological innovation, digital economy, ecology, and people’s wellbeing, and draw up and refine the timetable and roadmap for the fulfillment of the development tasks. According to the strategic tasks for regional development, as specified in this Plan, we will formulate and implement a number of plans for the implementation of national-level regional development plans, and ensure that the development strategy, main objectives, key tasks, and major projects proposed in this Plan are well embodied in local plans.
II. Better planning coordination
We will improve the planning management systems for lists and catalogs, and record compilation and coordination. We will formulate the lists and catalogs of national special plans during the 14th Five-Year Plan period, promote the filing of plans by relying on the National Comprehensive Planning Management Information Platform, and bring all kinds of plans under unified management. We will establish a sound plan coordination mechanism. The plans to be submitted to the CPC Central Committee and the State Council and provincial development plans must be coordinated with this Plan before being submitted for approval, to ensure that the national spatial plans, special plans, regional plans, and other plans at all levels are consistent with this Plan in terms of main objectives, course of development, overall agenda, major policies, key projects, risk control, etc.
Chapter 65 Mechanisms for Implementing This Plan
Implementation of this Plan requires organization, coordination, and oversight. Effective mechanisms are called for to monitor, evaluate, and oversee the implementation of the Plan, in addition to providing policy support.
I. Responsibilities for implementing this Plan
All regions and departments will, according to the division of functions and duties, formulate implementation plans for the main objectives and tasks involving their respective regions or departments in this Plan. For binding targets, major projects, and tasks in the fields of public services, environmental protection and security as specified in this Plan, we will clearly define the primary responsibility entities and schedule requirements, properly allocate public resources, and channel private sector resources, to ensure the tasks are completed as scheduled. The anticipatory targets and tasks in the fields of industrial development and structural adjustment as proposed in this Plan will be fulfilled primarily by giving play to the role of market entities, while governments at all levels should create an enabling policy environment with proper institutions and the rule of law in place. The annual plans should incorporate the development objectives and key tasks proposed in this Plan by breaking down the key targets set out in this Plan, and include well-balanced annual objectives as well as annual priorities.
II. Monitoring and evaluation of the implementation of the Plan
We will carry out dynamic monitoring, mid-stage evaluation, and final evaluation of plan implementation. The results of mid-stage and final evaluation will be submitted to the Standing Committee of the Political Bureau of the CPC Central Committee for deliberation in accordance with the procedures, and the plan’s implementation will be reported to the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress (NPC) in accordance with the law, as part of the NPC’s supervisory job. The central supervisory and audit authorities will play their supervisory role to promote the implementation of this Plan. The performance in plan implementation will be considered in the assessment of relevant departments, local leadership bodies, and officials, and will serve as an important measure of improvement in the work of the government. If it is necessary to adjust the plan, the State Council should prepare an adjustment plan and submit it to the Standing Committee of the NPC for approval.
III. Policy coordination and support
We will work to build a mechanism for coordination between this Plan and macro policies by following the directions set in this Plan, with the support of fiscal financial and other policies. The orientation of macro policies will be reasonably determined in accordance with the objectives and tasks specified in this Plan and in light of economic development. Public finance will be subordinate to and serve public policies, to strengthen the funding support for major national strategic tasks. The medium-term financial plans, annual budgets, and government investment plans will be better coordinated with the implementation of this Plan. The central government’s funding will be preferentially channeled into the major tasks and projects proposed in this Plan. The projects should be carried out according to the plan, and the funds and factors of production should be provided for the projects. Based on the list of major projects provided in this Plan, the approval procedures for the projects in the list should be streamlined, and site selection, land supply, and funding support for these projects should be prioritized. The land demand of each major project will be addressed by the central government.
IV. Legislation for development planning
The provisions, requirements and proven experience and practices of the CPC Central Committee and the State Council on developing unified planning systems and national development planning will be crystalized in the form of law by following the principle of formulating and implementing plans according to law. We will adopt the development planning law at a faster pace to strengthen the legal support for plan formulation and implementation.